Thermal Conductivity
What is physical
Identify the motion on this graph.
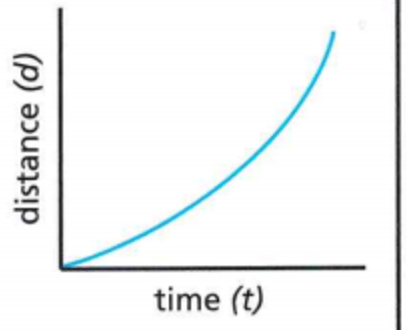
What is acceleration?
Table used to find elements
What is the Periodic table?
Heat transfer that does NOT require a medium.
What is radiation?
Positive(+) subatomic particle
What is proton?
He claimed that matter was made of small, hard particles that he called “atomos.
Who is Democritus?
A chemical reaction where heat is absorbed and the surrounding temperature falls
What is Endothermic?
The temperature at which an element or compound changes from solid to liquid.
Melting Point
Energy in motion
Kinetic Energy
Allows both matter and energy in and out of the system.
What open system?
An object weighs 4.5g/ml. When placed into a cylinder, the water rises from 10 ml to 18 ml. How much water was displaced?
What is 8 ml?
Particles found orbiting the nucleus.
What is electron?
His theory is based on the Law of Definite Proportions.
Who is Dalton?
Mass per unit volume of an object as compared to pure water.
What is Density?
F = ma
What is Newton's 2nd Law?
a positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom.
proton
Baking bread in an oven is an example of a chemical or physical reaction?
What is a chemical reaction?
Found in the nucleus.
What are protons and neutrons?
Name of Rutherford's experiment.
What is Gold Foil Experiment?
Which property is RUST? Physical or Chemical?
What is a chemical property?
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
what is Newton's 3rd Law?
EM wave with the longest wavelength.
What is radio waves?
What is the larger number on the periodic table?
atomic mass
Particles that keep the atom neutral?
What are protons and electrons?
He proposed that electrons move around the nucleus in specific layers, or shells.-Name the Scientist.
Who is Neils Borh?
Malleability-physical or chemical
What is Physical Property?
Forces that are unequal in magnitude and acting in different directions.
What is unbalanced force?
When heat moves from two things at different temperatures and must be touching
What is conduction?
a change in the size, shape, form, or state of matter that does not change the identity of the matter.
physical change
The reason scientific models of atoms have changed many times since Dalton’s original model
New information will modify earlier ideas.
The atomic model that shows, "It is impossible to know where an electron is at any given time.
What is the Cloud Model?