Which mutation leads to the majority of OI cases, and how does it impair bone strength?
COL1A1 or COL1A2 mutations → abnormal type I collagen production, reducing tensile strength of bone.
Why might a skeletal survey ordered in a child with multiple fractures?
To detect occult or healing fractures and help distinguish metabolic bone disease from abuse.
Differentiate intramembranous and endochondral ossification.
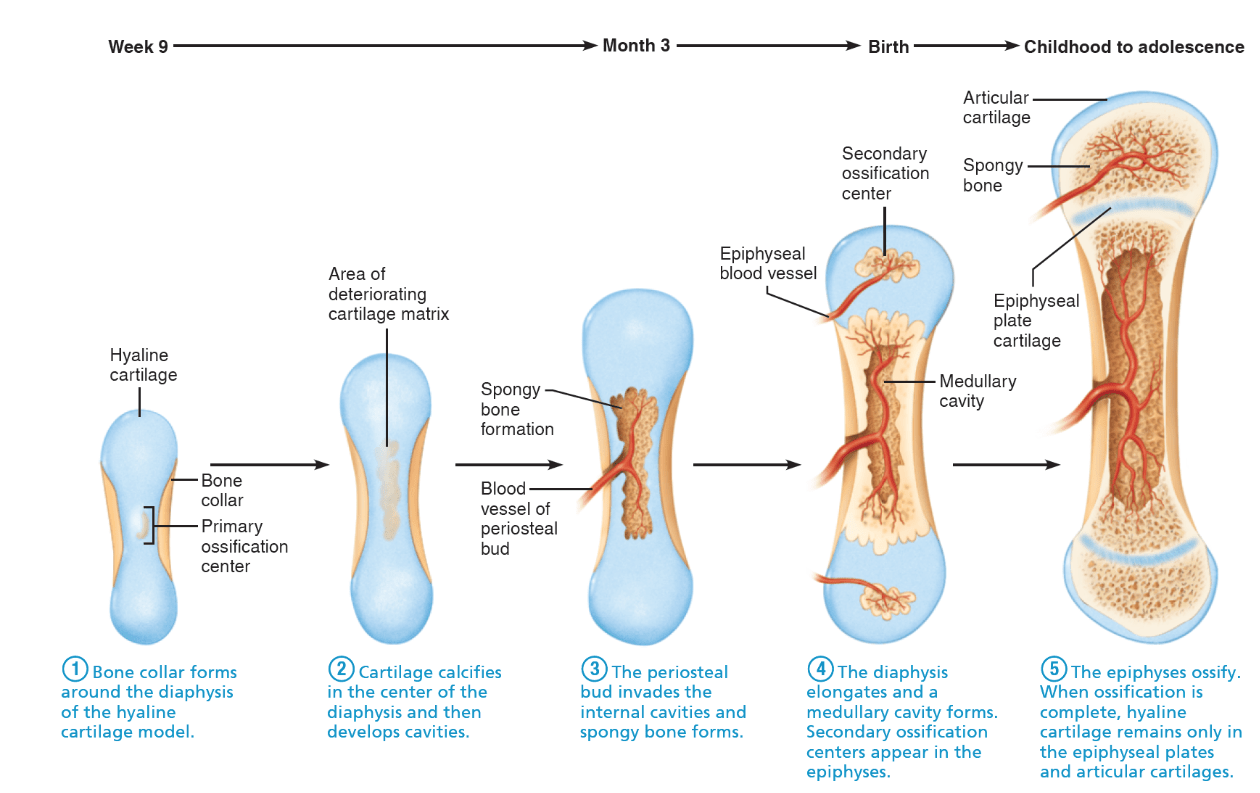
Intramembranous: mesenchymal cells → osteoblasts (flat skull bones, clavicle). Endochondral: cartilage model replaced by bone (long bones).
What is the predominant collagen type in bone, and what is its structural role?
Type I collagen; provides tensile strength
Why should non-accidental trauma (abuse) always be considered in children with unexplained fractures?
Because abuse is more common than OI, and missing it can place the child at ongoing risk of harm.
How does type I OI differ from type II OI in terms of clinical severity and prognosis?
Type I is mild with normal lifespan; type II is perinatally lethal due to severe skeletal fragility.
How do Wormian bones appear on radiographs, and what conditions are they associated with?
Small, irregular bones within cranial sutures; associated with OI, rickets, and other skeletal dysplasias.
What is the role of bone morphogenetic proteins? (and what cell type to they act on?)
They promote differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts, regulating bone growth and repair.
What vitamin is required for collagen synthesis and what pathology results if deficient?
Vitamin C, and lack of it results in scurvy
What clinical clue distinguishes rickets from OI in children with fractures?
Rickets shows bone pain, bowing, rachitic rosary, and widened growth plates. OI has blue sclera, bowing in severe cases, and normal mineral labs.
Why might patients with OI have hearing loss?
Abnormal ossicles and collagen in the middle ear → conductive hearing loss.
What radiologic feature helps differentiate accidental spiral fractures from those seen in OI?
Spiral fractures may occur with twisting accidents in ambulatory children, but in OI they can occur after minimal trauma and often coexist with multiple fracture sites.
How does PTH regulate bone morphogenesis differently when secreted continuously vs. intermittently?
Continuous → bone resorption (osteoclast activation via RANKL); intermittent → anabolic effect by stimulating osteoblast activity.
Why might patients with OI have poor dentition (dentinogenesis imperfecta)? (Dan isn't allowed to answer)
Collagen type I forms the scaffold for dentin; abnormal collagen → weak, discolored, easily worn teeth.
How can lab values help distinguish metabolic bone disease (e.g., rickets) from OI?
OI usually has normal Ca, P, Vit D, and ALP; rickets often shows low Vit D, hypocalcemia/phosphatemia, and elevated ALP.
Explain how bisphosphonates improve bone strength in OI patients.
They inhibit osteoclast-mediated resorption, increasing bone mineral density and reducing fracture rates.
Which baby has OI and why?
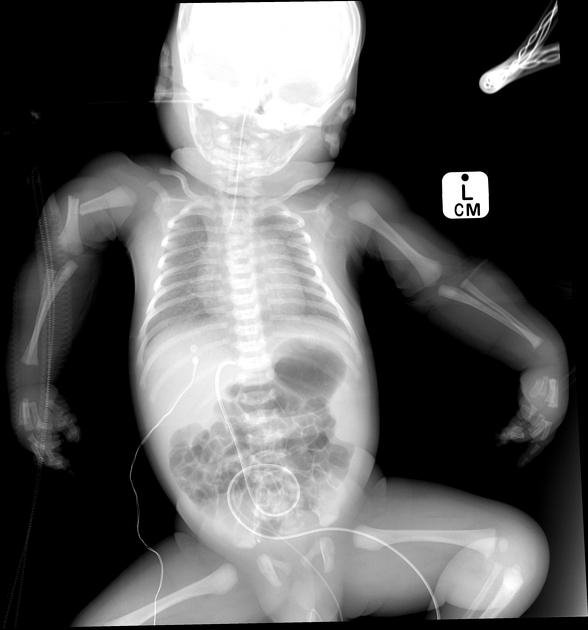
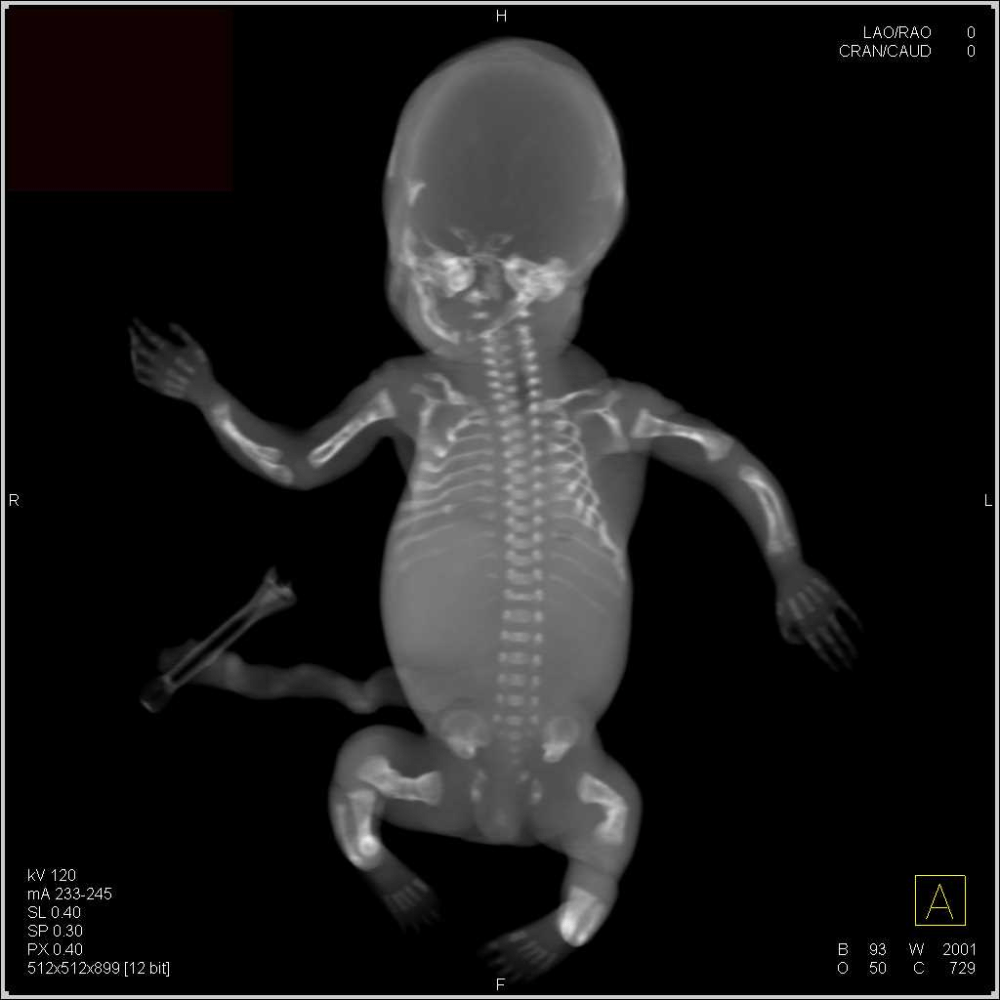
Bottom baby (bent bones in severe cases vs one broken bone)
How does FGFR3 mutation in achondroplasia disrupt endochondral ossification?
FGFR3 gain-of-function inhibits chondrocyte proliferation in growth plates, leading to short-limbed dwarfism.
Why do OI patients bruise easily in addition to having fractures?
Type I collagen also supports blood vessel walls; defective collagen → vessel fragility → easy bruising.
Why is it important to review family history when evaluating suspected OI?
Many cases are inherited (autosomal dominant), but absence of family history may suggest de novo mutation or abuse.
Genetic counseling is recommended for families with OI. What inheritance pattern does type I OI usually follow, and what is the recurrence risk?
Autosomal dominant; ~50% recurrence risk with affected parent.
Which imagine shows OI? (Dan? Dan? Dan? Dan?)
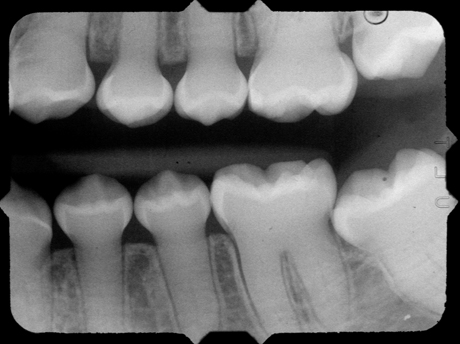
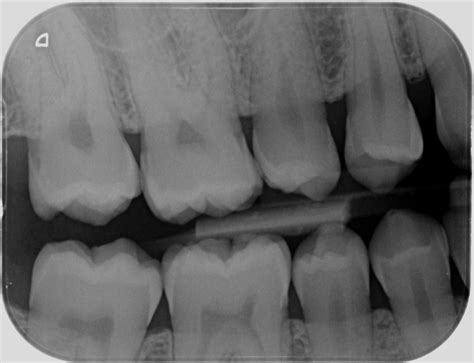
Top image (shell teeth)
This question is going to suck. What are the 5 main stages of endochondral ossification starting from gestation 9 weeks to adolescence?
In OI, abnormal collagen fibrils alter bone’s biomechanical properties. How does this explain fractures with minor trauma?
Weak, poorly cross-linked collagen reduces bone tensile strength, so normal forces cause fracture.
Case reasoning: A 2-year-old has multiple fractures, normal labs, no family history, metaphyseal corner fracture, and inconsistent parental history. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Non-accidental trauma (child abuse).