For a patient who continues to bleed after a 2nd attempt at endoscopic control of a bleeding ulcer, this is the next most appropriate intervention
Angiographic embolization

Name the 3 branches of the celiac axis
Splenic artery, left gastric artery, common hepatic artery

When operating for a bleeding ulcer, vagotomy should be considered in which group of patients?
Patients who have failed, or are unable to comply with, PPI therapy
This medication prophylactically reduces the risk of variceal bleeding
Propranolol
This UGIB source is classically characterized by emesis that turns from non-bloody to bloody
Mallory-Weiss tear

This underlying process is the #1 cause of aorto-enteric fistula formation
Aortic graft infection

Splenic vein thrombosis
This is the next step in acute management if rubber bandings and intravariceal sclerosing therapy do not control esophageal variceal hemorrhage
Balloon tamponade
(Sengstaken–Blakemore tube)

This is the recommended period of post-endoscopy NPO status following endoscopic control of a bleeding duodenal ulcer with low risk features
0 hours
Describe a Cushing ulcer
Name the classic triad of hemobilia
- obstructive jaundice
- RUQ pain
- UGIB
This vessel is the source of the gastroduodenal artery
Common hepatic artery

This is the recommended vascular reconstruction option for patients with an aortoenteric fistula
Axillary bifemoral bypass

This is the most sensitive imaging test to detect upper GI bleeding
Tagged RBC scan

In persons with a hiatal hernia, these are linear mucosal ulcerations of the stomach occurring where the stomach is constricted by the diaphragmatic hiatus
Cameron lesions

On initial EGD for diagnosis and management of a bleeding duodenal ulcer, name the location which should be biopsied and the reasoning for this biopsy
Biopsy gastric mucosa to evaluate for H. pylori
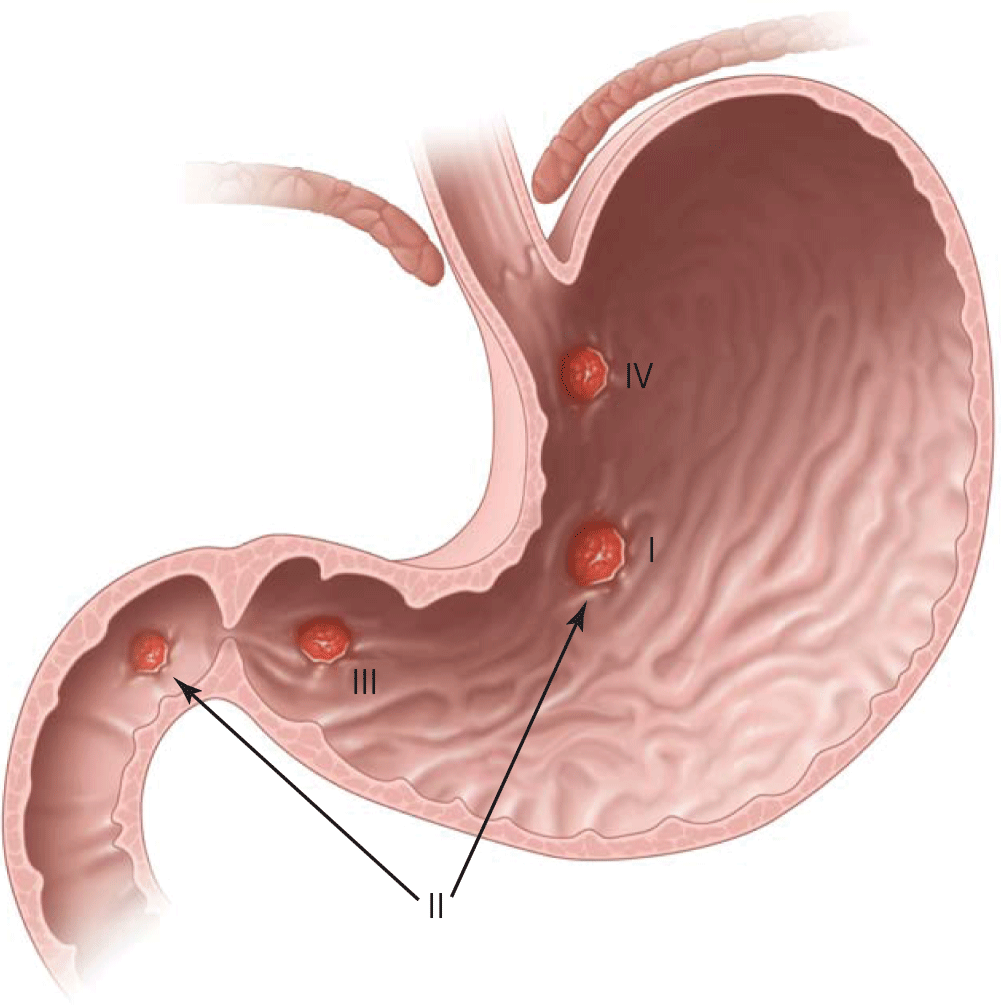
This is where Type II Gastric ulcers are located
Lesser curvature and duodenal bulb
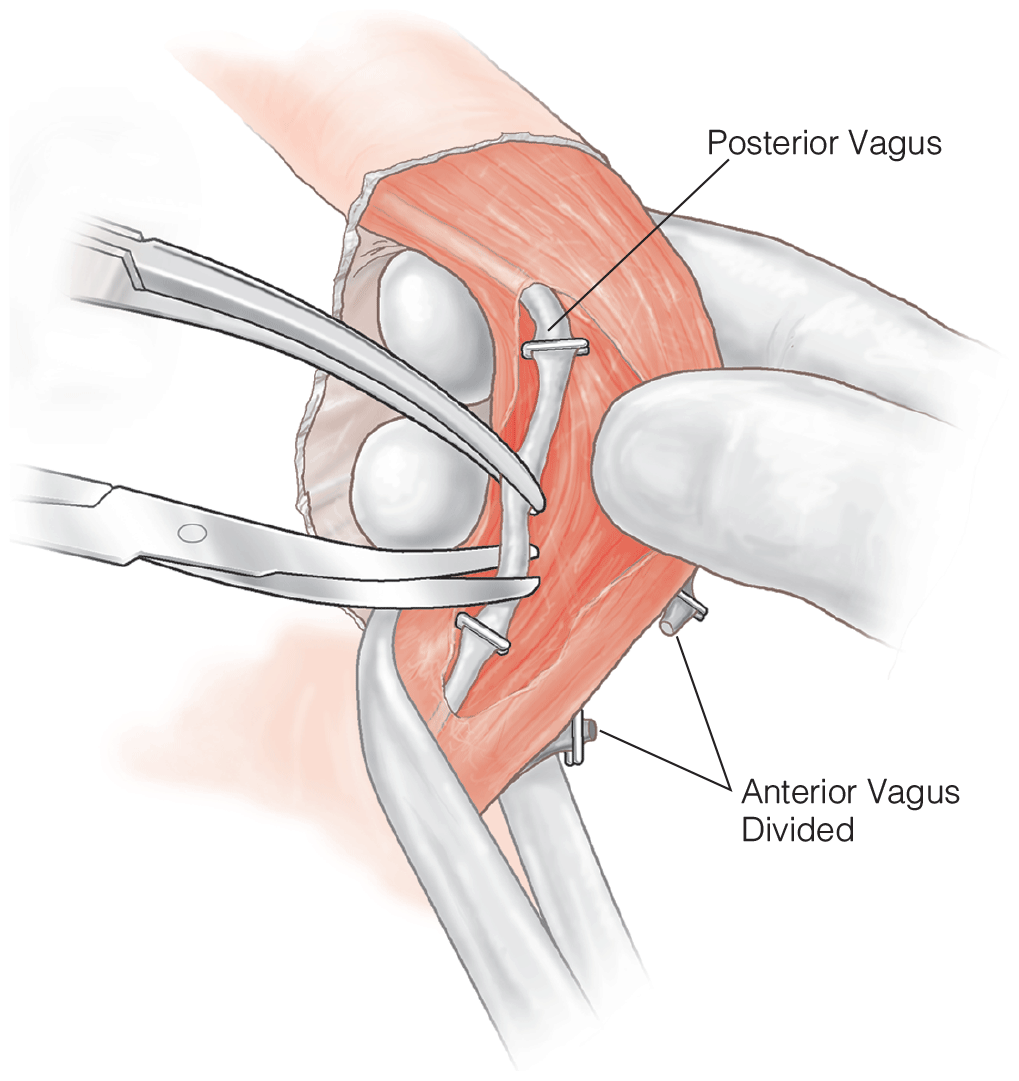
When performing a truncal vagotomy, this procedure must also be performed to prevent post-operative complication
pyloroplasty
E.g. Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty
Name the 3 hard indications for operative intervention in a bleeding ulcer
- hemodynamic instability
- transfusion >6 units
- EGD fails to control hemorrhage
This is a large submucosal arteriole in the stomach which is prone to bleeding
Dieulafoy lesion

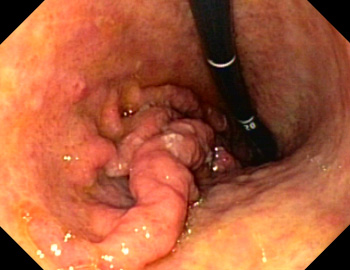
List the findings of an ulcer on EGD which predict the risk of rebleeding, from highest to lowest risk
(HINT: there are five)
1. active pulsatile bleeding
2. active oozing
3. visible vessel
4. adherent clot
5. flat pigmented spot
Example of #3:
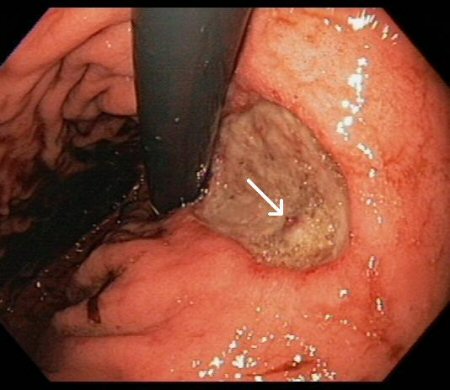
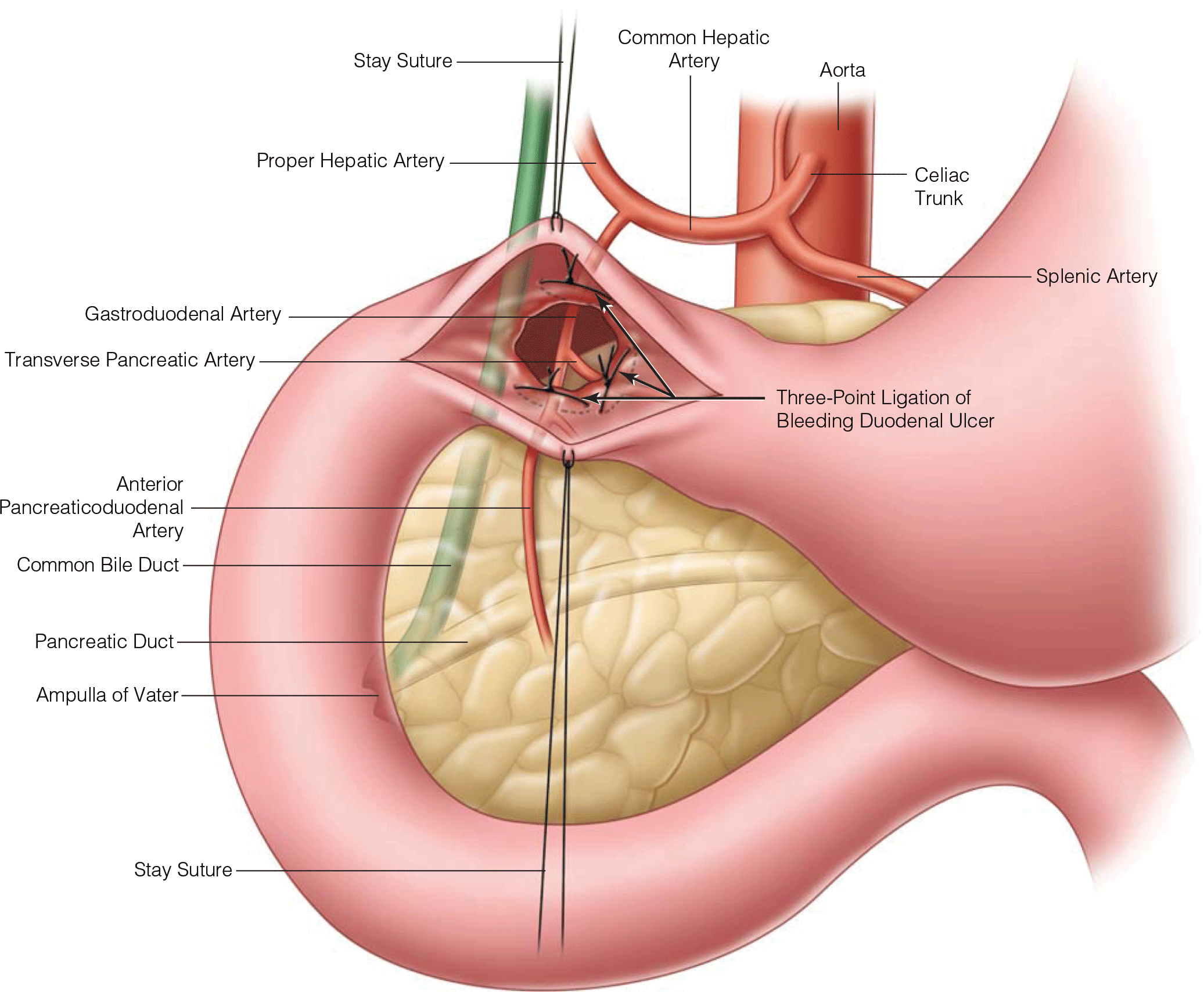
When ligating a bleeding GDA, three sutures are placed: superior, inferior, and medial. The medial stitch is intended to ligate this named structure
Transverse pancreatic artery
This is the surgical treatment for a persistently bleeding Type I gastric ulcer
Wedge resection
The AIMS65 score predicts mortality in patients with acute UGIB. Name the 5 variables which encompass the AIMS65 score
1. Albumin
2. INR
3. Mental status
4. Systolic BP < 90
5. Age > 65
Describe a Curling ulcer
Gastric ulcer resulting as a complication of severe burns
