What is an autotroph?
An organism that makes its own food such as plants and algae.
What are the parts of a virus?
A protein coat and genetic material.
Describe how an amoeba obtains its food.
Describe how a parameciumm obtains its food.
An amoeba uses its pseudopods to feed. The pseudopods wrap the food source which then gets engulfed into the cell.

Paramecium uses its cilia to sweep the food into its cell.

- Explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves. Use diagrams to illustrate your explanation.

Transverse waves: the waves travel perpendicular to the disturbance
Longitudinal waves: the waves travel parallel to the disturbance
- How can loud noises damage your hearing?
Extended exposure to loud sounds can damage the hair cells. If these cells are damaged by loud sounds, they can no longer transmit signals to the brain.
What is a prokaryote?
An organism whose cells do not have a nucleus.
Bacteria and archaebacteria are prokaryotes.
- Describe the similarities of and differences between active and hidden viruses.
An active virus invades the cell, takes over the cells and starts producing new viruses right away.
A hidden virus invades the cell, the genetic material of the virus becomes part of the genetic material of the cell. It remains hidden there until an environmental stimulus makes it active.
Compare how animal-like, funguslike, and plantlike protists obtain food.
Animal-like protists or protozoans are heterotrophs, they feed from other organisms.
Fungus-like protists are heterotrophs and they absorb food from their surroundings.
Plant-like protists are autotrophs and make their own food.
- How can you find the amplitude of a longitudinal wave?
The amplitude is the height of the wave.
It it measured from rest to crest or trough.
- When a drum vibrates, the air molecules that begin vibrating next to it do not reach your ear, yet you hear the sound of the drum. Explain.
Sound travels as a longitudinal wave. The vibration from the drum is sent to the air molecules. The sound waves travel through air with compressions and rarefactions.

Give the characteristics of these groups (# of cells, type of cells and how they feed):
Bacteria
Protists
Fungi
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotes and can be autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Protists are eukaryotes and can be unicellular or multicellular, can be autotrophs or heterotrophs.
Fungi are eukaryotes and can be unicellular or multicellular and are all heterotrophs (absorb food from their surroundings).
List three ways that viruses are different from cells.
Viruses do not have cells, do not make their own food, do not grow and develop.
- Explain how a fungus feeds. What do fungi feed on?

- How are a wave’s speed, wavelength, and frequency related?
Speed = wavelength X frequency
Units:
Speed: m/s
Wavelength: m
Frequency: Hz
- List in order of increasing frequency the kinds of waves that make up the electromagnetic spectrum. Name one use for each.

In order of increasing frequency:
radio waves used in radio transmissions
microwaves used in microwaves and Radar and MRI
infrared used in thermograms
visible
ultraviolet used in UV lamps to kill bacteria from surfaces
X-ray used in X-ray imaging
gamma rays used in gamma ray telescopes
Suppose that a new type of unicellular organism is discovered. Observations show that it has a nucleus. Would the organism be classified as a member of the archaebacteria, eubacteria, or protist kingdom? Explain.
If it has a nucleus then it is a eukaryote and can be a protist.
Archaebacteria and eubacteria are prokaryote, their cells do not have a nucleus.
Explain why a certain virus will attach to only one or a few types of cells.
The surface proteins of the virus needs to match the surface proteins of the cell like a lock and key mechanism.
What is the major difference between fungi and plants?
Plants make their own food while fungi feed from their surroundings.
Describe the difference between constructive and destructive interference.

Interference The diagrams show how identical waves can combine. A. When the crests align, the waves add together and produce a wave with twice the original amplitude. B. When the crests of one wave align with the troughs of another, they cancel each other out. C. If one wave travels a little behind the other, they combine both constructively and destructively at different places.
What type of image does a concave lens form?
As parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens, they are bent away from the center of the lens. The diagram below shows how the rays spread out, but appear to come from the focal point on the opposite side of the lens. Because the light rays never meet, a concave lens can produce only a virtual image.

Your friend thinks that plants are not alive because they do not move. How would you respond to your friend?
- cellular organization
- similar chemicals
- use energy to grow, develop and reproduce
- reproduce
- respond to their surroundings
- Draw how an active and how a hidden virus multiplies.
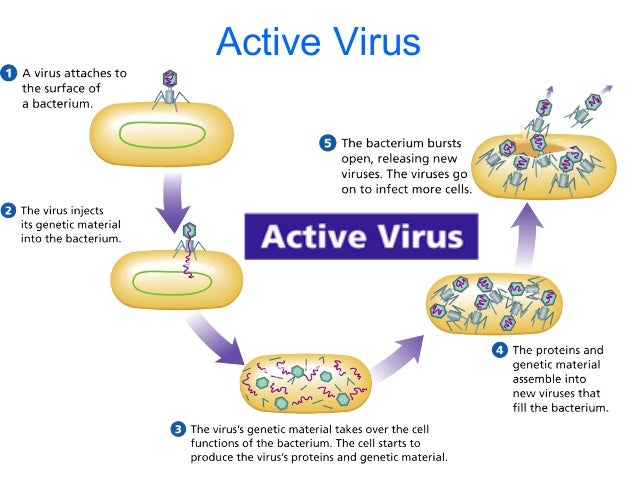
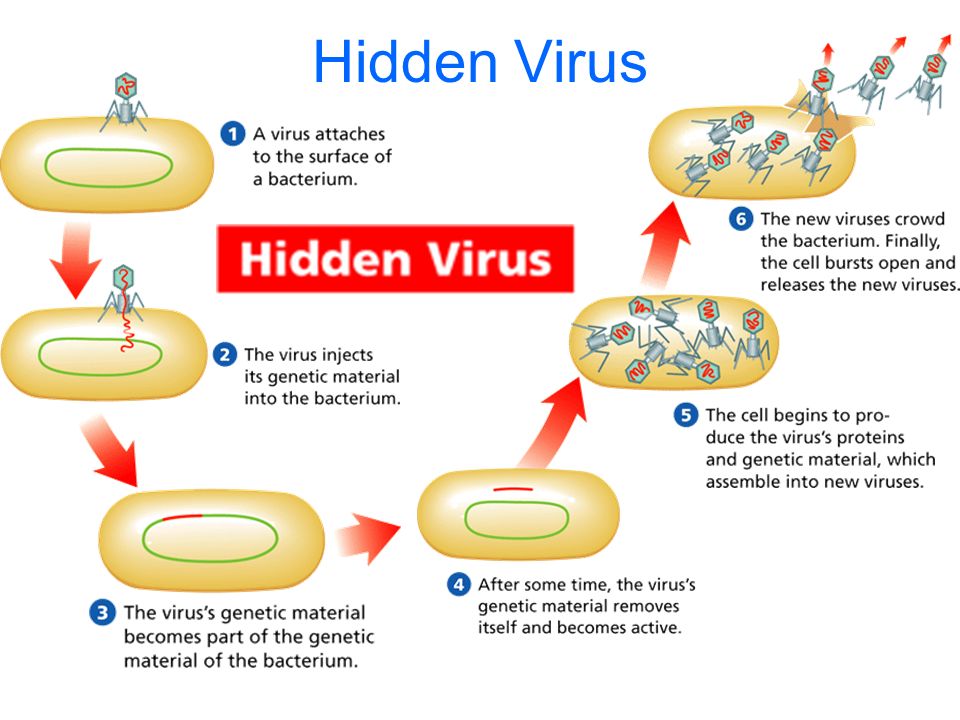
Describe three roles that fungi play in the world.
Fungi are:
- decomposers
- environmental recyclers
- food source
- disease-fighting fungi such as penicillin which is used as an antibiotic
- associate with plants and help plants grow larger and healthier
- lichen consists of a fungus and either algae or autotrophic bacteria that also live together in a mutualistic relationship
- Diffraction
- Reflection
- Refraction
Diffraction: When a wave passes a barrier or moves through a hole in a barrier, it bends and spreads out.

Reflection: When an object or wave hits a surface through which it cannot pass, it bounces back.

Refraction: When a wave moves from one medium into another medium at an angle, it changes speed as it enters the second medium, which causes it to bend.
Look at the diagram below and explain why we see a rainbow after rain?
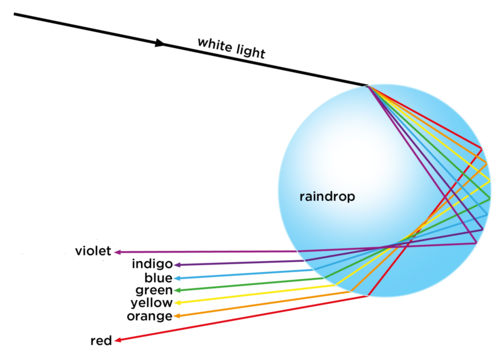
The raindrop acts like a tiny prism. Light is reflected and refracted.