What is the true shape of the earth?
The true shape of the Earth is Geoid
Diversity refers to:
- A. Similarities between people
- B. Differences among people
- C. The same culture
- D. Only religious differences
Differences among people
What is this called? 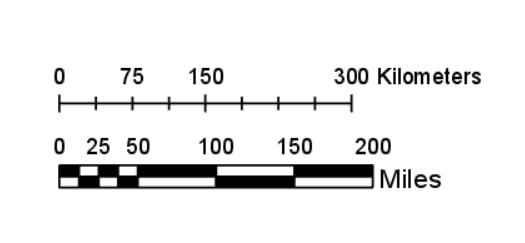
A Scale of a Map
What evidence suggests that the Indus valley civilisation practiced agriculture?
Discovery of the Plough.
Which things can be marked in their correct sizes on the globe?
Oceans,Countries and continents can be marked in their correct sizes on the globe .
Who coined the term ' Unity in Diversity'?
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru
This type of map shows landforms like deserts, mountains, plains, rivers, and lakes.
Physical / Relief Map
The Mesopotamian civilisation flourished on the banks of which river/rivers?
Euphrates and Tigris
Into how many heat zones is the earth divided?
The world is divided into 3 heat zones namely:
Torrid Zone (very hot)
Temperate Zone (moderate)
Frigid Zone (very cold)
What was the popular type of cotton that was once exported to Europe but later prohibited to safeguard their own products?
Chintz cotton.
Name the cardinal directions.
North, South, East and West.
In which part of the city were the major administrative buildings located?
Citadel/Western Part
If the time in London is 11:00PM, calculate the time at 45°East longitude?
The time at 45° E will be 2:00AM.
Textiles and clothing have been powerful tools for promoting unity in diversity in India. Explain how?
- Shared Heritage: Many textiles and clothing styles are shared across India, despite regional variations. For example, the sari, a traditional garment, is worn throughout the country, though the styles and fabrics may differ.
- Preservation of Traditions: Textiles and clothing help preserve traditional skills and crafts, ensuring that they are passed down from generation to generation. This helps maintain a sense of cultural identity and heritage
The science and art of map making is known as__________.
CARTOGRAPHY.
Give 2 reasons how we know that people of Indus Valley did trade with others.
1. Discovery of common seals across different cities
2. Dockyard at Lothal
3. Weighing scales and weights and measures
What is the value of the standard meridian of India and in which state is it passing through?
The longitudinal value of the standard meridian of Indian is 82.5°East. It passes through Mirzapur, in Uttar Pradesh.
How does India's geographical diversity impact its people and culture?
- Cuisine: Different regions have unique culinary traditions due to the availability of specific ingredients. For example, coastal areas have a strong seafood influence, while the northern plains, known for their fertile soil, have a focus on wheat-based dishes.
- Religion: The Himalayas, often considered sacred, have influenced many religious practices and beliefs, particularly Hinduism. The Ganges River, revered in Hinduism, has played a significant role in religious rituals and beliefs.
- Language: Geographical barriers have led to the development of numerous languages and dialects. For instance, the Himalayan region has distinct languages, while the southern peninsula has its own linguistic family.
- Architecture: The architectural styles in different regions reflect the local climate and materials. For example, the southern states, with their hot and humid climate, have developed structures with courtyards and open spaces to promote ventilation.
- Festivals: Many festivals are tied to the agricultural cycle and local customs. For instance, Onam, a harvest festival in Kerala, is celebrated to honor the mythical king Mahabali.
What do the following colors represent on map?
1. Blue
2. Green
3. Brown
Blue: Lakes, rivers or water bodies.
Green: Parks, Grasslands or forest areas.
Brown: Deserts or historical sites.
Give any 3 possible reasons why the Indus Valley civilisation ended.
1. Floods
2. Drying up of rivers
3. Large scale deforestation
4. Shortage of wood