What is the supercontinent called?
What is Pangea?
Relate how a cracked eggshell looks to to its corresponding layer of the earth?
What is the lithosphere?
What type of plate movement is shown?
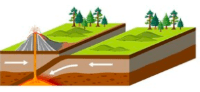
What is convergent/colliding plate movement?
What term is used to describe an upfold in the rocks?
What is anticline?
What does syncline mean?
What is a downfold in the rock?
In 1910 a German scientist named Alfred Wegener noticed that the shapes of the continents seemed to fit together like what?
What is a puzzle?
What do we call distinctive deep valleys under the oceans (usually near continent edges)?
What are trenches?
When the plates push together, the heavier, thinner oceanic crust is forced down below the lighter, thicker continental crust. What is this process called?
What is subduction?
What do we call a series of mountains?
What is a mountain range?
Are newer mountains or older mountains shaped by things that move fast like landslides, earthquakes, plates colliding?
What are newer mountains?
During the early 1900's, what was the accepted theory at the time to explain why continents drift?
What is the shrinking apple theory?
What are plates?
What are areas of solid rock that “float” on the partly melted layer of the mantle
This type of convection current occurs when the mantle material rises and moves apart at the surface. These currents push tectonic plates away from each other. What is it?
What is a diverging convection current?
Nearly 500 million years ago, Alberta had a much different climate than it does now, what was it?
What is a tropical climate?
Compression forces from plate collisions caused sedimentary rocks in the Rockies to ___i___ and ___ii___ resulting in Folding and Faulting
i: What is bend?
ii: What is break?
*Note: order matters*
What are the 4 pieces of evidence to support Wegener's hypothesis and briefly explain 1 of them?
Glossopteris Fossils
Folded Mountains
Glacial Deposits
Coal Deposits
- Students may choose any one of these to explain
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of what type of boundary?
What is a diverging boundary?
What type of boundary is it where plates slide sideways past each other?
What is a transform boundary?
What 2 plates collided that played a major part in the formation of the rockies and mount rundle?
What is the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate?
Faults can be so deep in the crust that we can’t see them, but sometimes they are visible on Earth’s surface. Where is one place we can see faults?
What is layered rock?
Why did the science community reject Alfred Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift?
What is many geologists thinking that Earth was slowly cooling and shrinking?
What is the force called that occurs when mantle material sinks and moves toward each other at the surface. (Hint: This force pulls tectonic plates together.)
What are converging convection currents?
There is a huge mountain range in Asia called the Himalayas. What type of boundary formed them?
What is a converging boundary?
Use the following description to determine if this is a newer mountain or older mountain: softer, sloped peaks that have undergone erosion
What is an older mountain?
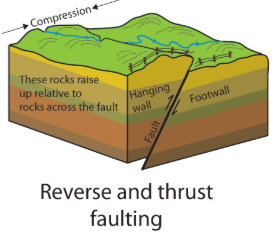
We learned about 3 types of faulting. What types of faulting is it when the rocks raise up relative to rocks across the fault?
What is reverse and thrust faulting?