This is the term for an organism's role in its environment
What is niche?
This is the term for the variety of life in an ecosystem
What is biodiversity?
The maximum population size that an environment can support indefinitely.
What is the carrying capacity of an ecosystem?
This type of succession occurs after a forest fire?
What is secondary succession?
This is the original source of energy in most ecosystems
What is the sun?
This symbioitic relationship is exemplified by bees consuming nectar and carrying pollen from one flower to another
What is mutualism?
This is the term for the introduction of non-native species into an ecosystem.
What is invasive species?
This percentage of energy is typically transferred from one trophic level to the next
What is 10%

What is carrying capacity?
This species has a disproportionately large effect on their ecosystems
What is a keystone species?
Thisi is an example of a K-selected species
(Answers vary) Elephants (species with long lifespans, few offspring, and high parental investment)
The first species to colonize barren or disturbed environments in ecological succession.
What is a pioneer species?
This type of organism is always at the base of a food chain
What are producers?
DAILY DOUBLE - CAN YOU EXPLAIN WHY?
This process converts solar energy into chemical energy
What is photosynthesis?
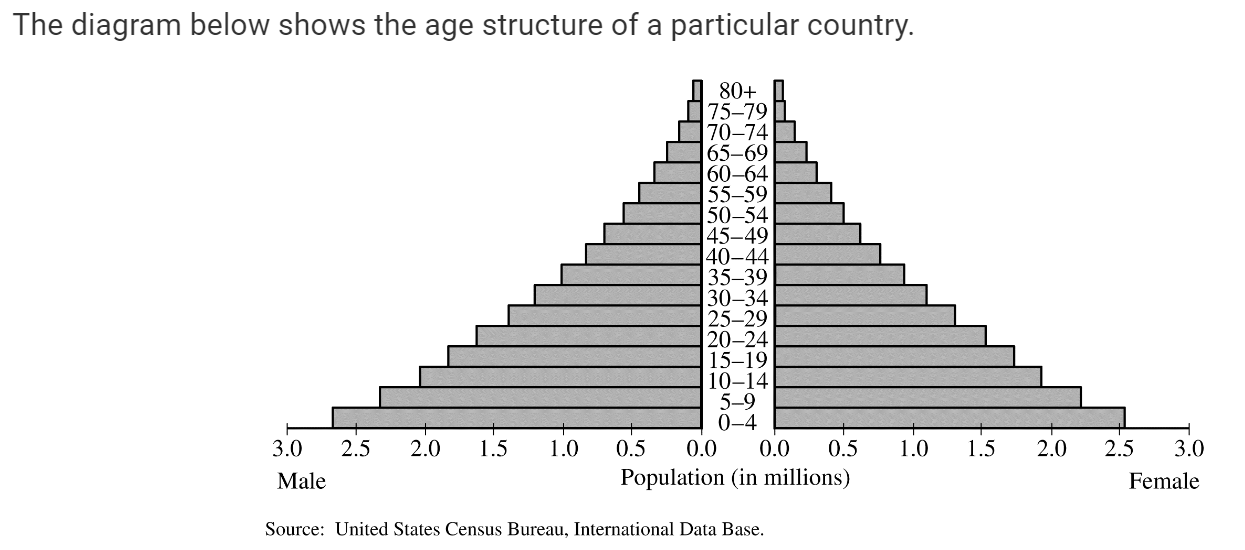 These are the characteristiics most closely associaited with a country that demonstrates the age strucutre diagram shown above?
These are the characteristiics most closely associaited with a country that demonstrates the age strucutre diagram shown above?
There is a high totaly fertility rate.
The following equation calculates this as a %?
(total births ÷ total population) ×100
This is the term used to describe organisms that break down dead matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem?
What are decomposers?
Explain how secondary succession is different from primary succession?
Secondary succession occurs in areas where soil is already present, usually after a disturbance like a fire. Primary succession is the development of an ecosystem in an area where no soil or organisms previously existed, such as after a volcanic eruption.
What isi the species richness on islands based on size and distance from the mainland.
Explain the difference between Type I and Type III survivorship curves.
Type I has low early mortality and high survival into older age (k-selected species), while Type III has high early mortality and lower survival past the early stages of life (r-selected species)
Explain the difference between density-dependent and density-independent factors?
Density-dependent factors are influenced by population size (e.g., disease, competition), while density-independent factors affect populations regardless of size (e.g., natural disasters).
The energy available to consumers after plants use some for respiration.
What is net primary productivity (NPP)?