What is the name of a single nerve cell?
Neuron
What is the difference between receptors and effectors?
Receptors detect stimulus, effectors cause the body's response to the stimulus
Which blood vessels transport blood towards the heart?
Veins
What does the endocrine system use to control the body?
Chemical messengers/signals
What is the purpose of the immune system?
Defend the body against pathogens
What could you say about the sensitivity of an area of skin if it contains a high number of touch receptors.
It will be more sensitive
Which type of receptors detect temperature stimuli?
Thermoreceptors
Approximately what percentage of the air is made up of nitrogen?
70%
What hormone helps regulate sleep cycles?
Melatonin
What is the first line of defence of the immune system?
Draw/List the steps of the stimulus-response model
Stimulus, Receptor, Control Centre, Effector, Response
What is a reflex action?
A reflex action does not require input and processing from the brain to perform
What is the name of the tiny air sacs that are lined with capillaries?
Alveoli
Which two hormones are associated with managing blood sugar levels?
Bonus points if you can name both.
Insulin, Glucagon
Which chemicals identify pathogens as foreign to the body?
Antigens
The sympathetic nervous system manages a particular response. Actions associated with this response include adrenaline production, raised heartbeat, and dilated pupils. What is the name commonly given to this response?
Fight or Flight response
What two organs make up the central nervous system?
Brain & Spinal Cord
Name the four main chambers of the heart.
Left atrium, Left ventricle, Right atrium, Right ventricle
Name the three endocrine glands of the brain (spelling not being marked)
Pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
What is the name of the specialised white blood cells that attack foreign material in the second line of defence?
Phagocytes
Give an example of a response the body might perform to manage decreased body temperature.
Shivering, constriction of blood vessels, decreased rate of sweating
What part of the brain is labelled as B?
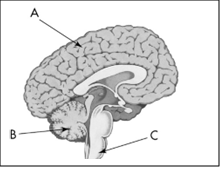
Cerebellum
What is the name of the protein in the blood that oxygen binds to?
Haemoglobin
Which hormone, produced by the pituitary gland, cause the reabsorption of water through the kidneys?
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
How does the immune system develop an immunity to a particular pathogen?
The body makes specific anti-bodies to target and identify specific pathogens. These anti-bodies help the body identify and respond to the pathogen if it is encountered again.