NSAIDs and H. pylori infection are common causes for this disorder.
What is peptic ulcer disease?
In addition to bronchodilators, a patient with this ABG: 7.14/78/68 with COPD exacerbation might benefit from this prior to intubation.
What is BiPAP (NIPPV)?
This opioid is often used during moderate sedation because it provides potent analgesia with a short onset and relatively short duration, allowing for quick recovery.
What is fentanyl?
What is IV fluid?
This type of dialysis is performed in the patient's home and involves the exchange of dialysis fluid in the abdomen.
What is peritoneal dialysis?
You would need the setup below to evaluate suspicion for this condition.
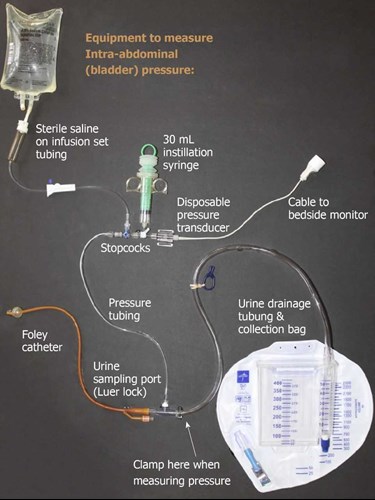
What is abdominal compartment syndrome?
Of one hour, four hours, or six hours, which is the optimal duration of a spontaneous breathing trial?
What is one hour?
During a bronchoscopy, you observe respiratory effort, but are concerned about lack of air movement. In addition to stimulation to generate arousal, administration of supplemental oxygen, and suctioning, this maneuver can be helpful to improve air flow into the trachea.
What is head tilt/chin lift?
This is a method of blood testing that assesses coagulation.
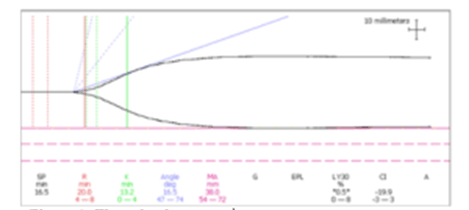
What is thromboelastography (TEG?)
This condition associated with kidney failure often requires patients to take exogenous erythropoietin.
What is anemia?
This common type of infection in the colon can perforate and cause peritonitis and shock.
What is diverticulitis?
This might be suspected based on the tidal volume numbers shown below:
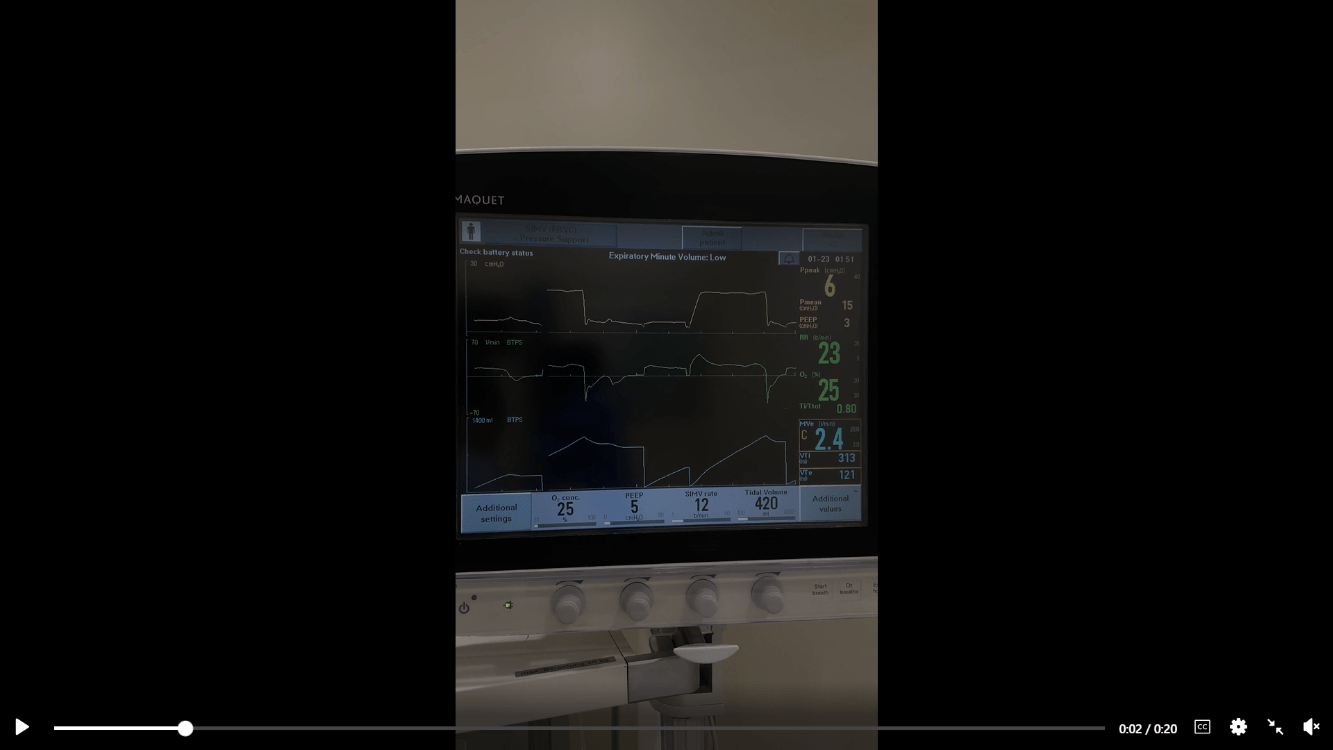
What is cuff leak?
The patient's eyes are closed, but she can follow simple commands when you tap her shoulder. She has reached this level of sedation.
What is moderate sedation?
This is the most commonly used ratio of blood products in massive transfusion protocols (PRBC:platelets:plasma).
What is 1:1:1?
This nephrotoxic antibiotic for gram positive organisms requires careful dosing and monitoring of drug levels to prevent acute kidney injury, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal impairment or those receiving high doses for prolonged periods.
What is vancomycin?
Intense emesis or retching can cause this, leading to mediastinal and pleural infections, pneumomediastinum, and pneumothorax.

What is esophageal perforation?
In addition to dexamethasone and nitrous oxide, this medication is useful for post-extubation stridor.
What is racemic epinephrine?
End tidal CO2 is valuable in detecting hypoventilation. But of the following: bradypnea, abnormal chest, reduced chest rise, oxygen desaturation, this one occurs first.
What is reduced chest rise?
This blood product is often used in disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) to provide fibrinogen and other coagulation factors, helping to restore clotting function in patients with massive bleeding.
What is cryoprecipitate?
This is the usual cause of the following EKG changes:
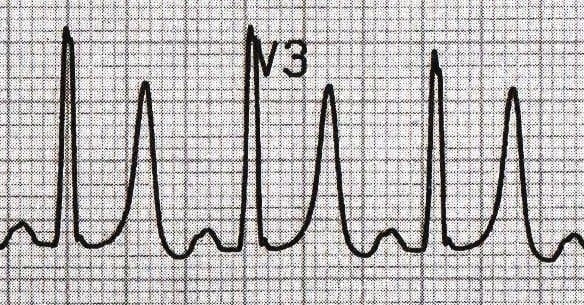
What is hyperkalemia?
Aggressive fluid resuscitation and sometimes bowel rest are first line treatments for this inflammatory condition that is common in alcohol abusers.
What is acute pancreatitis?
This is an immediate post intubation chest x ray on a patient with nearly absent breath sounds on the left. What might be a reasonable next step?

What is endotracheal tube retracion?
This benzodiazepine reversal agent is used to reverse sedation in cases of oversedation and respiratory depression.
What is flumazenil?
This transfusion associated condition is suspected after seeing this chest x ray, and no improvement is noted with diuresis.

What is TRALI (Transfusion associated acute lung injury)?
This condition resulting from kidney failure is implicated in encephalopathy, bleeding, and even pericarditis.
What is uremia?