What are the three major classes of rocks?
Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic
Identify the different types of igneous rock
Intrusive and Extrusive
What are sediments?
Sediment is small rock pieces or particles that make up sedimentary rocks.
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
Existing rocks are exposed to heat and pressure
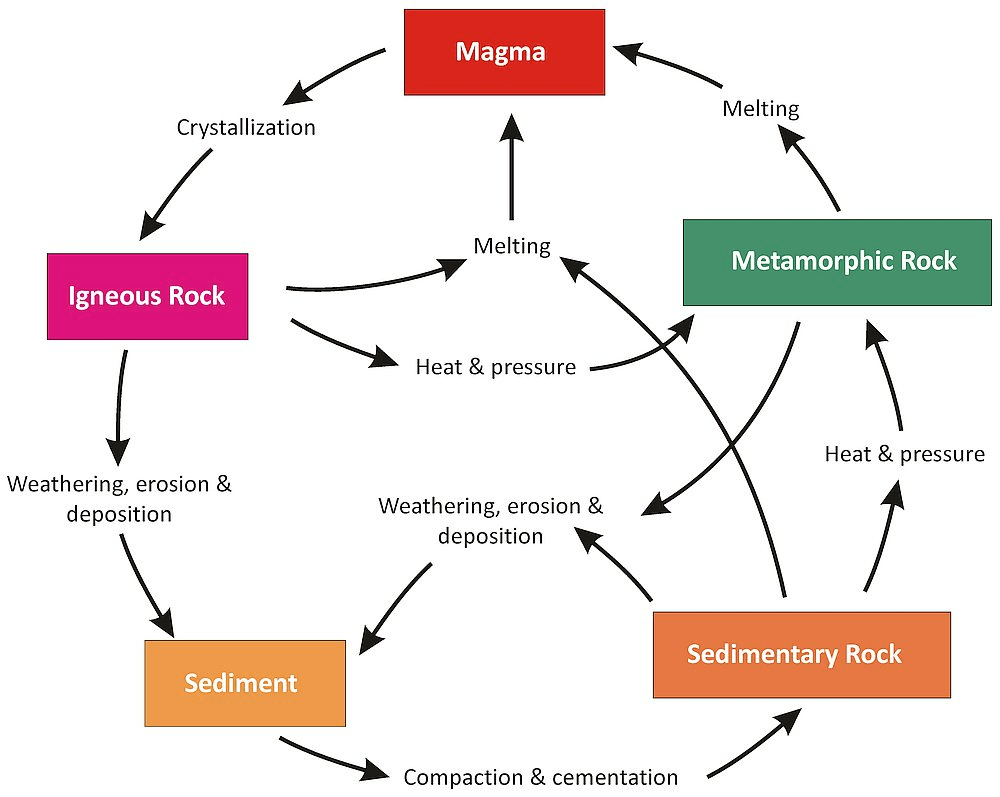
What is the Rock Cycle?
The Rock Cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks on Earth.
Define the term non-living.
An object that is not alive and never has been.
Name two different properties that can be used reliably to classify rocks.
Example responses (any two) -
Hardness, Lustre, Streak, Texture, Porous, Cleavage, Grain size, Crystal size (colour less reliable)
Define the process of igneous rock formation
Igneous rocks form when magma (inside the crust) or lava (above the surface) cools.
Detail the processes that are occurring at points A, B and C.
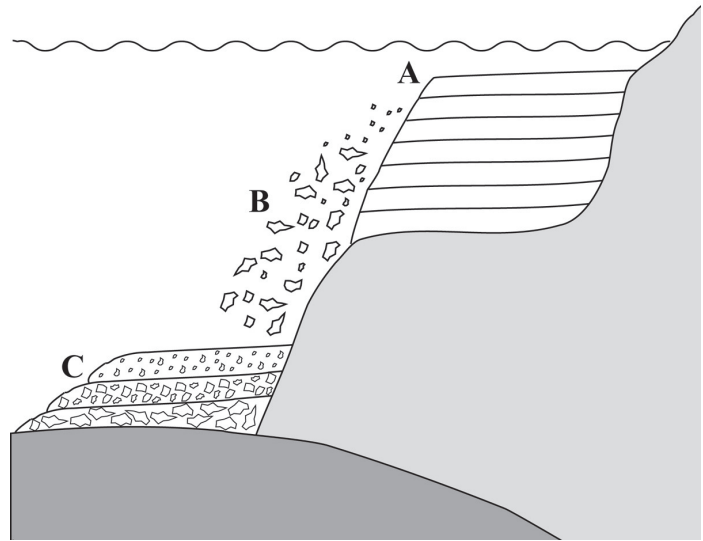
A = Weathering
B = Erosion and Transportation
C = Compaction and Cementation
What does the term foliated mean in Geology?
Foliated metamorphic rocks are layered or banded due to heat exposure or specific pressure.
Draw and label a diagram of the Rock Cycle.
(Remember: it is not like a life cycle and can have many paths)
Which outcrop contains the oldest layer?
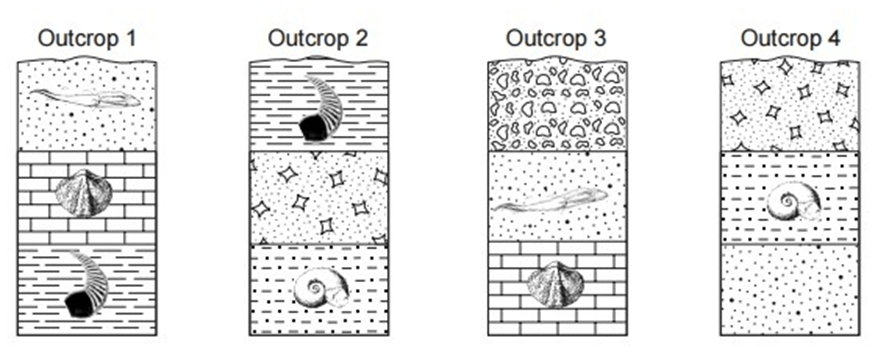
Outcrop 4
Compare the properties of granite and sandstone

Example response -
Granite has visible crystals compared to the grainy texture of sandstone. Granite has a somewhat glossy appearance, whereas sandstone has an earthy lustre. Granite is an intrusive igneous rock which cooled slowly whilst sandstone is a sedimentary rock with often visible strata.
Compare and contrast the different formation processes and related properties of igneous rocks.
Example response -
Igneous rocks are all formed from the cooling of magma/lava but vary depending on where they form and how quickly they cool. If magma cools slowly within the Earth's crust, it will form large crystals and be classified as an intrusive igneous rock. However if the magma makes its way above the surface it is called lava. Lava cools more quickly and have little to no crystals visible. These are called extrusive rocks.
Identify which is the oldest and youngest layer in the image, and state how you know.
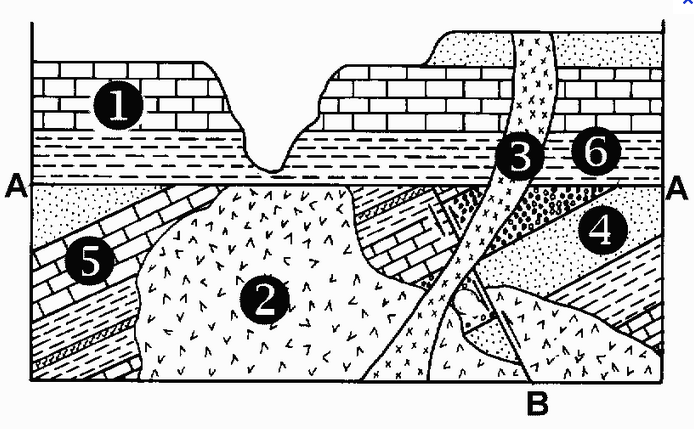
The oldest layer is layer 4 and the youngest is layer 3. Before the fault, the intrusion numbered 2 and layers on the right sat higher. That intrusion had to come after the layers it cut through, meaning layer 4 came first. Layer 6 is older than layer 1 as they formed on top of the previous ones. Both of those layers are cut through by intrusion 3, making it the youngest.
Describe what has to happen to Slate for it to become Quartzite.
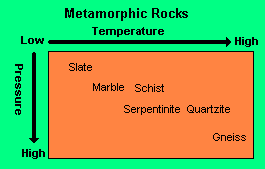
Quartzite is formed when Slate is exposed to medium pressure but high heat. If the levels are different for either pressure and/or temperature a different metamorphic rock would result.
Describe how plate tectonics and the water cycle contribute to the Rock Cycle.
Plate tectonics drive the Rock cycle through convection currents creating plate movement, that result in the creation, metamorphism and destruction of rocks.
The water cycle contributes to the rock cycle primarily through the role it plays in creating sedimentary rocks, as it wears down and carries particles to create new rocks.
What distinguishes the 'Ring of Fire' from other locations around the world?
The 'Ring of Fire' is a location that experiences a lot more earthquakes and volcanic eruptions from plate movement than anywhere else in the world. More than 75% of the world's volcanoes are located on its horseshoe shape.
Explain the term 'streak' in terms of Geology, and state how it is used for rock classification.
Example response -
A rock's streak is the rock in it's powdered form, also seen as the colour left behind when the rock is scratched on a surface. Streak colour can vary in comparison to that of the rock it came from. Streak is usually determined by doing a test using a streak plate or tile. Streak is reliable for classification because rocks of the same type will have the same streak.
Give a detailed description of how pumice is formed
Pumice is formed when explosive volcanoes erupt and frothy lava, with lots of trapped air bubbles, cools rapidly with the air still trapped inside. As the rock cools so quickly there is no time for crystals to form.
Describe the differences and similarities of the three types of sedimentary rocks.
All sedimentary rocks are formed from the compaction of sediments. Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments and rock fragments. Whereas biological sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments that will include plant and animal matter, however chemical ones contain a higher quantity of mineral content in the cementation stage.
Explain the two different types of metamorphism along with how and where they occur.
Contact metamorphism is a type of metamorphism where rocks are changed, mainly by heat, due to contact with magma. This normally occurs in small areas such as intrusions. Regional metamorphism is where rocks are changed by heat and pressure over a wide area or region. This is usually a result of converging plate movement.
Explain a scenario where magma might end up as a sedimentary rock.
Example response -
Magma rises to the surface and the lava cools. It crystalises and becomes an extrusive igneous rock. The rock is exposed to the elements such as wind and rain which weathers the rock. Sediments are eroded and carried in water to a riverbed, where they are compacted and cemented over time, under layers of other sediment and eventually become a sedimentary rock.
Describe what might happen to a meteorite that makes it's way through the atmosphere and impacts the Earth. Where do you think it would fit into the Rock Cycle?
Example response could include (otherwise check for reasonableness) -
- Breaks through the surface and causes magma to reach the surface - it melts to become igneous.
- Sits on the surface and is exposed to elements, erodes over time and eventually becomes sedimentary rock.
Predict which of these rocks would be the best to use for floor tiles, and explain your thinking -
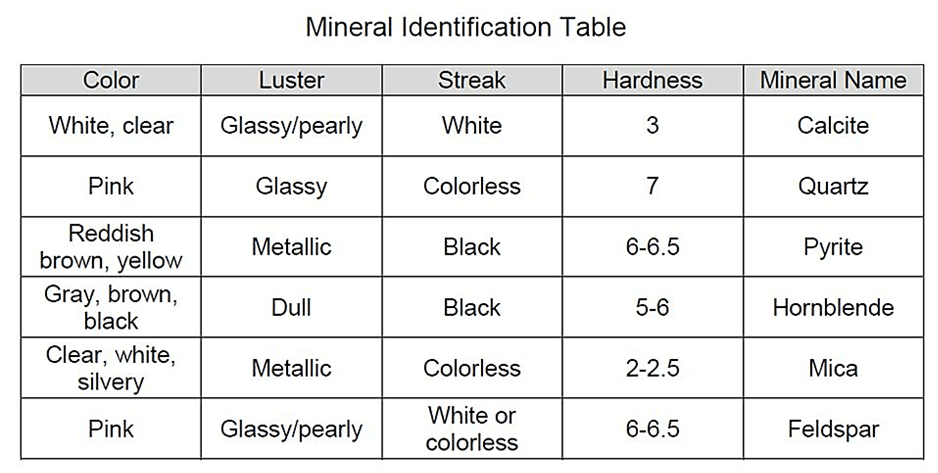
Example response should mention hardness, lustre and possible cost in relation to how that would be appropriate for floor tiles.
Evaluate the type/s of tectonic plate movement that would result in the creation of new igneous rocks.
Example response could mention one or both -
1) Divergent plates: separate and allow magma to reach the surface and new rock to form.
2) Convergent plates: plates converge, one plate is forced back into the mantle to remelt, pressure builds up and will release magma back through the surface to cool into new rock.
Justify why sedimentary rocks are the only type of rocks to contain fossils.
Fossils, preserved organisms, are mostly found embedded in rocks close to the surface. Sedimentary rocks are the one type of rock which can contain fossils because these rocks are formed on the Earth surface, usually under the water, at very low temperatures and pressures. The two other types are formed in conditions that would either destroy the remains or are too far away from where organisms would be found.
Predict two possible fates for a metamorphic rock. One should be natural and one artificial.
Example responses -
A piece of marble is located and dug up to be cut into a stone kitchen benchtop. Alternatively the marble could be in a location where there is a fault line and the area experiences convergent plate movement that results in subduction of the rock into the mantle. It melts and becomes magma. Pressure builds up over time and there is an eruption that results in magma being forced up towards the surface. The magma is trapped in a chamber and slowly cools to form an intrusive igneous rock such as granite.
Justify your opinion as to whether every rock has to go through a full rock cycle.
Response could include information such as -
Every rock could go through the complete rock cycle, but it may be very difficult for some based on factors such as location. If the rock is located in an area where things are constantly changing, it might be quite possible for a rock to go through the cycle. However others may only cycle through certain processes or stages.
Identify the four main layers of the Earth and justify why they are essential in plate tectonics.
The four main layers are the Crust, Mantle, Outer Core and Inner Core. The Outer Core generates heat that transfers to the magma within the Mantle. This creates convection currents, where the heated magma rises towards the surface and then cycles back down as it cools. This movement within the Mantle results in the plates that make up the Crust moving in different directions. Without these actions we would not experience plate tectonics.