What is the outermost compositional Layer of earth?
The crust
The solid center of the Earth and why is it solid even with so much heat?
Inner core is solid due to extreme heat and pressure.
This type of rock is formed when sediments broken down by weathering and moved and deposited by erosion and deposition then compact and cement into a rock over long periods of time.
Sedimentary rock
A rock is melted down into magma and rises through the crust of the Earth to become lava, then it cools into what kind of rock?
Extrusive Igneous Rocks as lava cools down
According to the law of superposition, which layer is the youngest?
C
What is the thickest compositional layer
The mantle
Continental Plate is mostly made up from this type of rock:
GRANITE
Rock formed when lava or magma cools.
Igneous rock
A rock is pushed to Earth's surface and is broken down by acid rain, then washed away in a local river. It falls into a basin and over time the layers form what kind of rock?
Sedimentary
Which of the following is the oldest?
Layer L
Intrusion D
Intrusion H
Layer E
Layer E
Which layer is the thinnest compositional layer?
The crust
The liquid outer portion of Earth's center
Outer core
If a rock has layers that look like they have been warped by heat and pressure what kind of rock is it?
Metamorphic
A piece of basalt from the bottom of the ocean sinks into the mantle and the pressure and heat cause its structure to change, forming what kind of rock?
Metamorphic
According to the law of superposition, the oldest fossils are found
At the top of the rock layers
Near the bottom of the rock layers
In the middle of the rock layers
Somewhat near the surface
Which layer/s is composed primarily of Iron and Nickel?
The core
This crust is mostly made up from Basalt
The Oceanic Crust
A rock has many small holes from where gas escaped as it was cooling, what kind of rock is it?
Igneous
What is the process that moves rock away from where it was broken down?
Erosion
What is the difference between absolute and relative dating?
Absolute dating uses exact numbers to tell age whereas relative compares rock layers to another
What is an indirect evidence that outer core and mantle are in liquid state?
S-waves only travel through solid, so it will stop at the mantle/outer core area indicating it is in liquid form.
What type of heat transfer occurs in mantle? Explain why?
Mantle goes through convection as it is in fluid form and convection only occurs in fluids.
A rock formed from an existing rock.
Metamorphic Rock
A rock formed from cooling magma beneath the crust, then it sank into the Earth and its structure was changed by the heat and pressure. It sank even deeper and the increasing temperature and pressure causes it change its structure again. What kind of rock did it begin as? What kind did it become after sinking into the Earth? After sinking deeper?
Igneous, Metamorphic, Metamorphic
Did the fault occur before or after the Basalt layer was laid down?
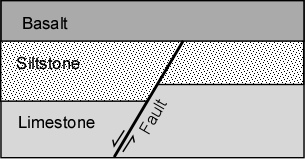
before


