Which natural occurrence causes the tectonic plates to move?
convection currents
What happens when the plate boundaries move?
Earthquake
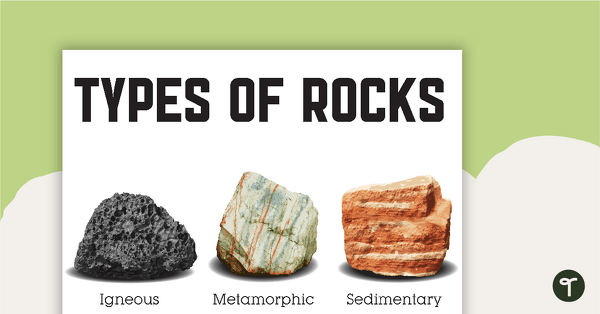
Name and define the three main rocks
Igneous- rock formed from the cooling of molten rock; can be extrusive or intrusive depending on if it cooled outside (extrusive) or inside (intrusive) the earth
Sedimentary- rock formed from sediments (clastic), plant or animal remains (organic), or chemical precipitates (chemical) in an aquatic environment.
Metamorphic- rock that has been changed by heat and pressure; can have banding (foliated) or no banding (non-foliated). Associated with mountain building
Where did oxygen come from?
photosynthesis of microorganisms
Describe where the water in Earth’s ocean originated.
volcanic outgassing, and asteroids, meteorites, and other objects that bombarded
What is the lithosphere?
upper most part of the mantle and lower part of the crust
Name 5 geologic features
mountains, volcanic mountains, trenches, earthquakes, mid-ocean ridges, seafloor spreading, rift valley, subduction.
What is weathering?
the breakdown of rock due to rain, wind, ice, sunlight, and living organisms
What is the current atmosphere composition?
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and tiny amount of carbon dioxide
What was the cause of the increase in oxygen gas in the atmosphere?
Tiny organisms called cyanobacteria caused the increase of oxygen in the atmosphere because since oxygen is a waste product, bacteria, protists, and plants can produce oxygen.
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
Crust, Mantle, Core
What are p and s waves?
P-waves: squeeze and push rocks in the direction along which the waves are traveling
S-waves: motion that causes rocks to move perpendicular to the direction of the waves
What is it called when water evaporates from plants?
Transpiration
what is Ozone?
Ozone is made up of three oxygen atoms located in the stratosphere which absorb UV radiation
What is volcanic outgassing and why was this important for the formation of the atmosphere?
Volcanic outgassing was a volcanic eruption that released large quantities of gas. This is important for the formation of the atmosphere because the volcanoes also release large amounts of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of nitrogen and other gases.
Why is the earth's core hot?
The melting temperature of iron under deep-earth conditions is high
What are the 3 types of convergence plate boundaries?
continental-continental convergence
continental-ocean convergence
ocean-ocean convergence
Name 6 of the processes of the hydrologic cycle.
precipitation, evaporation, condensation, infiltration, runoff, respiration, transpiration, discharge, uptake
How did volcanoes affect the earth's early primeval atmosphere?
Volcanoes were very active when the Earth was young and they released gases (Nitrogen (ammonia), Carbon Dioxide, Water vapor, and Sulfur oxides).
Identify the ingredients that Miller and Urey thought made up Earth’s early atmosphere.
carbon dioxide, water vapor, and traces of ammonia, methane, and hydrogen.
Based on density in what order would the following layer (least dense to most dense)?
outer core, crust, mantle, atmosphere, inner core
atmosphere, crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
What is a seismic wave?
a wave of energy that travels through the Earth's layers are - caused by earthquakes, explosions, or volcanos
What type of rock can you find on continental crust? Granite or Limestone.
Granite rock
How did the development of the ozone help life move to the land?
It protected living organisms from UV radiation.
Explain why an atmosphere rich in oxygen was important for the evolution of life on Earth.
An atmosphere rich in oxygen is important because it is required for animals' respiration and protects us from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.