This bone, which is composed of parts such as the greater and lesser wings and pterygoid plates, houses the pituitary gland.
What is the sphenoid bone?
This is the largest mobile articulator.
What is the tongue?
This is the name for the ball of food or liquid to be swallowed.
What is the bolus?
This structure is responsible for the sensation of the head's movement in space.
What are the semicircular canals?
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-masseter-pars-superficialis/oAPdPmNbdtw72ztxq0pZg_Masseter_muscle_-_pars_superficialis_01.png) This is the most massive and superficial mandibular elevator which is shaped like a quadrilateral.
This is the most massive and superficial mandibular elevator which is shaped like a quadrilateral.
What is the masseter?
This bone houses the hearing mechanism. 
What is the temporal bone?
These large teeth meant for grinding food are located in the most posterior part of the dental arch.
What are molars?
This reflex in infancy involves head rotation and mouth opening towards tactile contact (e.g. a finger against the face)
What is rooting?
The outer ear terminates at this structure.
What is the tympanic membrane?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13051/ffRKTrgzyay0Z39clZKOw_Risorius_muscle_01.png) This is the primary muscle for smiling.
This is the primary muscle for smiling.
What is the risorius?
This porous component of the ethmoid bone provides a channel for olfactory nerves to pass. 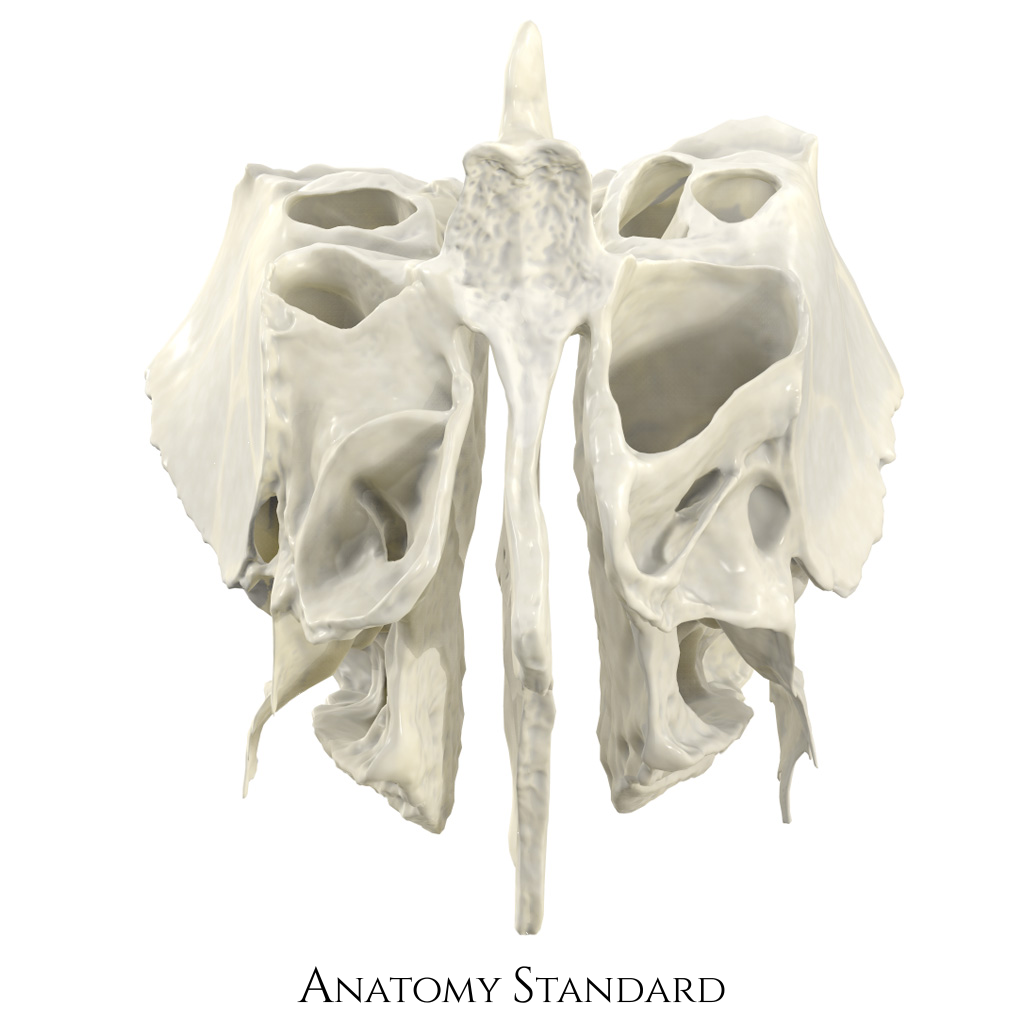
What are the cribriform plates?
This is the visible 1/3 of the tooth.
What is the crown?
During this stage of swallowing:
the tip of the tongue is elevated
the back of the tongue is elevated to hold the bolus up into the hard palate
the mouth is sealed
What is the oral preparatory phase?
This structure equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the atmospheric pressure.
What is the Eustachian tube?
This muscle helps to protrude the lip out, or pout:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13033/XZyHj5YSlZlu070CzBopDg_Mentalis_muscle_01.png)
What is the mentalis?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-vomer/v56RxH9lpvFJXw9P0Bzw_vomer_2_atlas_Xwn6Q6WYFaX2Ox9zHu8HNg.png) This bone divides the nasal cavities, therefore making up the inferior and posterior nasal septum.
This bone divides the nasal cavities, therefore making up the inferior and posterior nasal septum.
What is the vomer?
This thin layer of bone holds the teeth in their sockets.
What is the cementum?
During this phase of swallowing, the cricopharyngeus muscle contracts to prevent reflux.
What is the esophageal phase?
This part of the malleus protrudes into the epitympanic recess of the middle ear and articulates with the incus.
What is the head/head of the malleus?
This mandibular elevator appears to be capable of more rapid contraction than the masseter.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13538/Vc1ICDIQi6PinabT9JHbIA_Temporalis_muscle_01.png)
What is the temporalis?
This portion of the ethmoid bone makes up the superior nasal septum, therefore partially separating the nasal cavities.
What is the perpendicular plate?
In the source-filter theory of vowel production, the vibrating vocal folds are the source, and this is considered the filter that shapes the voice.
What is the vocal tract?
OR
What are the oral and nasal cavities?
During this phase of swallowing, the tongue makes an anterior-posterior rolling motion to push the bolus to the posterior part of the oral cavity.
What is the oral transport phase?
OR
What is the oral transit phase?
This muscle dilates, or opens, the opening of the Eustachian tube.
What is the tensor veli palatini?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12735/1bXEPFwhyKmS3BM2SKVqjQ_M._palatopharyngeus_01.png)
This muscle makes up the anterior faucial pillars (the anterior prominent arches marking entry into the pharynx)
What is the palatoglossus?