This is a quantity with magnitude and direction
Vector
Acceleration is this type of quantity
This quantity is usually on the x-axis
Time
This is used to calculate the length of yellow lights at intersections
Stopping Distance
The net force on a box that is being pushed with 150N [W], 50N [E], and 100N [W]
200N [W]
Mass and time are this type of quantities
Scalar
These are the units for acceleration
m/s^2
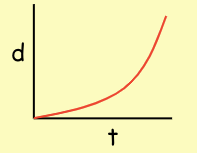
The sum of the reaction distance and braking distance
Stopping distance
An object in motion will stay in motion, and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
Newton's 1st Law of Motion
This is my displacement if I move 150m [N], then 50m [S], then 100m [N]
200m[N]
When acceleration and velocity are in the different directions
Slowing Down / Negative Acceleration
You can use this on your graph to calculate speed on a distance-time graph
This is the typical reaction time for drivers
1.50s
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion
Inertia
This is the formula for velocity
vec v=(∆vecd)/t
This is the formula for acceleration
veca=(vecv_f-vecv_i)/t
You can use this to find displacement on a velocity-time graph
Area under the curve
The stopping distance can be thought of as the length of this for the intersection
Area of no return
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
The time is takes for a car moving 40km/h to travel 25m.
2.3s
These are the formulas for non-uniform motion
vecd=((vecv_f+vecv_i)/2)t
vecd=vecv_it+1/2vecat^2
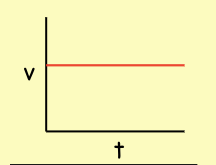
The distance travelled when the driver must recognize a need to stop and must move their foot from the gas to the brake pedal.
Reaction distance
An object acted upon by an unbalanced force experiences an acceleration in the direction of the force.
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion