This is the only bone in the body that does not articulate with another bone.
What is the hyoid bone?

These structures (R) are also known as ventricular folds.
What are the false vocal folds?
The word for vocal folds coming together.
What is adduction?
 This is the largest laryngeal cartilage.
This is the largest laryngeal cartilage.
What is the thyroid cartilage?
This area is the space between the vocal folds.
What is the glottis?
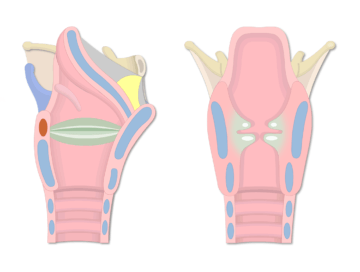
This structure (in green) is defined by the margin between the false and true vocal folds.
What is the laryngeal cavity?
 These paired, pyramid-shaped cartilages reside on the superior posterior lateral surface of the cricoid cartilage.
These paired, pyramid-shaped cartilages reside on the superior posterior lateral surface of the cricoid cartilage.
What are the arytenoid cartilages?
This is the deepest layer of the vocal folds.
What is the thyroarytenoid muscle?
These muscles are the sole abductors of the vocal folds (i.e. making the vocal folds come apart).
These cartilages support the membranous laryngeal covering.
What are the cuneiform cartilages?
These protective cells in the top layers of the vocal folds keep vocal folds moist and prevent them from damage.
What are squamous epithelium?
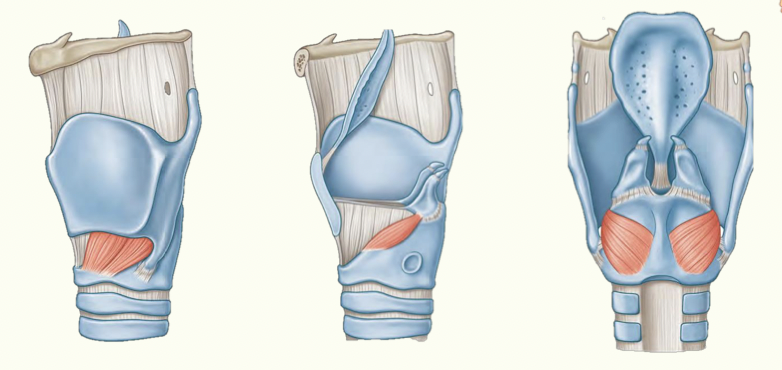 This is the primary tensor of the vocal folds.
This is the primary tensor of the vocal folds.
What is the cricothyroid muscle?
These are the two processes, or points of attachment, for the arytenoid cartilages.
What are the vocal and muscular processes?
The thyroarytenoid of the vocal folds is made up of these two muscles.
What are the thyrovocalis and the thyromuscularis?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/mylohyoid-muscle/FFu5f6yBZtUYjtG3m6zeg_2bsbsqhogtuMMPnDBwRSMQ_Musculus_mylohyoideus_01.png) This muscle forms the floor of the oral cavity.
This muscle forms the floor of the oral cavity.
What is the mylohyoid muscle?