Name the nerve with a sensory distribution illustrated in dark orange.
Deep fibular
For patients with Achilles tendinopathy, the CPG recommends which type of exercise?
Concentric/Eccentric (A) LOAD IT!
Name 1 contraindication for NMES.
Pacemaker, pregnancy (over or around abdomen/LB), contraction may delay healing.
In a patient with gradual onset of medial knee pain, what areas of the body need to be cleared for contribution?
Which treatment classification is best for patients with acute low back pain and severe mobility deficits?
Manipulation/Mobilization

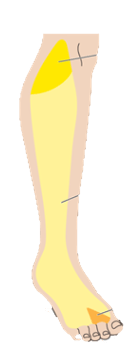
Name the nerve with a sensory distribution illustrated in yellow.
Saphenous
According to the PFPS CPG, what intervention should be used in conjunction with exercise therapy to reduce immediate pain and improve short-term outcomes (4 weeks) for a patient with hypermobility?
Patellar taping (B) MCConnell!
What PNF technique is defined by muscle work performed concentrically in one direction followed by concentric muscle work in the opposite direction?
Dynamic Reversals
17yo football player reports hearing a "pop" while quickly changing direction to avoid a tackle. He experienced immediate swelling and instability in his knee and was unable to return to play. Based on his symptoms, which special test would you perform?
What intervention is emphasized for patients classified under the "Directional Preference" category?
Repeated movements or specific directional exercise
During a (SLR) with inversion and plantar flexion, the pain increases as the leg is raised higher with added hip flexion. Fibularis muscles or Fibular N?
Fibular/Peroneal N
According to the 2021 CPG for lateral ankle ligament sprains, what clinical test is commonly used to assess for the integrity of the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL)?
Anterior drawer test
In PNF, which direction of pelvic movement improves a patient’s ability to go down stairs?
Pelvic anterior depression
A patient reports injuring their knee about 6 months ago while playing tennis, describing a twisting action. They report improvement in pain but notice recurrent knee effusion after activity. Based on this hx, what special test would you perform?
Thessaly, McMurray
A 68-year-old patient reports chronic low back pain that worsens with standing and walking but improves when sitting or leaning forward, such as on a shopping cart. What intervention would be MOST appropriate for this patient?
During an SLR with eversion and dorsiflexion, the pain stays the same increases as the leg is raised higher with added hip flexion. Tibial nerve or Posterior Tib tendon?
Posterior Tib
According to the 2017 Knee Ligament Sprain CPG, when should clinicians implement mobilization after ACL reconstruction to improve range of motion, reduce pain, and prevent soft tissue complications?
Within 1 week (B)
Which of the PNF techniques is defined by resisted concentric contraction of agonist muscles moving through the range, followed by a stabilizing contraction (hold) and then eccentric, lengthening contraction, moving slowly back to the start position?
Combo of isotonics
You suspect a patient has hip osteoarthritis. Name 2 key components should be included in your examination to assess for this condition?
Hip ROM, Hip MMT, FABER; can also include balance, 6-minute walk test, 30-second chair stand, stair measure, timed up-and-go test, self-paced walk, timed single-leg stance, 4-square step test, and step test.
A 45-year-old patient presents with low back pain radiating down the left leg to the foot. They have a positive crossed straight leg raise test, report worsening symptoms with standing or walking, and do not experience centralization with repeated movements. Which low back pain treatment classification would best match their presentation?
Traction
During an SLR with inversion and dorsiflexion, the pain increases as the leg is raised higher with added hip flexion. Sural nerve or achilles tendon?
Sural N
According to the 2018 CPG for meniscal and articular cartilage lesions, name 3 clinical findings that are commonly associated with meniscal tears?
Twisting injury • Tearing sensation at time of injury • Delayed eusion (6-24 hours post injury) • History of “catching” or “locking” • Pain with forced hyperextension • Pain with maximum passive knee flexion • Pain or audible click with McMurray’s maneuver • Joint-line tenderness • Discomfort or a sense of locking or catching in the knee over either the medial or lateral joint line during the Thessaly test when performed at 20° of knee flexion • Meniscal Pathology Composite Score: the combination of history of “catching” or “locking,” pain with forced hyperextension, pain with maximum passive knee flexion, and pain or audible click with McMurray’s maneuver
According to Cameron, what is the recommended starting traction force for lumbar spine? Hint: It's in pounds.
After clearing the lumbar spine for contribution to a patient’s pain, which two tests are performed initially to assess for SIJ dysfunction?
Posterior Shear (POSH)/Thigh Thrust (most sensitive), SIJ Distraction (most specific)-- If both are +, no further testing indicated.
Name 5 key clinical features used to classify a patient into the stabilization category.
Younger age
Positive prone instability test
Aberrant motions present
Greater SLR ROM
Hypermobility with spring testing
Increasing episode frequency
Three or more prior episodes