A SANE is examining a patient who was sexually assaulted 72 hours ago. The patient reports being sexually active. Which is an accurate statement regarding testing this patient for sexually transmitted infections?
A. Testing in this situation violates the Rape Shield Act.
B. Testing may or may not identify infection that was acquired before, during, or after the assault.
C. Testing will identify any infection that was acquired during the assault.
D. Testing will identify whether a given infection was acquired before or after the assault.
What is B. Testing may or may not identify infection that was acquired before, during, or after the assault?
*Key Points*
- The medical forensic exam presents an opportunity to identify preexisting STIs, regardless of when they were acquired, and for examiners to make recommendations about specific treatments.
- Trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis (BV), gonorrhea, and chlamydial infection are the most frequently diagnosed infections among sexually assaulted women.
- If prophylaxis treatment is accepted during examination, then testing during exam is not indicated medically. Follow up testing with us is only indicated if patient is symptomatic (recommendation from CDC).
- Educate patient that follow up appointment with PCP or other healthcare clinic in 1 to 2 weeks would be best for follow up testing and assessment.
- Incubation periods differ for each STI
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
After the SANE completes a medical-forensic examination with evidence collection for submission to law enforcement per the patient's request, the patient asks, "Whom do I contact for the results of the evidence kit?" The SANE provides the phone number for the:
A. Crime Laboratory
B. Police Department
C. Primary Care Provider's Office
D. SANE Program
What is B. Police Department?
- SANE should provide any and all appropriate contact information for the members of the multidisciplinary team (law enforcement if involved, advocacy)
- Questions has the answer: "submission to law enforcement"
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
A bruise is accurately described as:
A. a scraping away of the upper layers of the epidermis
B. an indentation of the skin caused by pressure
C. blood leaking into the tissues as a result of a blunt force
D. pinpoint areas of hemorrhage often noted on the eyelids
What is C. blood leaking into the tissues as a result of a blunt force?
BONUS (+100): True or false: A bruise and ecchymosis are the same thing. Why?
*Key Points*
- Mechanism of Injury: blunt force trauma
A = abrasion (MOI: blunt force trauma, "scratches & scrapes" confined to epidermal and dermal layers of the skin)
B = pitting edema? [Laceration (MOI: blunt force trauma), impact that causes tearing, ripping, crushing, over-stretching, or shearing of soft tissue; tissue bridging - incomplete separation of tissue!]
D = petechiae (MOI: blunt force trauma or increase in internal capillary pressure (e.g. strangulation))
*Source: Atlas of Sexual Violence (2013) - IAFN
During the earliest moments of the assessment process, a SANE takes measure to help the patient regain a sense of control. The purpose is to:
A. facilitate cooperation
B. maximize evidence collection
C. prolong the patient encounter
D. promote healing
What is D. promote healing?
*Key Points*
- Provide crisis intervention to the patient and family members or caregivers (SANE-A test content outline)
- Conduct the medical forensic exam with trauma-informed care principles
- Every patient has a different "lived experience" in addition to unique reaction to trauma - must use empathy
- Sensitive and timely medical care (in addition to helping patients physically) can help reduce the likelihood of acute psychological trauma and its aftereffects, support patients' existing and emerging coping skills, and set the tone for patients' resumption of normal functioning. (National Protocol)
*Source: Medical response to adult sexual assault: A resource for clinicians and related professionals (2011) STM Learning Textbook.
A mother accompanies her 14-year-old daughter tot he ED, reporting that the daughter's boyfriend sexually assaulted her. The patient is referred to the SANE for examination. While performing the examination, the SANE finds that the patient's vital signs are within normal limits, her underwear is filled with bright red blood, and she is beginning to cry. The SANE's action is to:
A. Assess the patient for any genital injuries
B. Assess the patient for any non-genital injuries
C. Have the mother provide the patient with support
D. Report the findings to law enforcement or child protective services
What is A. Assess the patient for any genital injuries?
*Key Points*
- Promote safety and provide reassurance
- Medical treatment will ALWAYS be more important than evidence collection
- What if vital signs were not within normal limits? What action would you take?
- B: If another area had blood present, would be more appropriate
- C: Often times, you will need to provide crisis intervention to both
- D: This is illegal in the state of CA - it is the patient's choice whether or not to report (12 years old and older), unless a parent is suspect.
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
The SANE is called to the ICU to conduct a medical-forensic examination of an adult female patient who is intubated. To facilitate the physical examination, the SANE considers what adaptation?
A. Collecting evidence samples from the patient's mouth
B. Collecting the patient's history of the assault in writing
C. Positioning the patient in a lateral recumbent position for collecting genital swabs
D. Positioning the patient on an inverted bedpan for the anogenital assessment
What is D. Positioning the patient on an inverted bedpan for the anogenital assessment?
*Key Points*
- This is applicable not only for the intubated patient, but also any female patient that is unable to transfer to the exam table and place their feet into stirrups
*Source: Lynch & Duval (2011): Forensic Nursing Science (2nd Ed.)
A mother accompanies her 14 year old daughter to the ED, reporting that the daughter's boyfriend sexually assaulted her. The patient is referred to the SANE for examination. Which of the following specimens should the SANE collect while the patient is receiving treatment for her injuries?
A. Buccal swab
B. Clothing and underwear
C. Hair sample
D. Vaginal and anal swabs
What is B. Clothing and underwear?
*Key Points*
- SANE can collect other items of evidence (e.g. clothing, underwear, pad/tampon/diaper, etc.)
- "As soon as possible after the initial triage, management, and stabilization of acute medical problems and before treating non-acute injuries, the evidentiary exam can be conducted...with patient's consent."
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
Location: Anterior left leg
What is an abrasion?
*Key Points*
Abrasion (AB) - caused by the rubbing or scraping away of the superficial layer of skin from a mechanical means such as blunt impact.
* Typically confined to epidermal and dermal layers of the skin
* May occur in conjunction with a contusion/bruise
* Important injuries because they can reveal exact point of contact between an object and the patient's body
* Patient's history can help identify what could have been consistent with making this marking
*Source: Atlas of Sexual Violence (2013) - IAFN
The SANE should address the female patient's risk of pregnancy by:
A. Administering a pregnancy test only to women who are using condoms for contraception
B. Declining to offer emergency contraception when the nurse has a conscientious objections
C. Discussing the probability of pregnancy with all patients of reproductive capability
D. Providing teaching about emergency contraception in the provider's primary language
What is C. Discussing the probability of pregnancy with all patients of reproductive capability?
*Key Points*
- Use patient's preferred language
- Probability: 2-5%, same as a one-time sexual encounter
- Tanner Stage 3 and above (irrespective of menarche) can potentially become pregnant from any single exposure. [reference: Tanner Stage 3 is darker, coarser, curlier hair and hair is beginning to spread upwards on the mons pubis; breasts continue to enlarge - no separation of contour between nipple and breast]
- With patient's consent, administer a pregnancy test (POCT) prior to medication administration
- Plan B (levonorgestrel): when initiated within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse, 85% of pregnancies were prevented. Can be given up to 5 days if patient wants - some continued preventative efficacy. Side effects: nausea, vomiting
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW and Forensic Nursing Science: Lynch & Duvall (2011).
The SANE is testifying in a case of a female patient who reported being sexually assaulted by her spouse. The defense attorney asks the nurse, "Have you ever been a victim of domestic or sexual violence?" The prosecutor does not object. The SANE's most appropriate response is:
A. "I do not have to respond to that question."
B. "My personal life is not relevant to this case."
C. "Why would you need to know that?"
D. "Your honor, do I have to answer that?"
What is D. "Your honor, do I have to answer that?"
*Key Points*
*If the prosecutor fails to object to the question that sounds inappropriate to the witness, the best course of action is to ask the judge for clarification. Is it not usually appropriate or productive to respond to the attorney in a confrontational or non-responsive manner.
*Pretrial preparation is a must - attorneys and examiners should review and discuss the initial examination of the patient and also any subsequent contact between patient and examiner. Also, examiners should review records of the examination and keep a log of materials reviewed.
*Expert witnesses vs. factual witnesses - expert witnesses should be prepared to educate the court (jurors) and should use appropriate terminology for global level of understanding. Factual witness are not allowed to present opinions, on focus on the facts of the case: evidence collection, chain of custody, etc. - testify on what you witnessed)
*Dress in business attire, be sincere/polite/ appear in control and make eye contact with those questioning as well as the jury.
*Allow time to compose answers before speaking and avoid terms such as "I believe" or "I think" - be concise and correct in responses.
* Answer only questions that are asked (do not elaborate unless asked to do so) and if the answer to a question is not known, say so. There is no reason for examiners to explain why they do not know the answer - they can ask to refer to records if their memories need refreshing.
*Source: Core Curriculum for Forensic Nursing (2016) and A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
When examining a 13-year-old female patient, the SANE notes a Tanner stage 3 level of breast development and shaved pubic hair. The patient's hymen is elastic, thick, and redundant. The patient denies being sexually active and reports a sexual assault that includes penile penetration and ejaculation. Given these findings, the SANE's intervention is to:
A. Forgo the urine pregnancy test and not offer emergency contraception.
B. Forgo the urine pregnancy test and offer emergency contraception.
C. Obtain a urine pregnancy test and offer emergency contraception.
D. Obtain a urine pregnancy test and not offer emergency contraception.
What is C. obtain a urine pregnancy test and offer emergency contraception?
*Key Points*
* This scenario describes a Tanner stage that requires intervention. (Source: Medical Response to Child Sexual Abuse: A resource for professionals working with children and families (2011) STM Learning Textbook)
* Any female of reproductive capability (Taner Stage 3 and above, irrespective of menarche) can potentially become pregnant from any single exposure.
* Determination of the probability of conception is affected by many different factors (e.g. use of contraceptives, fertility of victim/perpetrator, time in the cycle of exposure, etc.)
* Transgender male patients may believe they are infertile because of using testosterone, but cases have been reported of unexpected pregnancies, therefore if no hysterectomy has taken place and the nature of the assault suggests it, the possibility of pregnancy should still be discussed, even if no menstruation is occurring.
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
The SANE is examining a 12-year-old female patient who reports being sexually assaulted by her father. The patient left the home and called law enforcement officers, who brought her to the emergency department. The patient reports that her father vaginally penetrated her with his fingers. Which evidence is most likely to corroborate the patient's statements?
A. A DNA reference sample from the patient.
B. Finger swabs from the patient's father.
C. Photographs of the patient's genitalia.
D. The patient's torn underwear.
What is B. finger swabs from the patient's father?
* This evidence would directly support the adolescent's description of the assault. Other options are distracters because they do not provide direct corroboration and could be attributed to multiple other sources.
*Source: Forensic Nursing Science: Lynch & Duvall (2011).
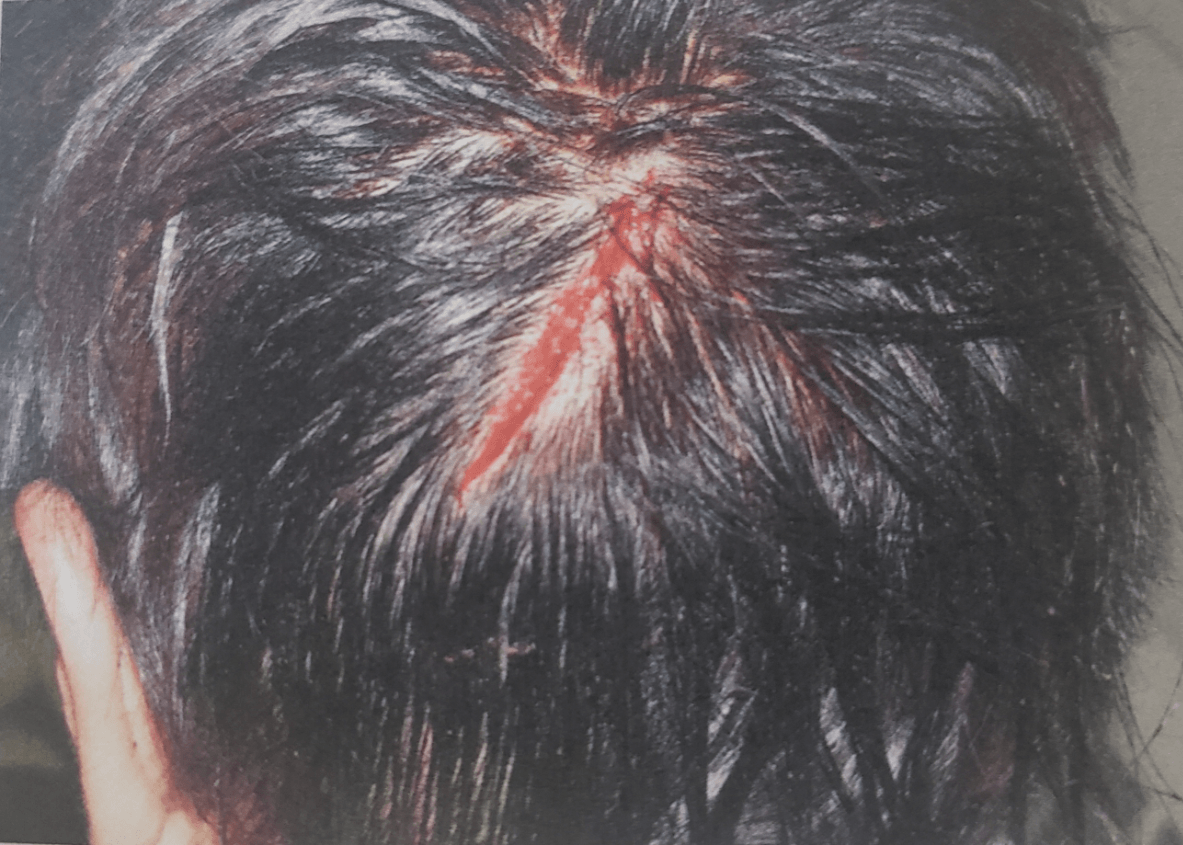 Location: Posterior head
Location: Posterior head
What is a laceration?
*Key Points*
* Lacerations (LA) are caused by an impact that results in tearing, ripping, crushing, overstretching, or shearing of soft tissue.
* In soft tissue tearing, there is an incomplete separation of tissue, resulting in tissue bridging.
* Edges of lacerations are typically irregular or jagged, with possible abrasions and bruising present along the wound margins (AB) and in the surrounding tissues (EC)
*Source: Atlas of Sexual Violence (2013) - IAFN
A 19-year-old female patient reports that she may have been sexually assaulted 3 days ago at a party. Two indicators that she experiences a possible drug-facilitated sexual assault are:
A. anorexia and insomnia
B. drowsiness and some amnesia
C. urinary discomfort and bleeding
D. vomiting and diarrhea
What is B. drowsiness and some amnesia?
(two main symptoms seen)
*Key points*
- Other indicators: fatigue, light-headedness, dizziness, physiologic instability, impaired motor skills, or severe intoxication
- Collect first available urine sample in suspected DFSA (within 96 hours -- BUT depends on jurisdictional rules)
- Collect blood if within 24 hours, but urine is the better sample for DFSA if drugs, not alcohol, used
- Plan response to voluntary use of drugs (legal or illegal) and/or alcohol
*Source: A national protocol for sexual assault medical forensic examinations:Adults/adolescents (2nd ed.) DOJ OVW
The SANE is caring for a female patient who reports forced oral-vaginal penetration by an unknown male perpetrator within the past hour. The law enforcement officer who accompanied the patient to the facility now informs the SANE that a suspect is in custody. The SANE's action is to:
A. Ask the investigating officer to secure a warrant to obtain a blood specimen from the suspect.
B. Direct the investigating officer to obtain a buccal swab from the suspect.
C. Recommend that the investigating officer obtain a buccal swab from the suspect.
D. Recommend that the investigating officer swab the suspect's hands and fingers for evidence.
What is C. recommend that the investigating officer obtain a buccal swab from the suspect?
*Key Points*
- Routinely collected items from suspects (in literature): all clothing believed to be wearing at the time of the assault, pubic hair combings, pulled head and pubic hair controls (now it is NOT recommended to pull hairs, rather clip close to skin and only collect if hair was found in victim exam), blood or buccal swab, penile swab
- SANE is never left alone with suspect, always have law enforcement present in the room
- No interview or history is obtained
- This scenario, the buccal swab may yield reference sample evidence that can be matched to swabs collected from patient and the SANE may recommend but is NOT authorized to direct any other multidisciplinary member
*Source: Lynch & Duval (2011): Forensic Nursing Science (2nd Ed.)
A SANE is evaluating a 13-year-old male patient as part of a child protective services' investigation into his home. His mother states that she wants her son to get "that shot that prevents warts and cancers in his privates." When educating the mother, the SANE explains that the human papillomavirus quadrivalent vaccines (Gardasil) is recommended for:
A. both boys and girls, starting at or after age six years.
B. both boys and girls, starting at or after age nine years.
C. boys in certain situations.
D. girls, but is controversial for boys.
What is B. both boys and girls, starting at or after age nine years?
*Key Points*
- Trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis (BV), gonorrhea, and chlamydia infection are the more frequently diagnosed infections among women who have been sexually assaulted
Treatment for STD/STI post sexual assault, as indicated by CDC:
- Empiric antimicrobial regiment for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomonas: Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM x1 dose, Azithromycin 1 g PO x1 dose, and Metronidazole (or Tinidazole) 2 g PO x1 dose. (alcohol contraindicated within 24 hours for "azole" meds).
- Emergency contraception: Plan B (levonorgestrel) - when initiated within 72 hours of unprotected intercourse, 85% of pregnancies were prevented. Can be given up to 5 days if patient wants - some continued preventative efficacy. Side effects: nausea, vomiting. Ella (ulipristal) - more effective and prevents pregnancy up to 5 days after intercourse; also has better efficacy for patient's with higher BMIs.
- Postexposure hepatitis B vaccine (without HBIG) is indicated if the hepatitis status of the assailant is unknown and the survivors has not been previously vaccinated. If assailant is known to be HBsAg-positive, unvaccinated survivors should receive both hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG. Administration: first dose at initial exam, then 1-2 months later, then 4-6 months after initial dose.
- HPV vaccination is recommended for females ages 9-26 and males ages 9-21 (for MSM, administer up to age 26). Administration: first dose after initial exam, second dose to be given 6-12 months later (update: 12/2016).
- nPEP: follow algorithm, with highest risk of HIV acquisition occurring with: exposure of vagina/rectum/eye/mouth or other mucous membrane/non-intact skin/ or percutaneous contact with blood/semen/vaginal secretions/rectal secretions/breast milk/ or any body fluid that is visibly contaminated with blood when the source is known to be HIV infected.
*nPEP Doses (ages 13+):
- Truvada (tenofovir DF/emtricitabine) 300/200 mg: 1 tablet PO daily x28 days WITH Tivicay (dolutegravir) 50 mg: 1 tablet PO daily x28 days
- Truvada (tenofovir DF/emtricitabine) 300/200 mg: 1 tablet PO daily x28 days WITH Isentress (raltegravir) 400 mg: 1 tablet PO twice daily x28 days
- Truvada (tenofovir DF/emtricitabine) 300/200 mg: 1 tablet PO daily x28 days WITH Prezista (darunavir) 800 mg: 1 tablet PO daily WITH ritonavir 100 mg: 1 tablet PO daily x28 days
*Source: CDC STD Treatment Guidelines (2015).
After contacting the police department to arrange for pick-up of an evidence kit, a new SANE is advised that someone will arrive within the hour. The SANE places the kit on the counter at the nurse's station within easy view and leaves. Which of the following events has occurred because of the SANE's actions?
A. The chain of custody of the evidence has been compromised.
B. The dried DNA specimens can no longer be analyzed.
C. The rape shield statue has been violated.
D. The sterility of the biological samples cannot be ensured.
What is A. The chain of custody of the evidence has been compromised?
*Key Points*
* Leaving evidence unattended in a public place allows the possibility for tampering, thus potentially breaking the chain of custody of the evidence.
* Chain of custody is essentially a paper trail that records where the evidence was, on what date, and who held responsibility for it from the time it was collected until the time it was presented in court.
* Process begins with our evidence collection - then evidence is packaged, sealed, and labeled with appropriate information per jurisdictional protocol. Once sealed, evidence is either given to law enforcement or placed into a locked refrigerator or cabinet with limited access.
*Source: Forensic Nursing Science: Lynch & Duvall (2011).
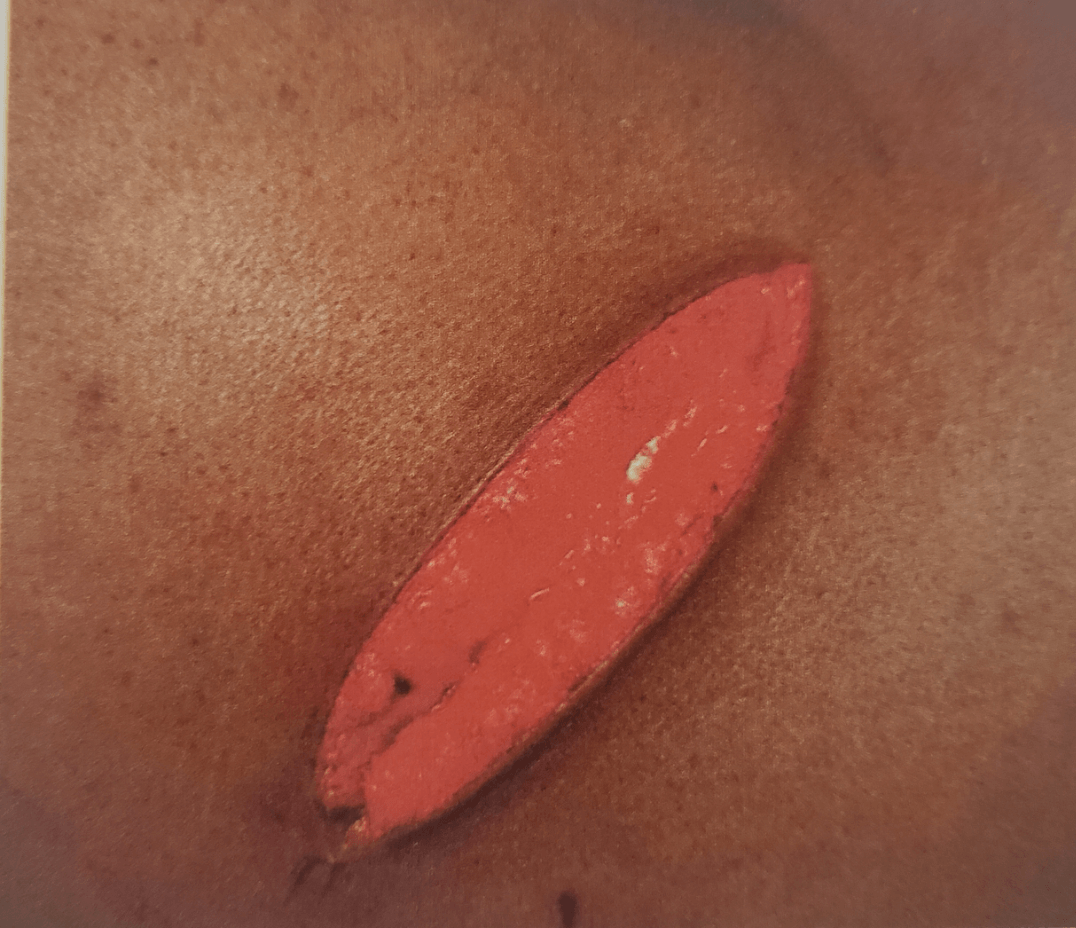 Location: Left hip
Location: Left hip
What is an incised wound?
*Key Points*
Incised wound (IW) - cut; results when a sharp instrument is dragged along a body tissue. Often longer than they are deep.
* Under the category sharp force trauma, these wounds are characterized by having clearly defined, smooth edges, without tissue bridges and without surrounding abrasions or contusions.
* Stab wounds, under the umbrella of incised wound (IW) - characterized by being deeper than they are wide in addition to the bulleted point above. May have AB/EC present at the wound edges from a hilt guard pattern (pattern injury).
*Source: Atlas of Sexual Violence (2013) - IAFN
The SANE provides crisis counseling and helps normalize reactions to trauma when educating a 17-year-old male patient about possible posttraumatic reactions. Which of the following symptoms does the nurse address?
A. Fatigue, lethargy, nausea
B. Fear, irritability, suicidal thoughts
C. Intrusive thoughts, depression, dissociation
D. Palpitations, sweating, chills
What is C. intrusive thoughts, depression, dissociation?
*Key Points*
*Possible posttraumatic symptoms among male and female patients include depression, anxiety, fear, and hostility. However, male patients, although less likely to report, evidence more instances of intrusive thoughts, emotional distancing, depression, anxiety, and hostility than female patients.
*Source: Medical response to adult sexual assault: A resource for clinicians and related professionals (2011) STM Learning Textbook.
A SANE is called to examine a female sex trade worker who was a victim of sexual assault. The patient is well known to both law enforcement and the emergency department staff, as she frequently comes in intoxicated. When the SANE contacts law enforcement officials, they express reluctance to collect the evidence collection samples. From which forensic nursing standards of performance does the nurse seek guidance?
A. Collaboration and ethics
B. Collegiality and resource utilization
C. Education and quality of care
D. Research and performance appraisal
What is A. Collaboration and ethics?
*Key Points*
* SANE should seek guidance from the professional performance standards to ensure effective forensic outcomes by facilitating open communication and collaboration
*Ethical values that guide forensic nurses: objectivity, confidentiality, and beneficence
* Standards of Professional Performance for Forensic Nurses:
* Standard 7: Ethics - The forensic nurse practices ethically.
* Standard 8: Culturally Congruent Practice - The forensic nurse practices in a manner that is congruent with cultural diversity and inclusion principles.
* Standard 9: Communication - The forensic nurse communicates effectively in all areas of practice.
* Standard 10: Collaboration - The forensic nurse collaborates with patient, family, and other key stakeholders in the conduct of nursing practice.
* Standard 11: Leadership - The forensic nurse leads within the professional practice setting and the profession.
* Standard 12: Education - The forensic nurse seeks knowledge and competence that reflects current nursing practice and promotes futuristic thinking.
* Standard 13: Evidence-Based Practice and Research - The forensic nurse integrates evidence and research findings into practice.
* Standard 14: Quality of Practice - The forensic nurse contributes to quality nursing practice.
* Standard 15: Professional Practice Evaluation - The forensic nurse evaluates one's own and others' nursing practice.
* Standard 16: Resource Utilization - The forensic nurse utilizes appropriate resources to plan, provide, and sustain evidence-based nursing services that are safe, effective, and fiscally responsible.
* Standard 17: Environmental Health - The forensic nurse practices in an environmentally safe and healthy manner.
*Source: Forensic Nursing (2nd Ed.): Scope and Standards of Practice
A SANE provides a provides a patient with instruction for photodocumentation follow-up that includes a measurable goal and a time frame for attainment. Which standard of practice for forensic nursing is the nurse demonstrating?
A. Consultation
B. Diagnosis
C. Evaluation
D. Outcomes Identification
What is D. Outcomes Identification?
*Key Points*
* There are 6 standards of practice: assessment, diagnosis, outcomes identification, planning, implementation, and evaluation. These Standards of Practice for Forensic Nurses describe a competent level of forensic nursing care as demonstrated by the critical-thinking model known as the nursing process.
*Standard 1: Assessment - The forensic nurse collects pertinent data and information relative to the patient's health, death, or the situation.
*Standard 2: Diagnosis - The forensic nurse analyzes the assessment data to determine actual or potential diagnoses, problems, and issues.
*Standard 3: Outcomes Identification - The forensic nurse identifies expected outcomes for a plan individualized to the patient or the situation.
*Standard 4: Planning - The forensic nurse develops a plan that prescribes strategies to attain expected, measurable outcomes.
*Standard 5: Implementation - The forensic nurse implements the identified plan.
-5A: Coordination of care
-5B: Health Teaching and Health Promotion
*Standard 6: Evaluation - The forensic nurse evaluates progress towards attainment of goals and outcomes.
*Source: Forensic Nursing (2nd Ed.): Scope and Standards of Practice
Locard's principle addresses:
A. chain of custody
B. informed consent
C. medical ethics
D. physical evidence
What is D. physical evidence?
*Locard's principle: when a person or object comes into contact with another person or object, there exists a possibility that an exchange of materials will take place.
*The presence or absence of physical evidence can corroborate or disprove a person's recollection of events.
*Note: Evidence is only of value in an investigation or in a court of law if its integrity is upheld through careful handling, proper collection, and a documented chain of custody.
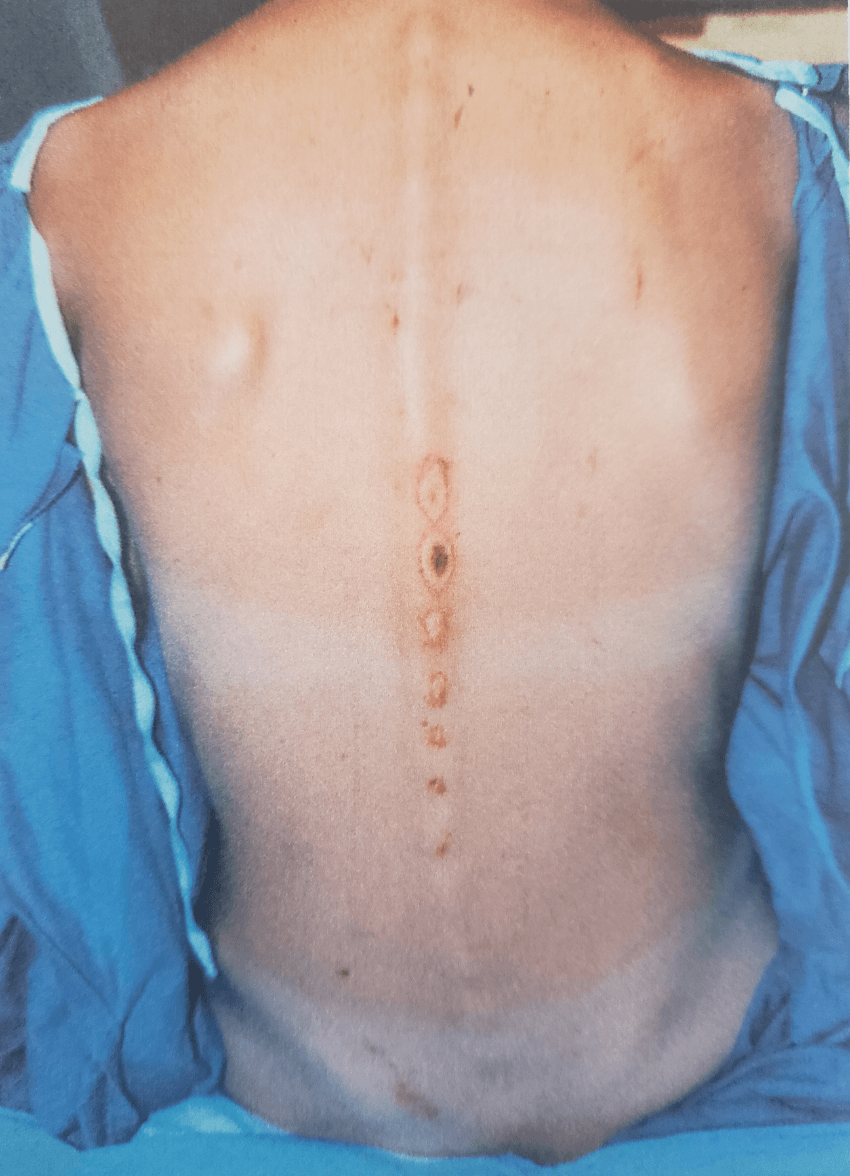 Location: Midline back
Location: Midline back
What are drag marks? (What are drag mark patterned abrasions?)
*Key Points*
* Drag marks - oval-shaped bruises (EC) and abrasions (AB) on the skin overlying the spinous processes (commonly seen when person is dragged across the floor/ground in supine position)
* Other types of common pattern injuries:
- Finger pad marks - 1 to 2 cm circular bruises (EC), caused by pressure of the finger pad/tip during grabbing, holding, pressing, or squeezing.
- Grip marks - bruise pattern (EC) that reflects the grip impression left by the hand/fingers. Most common grip mark is a cluster of finger pad bruises (with 3 marks - index, middle, ring finger) on one side of the extremity and one mark (thumb) on the directly opposite side. Can have large bruises (EC) or abrasions (AB) when significant pressure is applied.
- Slap marks - redness with swelling (welts) or bruise (EC) patterns that reflect the outline of the palm and fingers as a result of force of an open hand against the skin.
*Source: Atlas of Sexual Violence (2013) - IAFN
A 14-year-old male patient reports, "I have to tell you this before the coach does it to anyone else. He says that if I want to play Friday night in the game, I have to let him stick his dick in my ass first, then suck on it till he finishes. Last night, he made me bring my girlfriends. She's 13 and he did the same thing to her and made a video of it on his phone. He told me, 'If you tell, I will send it to everyone in the school.' " To facilitate emotional healing, the SANE refers the patient to which mental health resource?
A. Individual therapist
B. Local support group
C. Online support group
D. School psychologist
What is A. Individual therapist?
*Key Points*
*Sexual assault/abuse of adolescents may cause adverse short-term and long-term consequences.
*SANE should encourage the patient to access available mental health services - all children and adolescents who have been sexually assaulted should be evaluated by a mental health practitioner -- in this instance, an individual therapist is the best option
*Source: Medical response to adult sexual assault: A resource for clinicians and related professionals (2011) STM Learning Textbook.
The SANE is called to see a 30-year-old female patient who recently emigrated from Syria - where she experienced violence and conflict, and witnessed the torture of her family members - and immigrated to the United States. She arrives at the ED, reporting a sexual assault by her husband. Which of the following interventions does the nurse use when demonstrating culturally competent care?
A. Arranges for a psychiatric assessment to ensure that the patient is not suffering from a pathological disorder.
B. Provides education to the patient about normal responses to trauma and develops a safety plan with her.
C. Questions and listens to the patient about cultural values, beliefs, and healthcare practices, including home or folk practices.
D. Researches Syrian history and cultural practices to gain an understanding of the patient's perspective.
What is C. Questions and listens to the patient about cultural values, beliefs, healthcare practices, including home or folk practices?
*Key Points*
* To provide culturally competent care, a SANE should "listen to and learn from the client about cultural values, beliefs, and daily practices related to care and health in their environmental context, specifically home or folk practices." (Price & Maguire, p. 23)
* Develop culturally competent and sensitive care by building awareness about and sensitivity to the ways that culture can impact a person's experience in the immediate aftermath of sexual assault and across the lifespan.
* Be aware and responsive to the ways in which cultural identities may influence a person's experience during the exam process
* Build an understanding of the perspectives of a specific population, as it may help increase the likelihood that the actions and demeanor of responder will mitigate victim trauma.
* Other recommendations made for this and Victim-Centered Care in A National Protocol for Sexual Assault Forensic Examinations:
- Give the sexual assault patients priority as emergency cases and provide necessary means to ensure patient privacy
- Adapt the exam processes as needed to address the unique needs and circumstances of each patient.
*Develop culturally responsive care and be aware of issues commonly faced by victims from specific populations.
- Recognize the importance of victim services within the exam process.
- Accommodate patient's request for support person (e.g. family, friend, religious or spiritual support, etc.) unless considered harmful by responders
- Accommodate patient's request for responders of a specific gender throughout the exam as much as possible.
- Prior to beginning exam and each piece of the procedure (the what and why), explain to patients in a language that is understood well by the patient
- Assess and respect patient's priorities, and also address patient's safety during the exam
- Integrate medical and evidentiary procedures where possible
- Provide information that is easy for patients to understand, in the patient's language, and that can be reviewed at their convenience (e.g. discharge instructions)
- Address physical comfort needs of patients prior to discharge
*Source: Core Curriculum for Forensic Nursing (2016)