The backbone of DNA consists of...
phosphate and sugar (deoxyribose)
This enzyme unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork.
helicase
This term describes DNA replication, describing how one old DNA strand combines with one new DNA.
Amino acids are connected by these type of bonds.
peptide bonds
Where must an mRNA attach before protein production can begin?
ribosome
What is removed from pre-mRNA to create mature mRNA?
introns
D
The concept of humans selecting desired traits in species is known as...
artificial selection
The purpose of PCR is to...
(looking for a specific term)
This enzyme adds DNA nucleotides to the 3' end of an elongating strand.
DNA polymerase (III)
Beta pleated sheets and alpha helices are two types of this structural level in protein folding
secondary structure
Explain the difference between a codon and an anticodon.
codon: 3-nucleotide sequence on mRNA
anticodon: 3-nucleotide sequence on tRNA
--> A specific codon will be complementary to a specific anticodon
What type of mutation is illustrated in the following diagram:
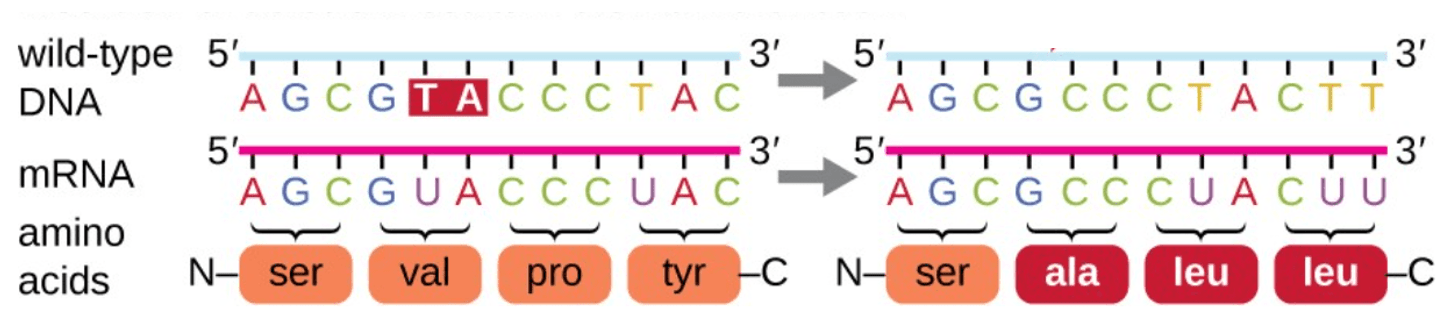
frameshift via deletion
The ability of an individual to survive and reproduce is known as ...
fitness
TRUE, FALSE or UNCERTAIN: (+ give justification)
"Humans are descended from monkeys."
FALSE: We both evolved from a common ancestor, which lived millions of years ago.
Differences between RNA and DNA
DNA: double stranded, deoxyribose sugar, ATGC bases
RNA: single stranded, ribose sugar, AUGC bases
Quick response question: choose ONE team member to answer. This person must answer within 2 seconds of the question being read aloud.
leading or lagging: this strand is replicating in the opposite direction as the DNA is unwinding.

What role does temperature play in PCR?
The fancy term for protein shape is protein ___.
conformation
This type of mutation will result in the creation of a functional protein, but the protein will be different and/or its function will be altered (with varying levels of effect)
substitution --> missense mutation
What is located at each end of the tRNA molecule?
anticodon // amino acid
A population of birds is blown by a storm to an island off the mainland. The island has very few trees, and the bird population on the island develops new nesting behaviors. Mainland birds nest in trees, island birds nest on the ground. After a long period of time, the island birds are reunited with the mainland birds, it is observed that the two populations can no longer interbreed.
This is an example of what type of speciation?
allopatric speciation
The concept that organisms who are the best suited to their environment will be the most successful
survival of the fittest
The building blocks of DNA and RNA are called...
nucleotides
Explain why both strands of DNA cannot be replicated continuously.
DNA polymerase can only work in 5' to 3' direction, so nucleotides can only be added continuously from 5’ to 3’. On the lagging strand, primer needs to be added at several spots, and then the fragments need to be "stitched" together.
In this replication stage, single stranded binding proteins (ssBP) are present.
initiation
This part of the amino acid contains the nitrogen
amine group / amino group
Explain the difference between the coding strand and template strand.
The coding strand is the DNA strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (RNA).
The term template strand refers to the DNA sequence that is used to produce mRNA and is complementary to the primary transcript.
collectively, all of the alleles of the population’s genes
gene pool

A major misconception about natural selection is that this mechanism “gives organisms what they want or need so they can adapt to an environment.”
Explain why this is not correct.
Speciation mechanism that occurs due to different breeding seasons
temporal isolation
An RNA nucleotide consists of...
phosphate group; ribose sugar; one of 4 nitrogenous bases (cytosine, guanine, adenine, uracil)
What is the name of the point where the DNA molecule splits? (where one strand splits into two)
The Replication Fork
Adds a short run of RNA nucleotides and does not need a primer.
primase
This is the only level of protein structure not disturbed by denaturation.
primary structure
What is the product of transcription and where does it take place?
mRNA -- nucleus
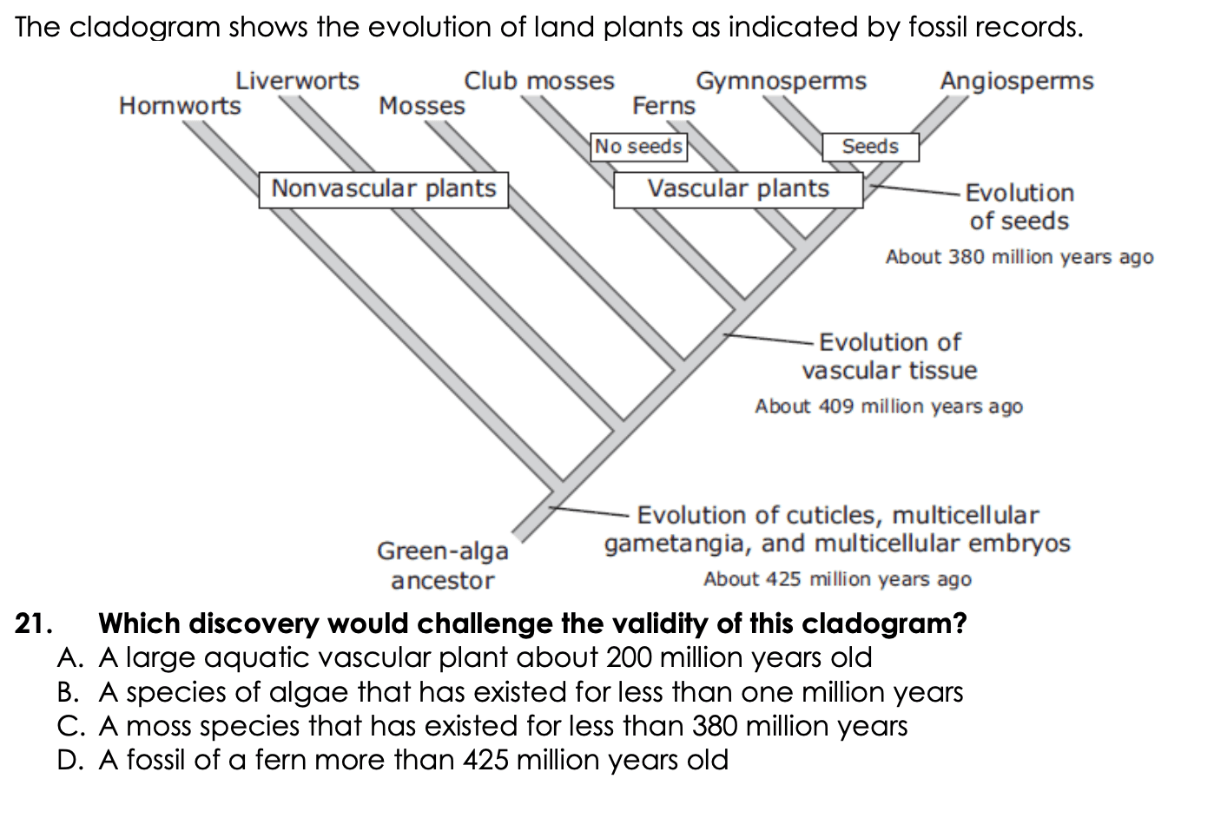
Diagram showing the evolutionary relationships between organisms is a...
cladogram
Cheetahs nearly became extinct but recovery efforts managed to save them. Now, most cheetahs are genetically identical. This is due to:
genetic drift (bottleneck effect)
geographic - street, mountain, river
temporal - active at different times of day/year, mature differently
behavioral - dances, songs, recognizable
mechanical - reproductive organs don't fit together