What is the function of DNA?
Store and transmit genetic information
What happens to electrons in ionic bonds?
What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
kinetic - energy in motion
potential - stored energy due to position
What type of energy transformation occurs when a plant absorbs sunlight?
solar energy turns into chemical energy
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy it takes to heat 1 gram of substance up by 1 degree Celcius.
What are the three main components of DNA?
sugar-phosphate backbone
nitrogenous base pairs (adenine-thymine, guanine-cytosine)
Is NO an example of an ionic or a covalent bond?
Covalent (two non-metals)
Name three types of kinetic energy.
mechanical, radiant, thermal, sound
Name two energy transformations developed by humans that provide us with benefits. What are the negative impacts of these?
cement - CO2 emissions
Steam engines - air pollution
batteries - toxic waste
gas powered vehicles - air pollution
nuclear reactors - radiation is harmful to life
fuel cells - CO2 emissions
What are the four stages in the water cycle?
condensation
precipitation
evaporation & transpiration
run-off
What is a DNA mutation? What do they do?
A change in the code of the nitrogenous base pair sequence.
It changes the structure or function of something in that organism. May be good or bad.
What is the law of conservation of mass?
Mass is neither created nor destroyed.
Why does some of the incoming solar energy not reach the surface of the earth?
What is condensation?
change of matter from gaseous to liquid state (formation of clouds in the atmosphere)
What is natural selection?
Survival of the fittest. The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment survive and produce more offspring.
They get warmer. Endothermic reactions take in energy (heat) from the environment. Exothermic give off energy (heat).
Why is thermal energy a type of kinetic energy?
Thermal energy is the random motion of the particles in a substance. Kinetic energy involves anything in motion.
What is the difference between conduction, convection, and radiation? How do they all impact atmospheric temperature?
conduction - heat transfer by touching (land warms air)
convection - heat transfer by current (warm air rises)
radiation - heath transfer by electromagnetic waves (land heats air)
Compare and contrast (name similarities and differences) of evaporation and transpiration.
similarities - both release water vapour (gas) to the atmosphere
differences - evaporation is when water from the earth's surface turns from liquid to gas; transpiration is the release of water vapour from plants
What is an example of an adaptation of a species living in Norman Wells?
smaller trees - shorter growing season
ptarmigan changing colour in winter
musox - warm quiviut for cold temperatures
What are four types of reactions?
synthesis: A + B --> AB
decomposition: AB --> A + B
single replacement: AB + C --> AC + B
double replacement: AB + CD --> AD + BC
combustion: AB + 02 --> AO (CO2) + BO (CO2)
In a Rube Goldberg machine, a candle pops a balloon, which is holding up a ruler. When the balloon pops, the ruler falls onto a bell that rings.
Outline the energy transformations that occur.
chemical PE --> thermal KE -->mechanical KE --> elastic PE + gravitational PE --> mechanical KE + sound KE
What is the greenhouse effect?
Greenhouse gases (CO2, water vapour, methane, nitrous oxide) trap the heat of the atmosphere (absorb incoming infrared radiation from the sun), preventing it escaping to space.
As a result, we have an environment on earth capable of life, but also global warming (climate change) negatively impacting global ecosystems.
Evaluate this graph, comparing aluminum to water. Analyze what this means.
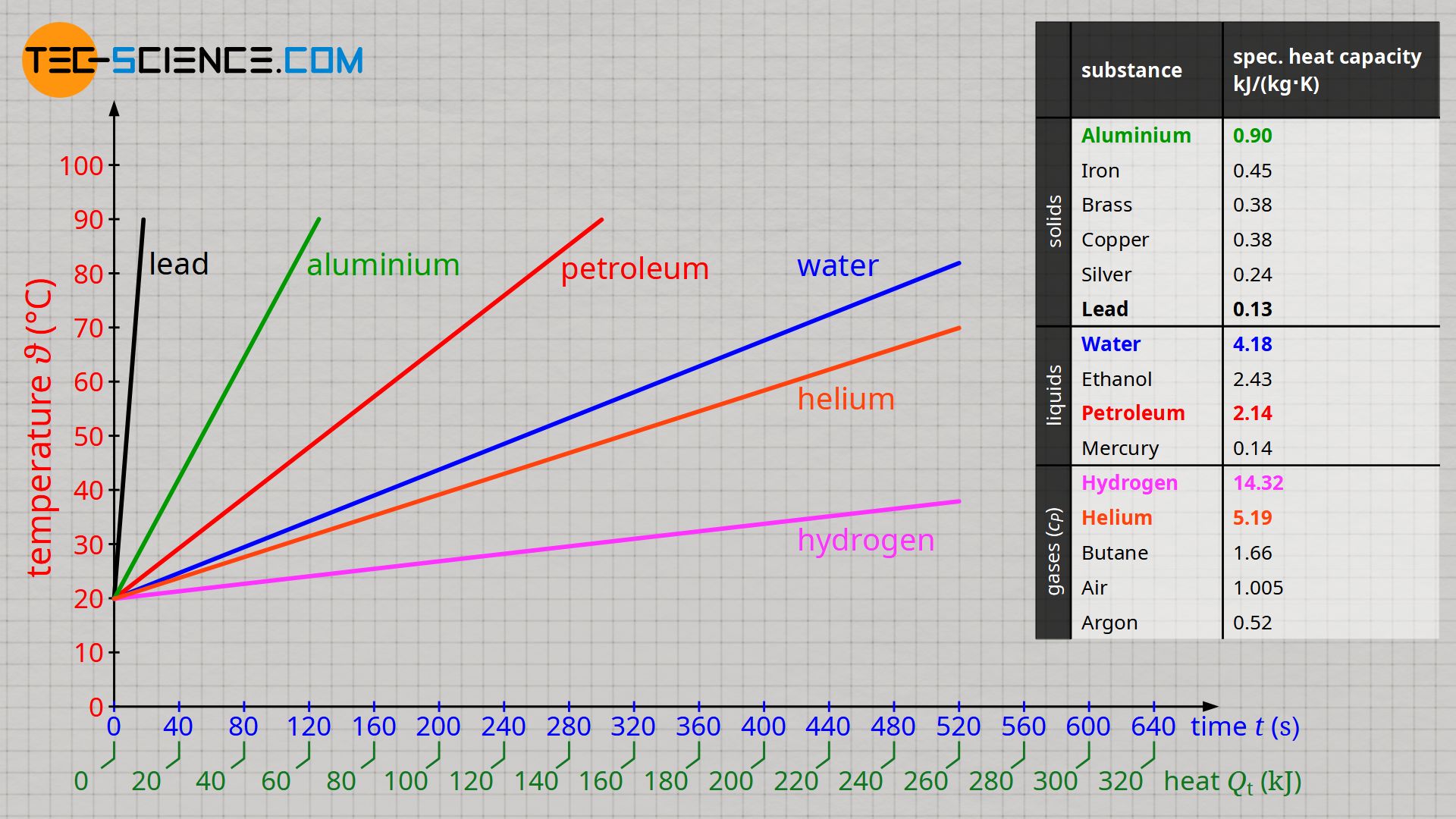
Water has a higher specific heat capacity than aluminum. That means that it takes more energy to heat the same amount of water up than it does aluminum. However, water will hold onto the heat for longer than aluminum, staying warmer for longer.