Name the supercontinent that existed 300 million years ago when all continents were joined together.
Pangea
What do we call breaks in the Earth's crust?
Faults
What do we call the force on Earth's crust that can change it's shape or volume?
Stress!
The vibrations that are similar to sound waves that travel through Earth carrying energy released by an earthquake
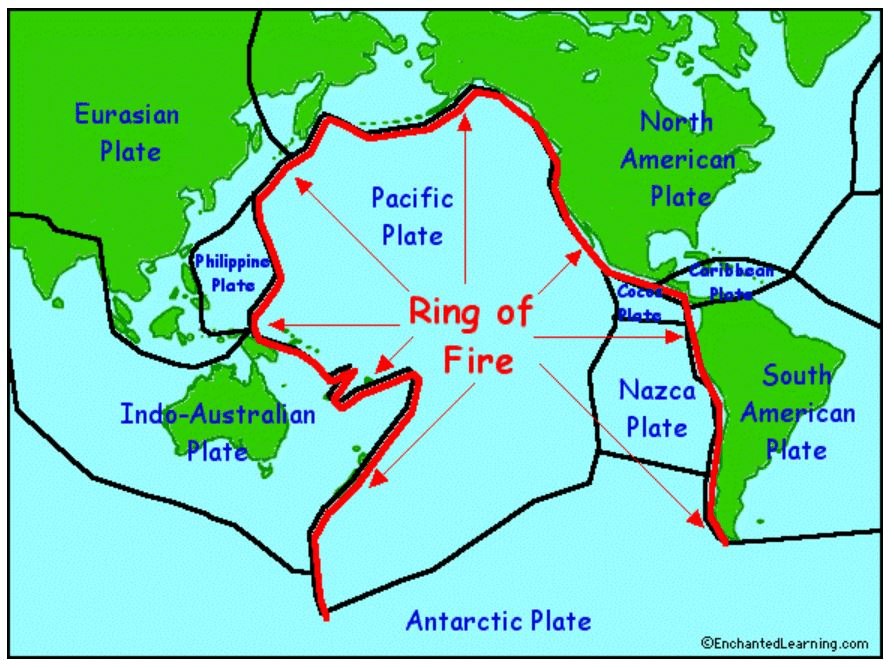
Name the place where most of the world's earthquakes occur.
HINT! It circles the Pacific Ocean
Name the scientist who proposed the theory of drifting continents.
Alfred Wegener
What causes the plates to continually move?
Convection currents
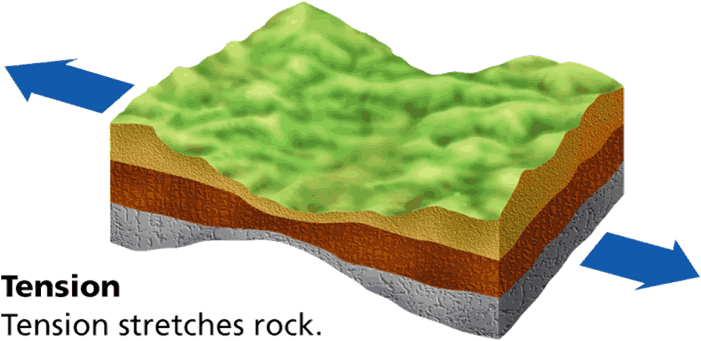
What type of stress describes pulling on the crust and thinning of rocks?
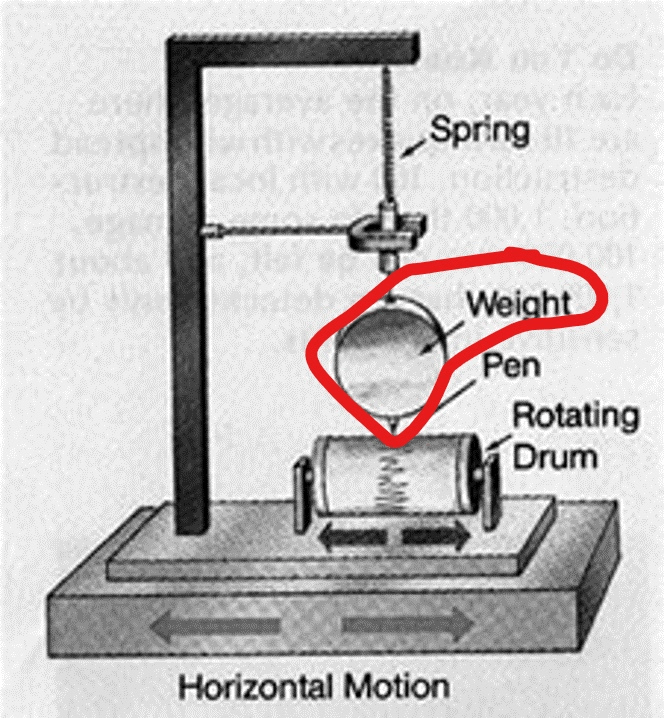
Name the instrument that measures an earthquakes seismic waves
seismograph
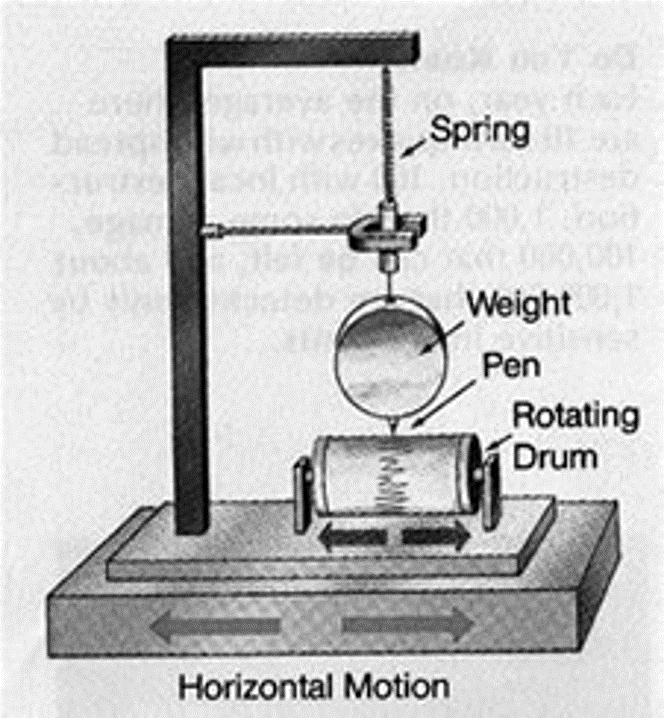
On a seismograph, more severe earthquakes will have what kind of lines?
higher or greater or larger
Name the long chain of underwater mountains
mid-ocean ridges
At what boundary do rift valleys form?
Divergent boundary
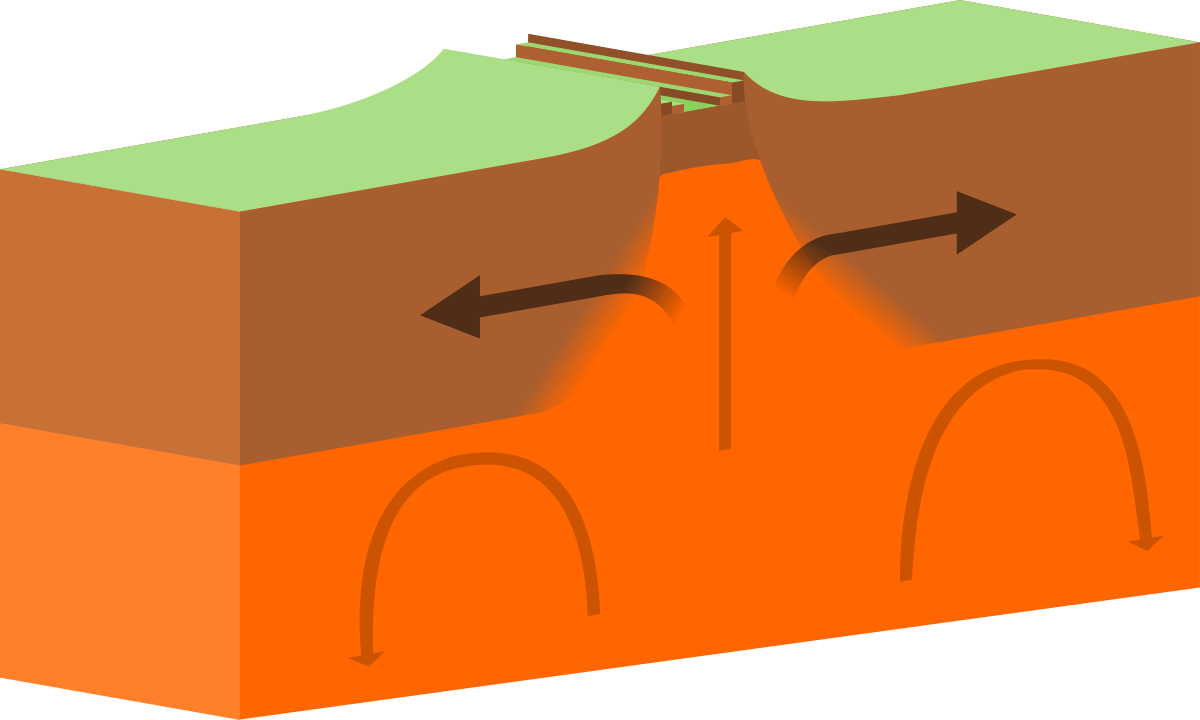
What type of stress causes plates to slip past one another in opposite directions?
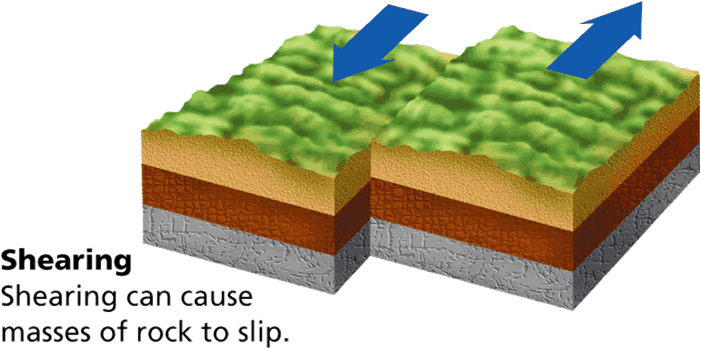
Name the area beneath Earth's surface where rock begins to break or move.
Focus
Name the pattern of lines that record an earthquakes seismic wave activity.
seismogram
Name the device used to measure distance using sound waves that helps map the ocean floor.
Sonar
At which type of boundary can subduction occur?
Convergent boundary
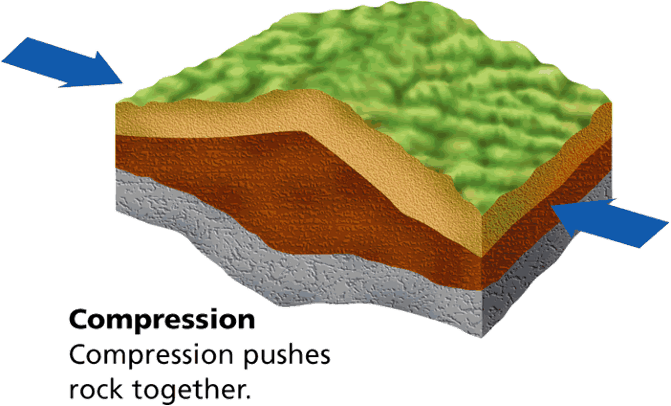
What type of stress squeezes rock until it folds or breaks?
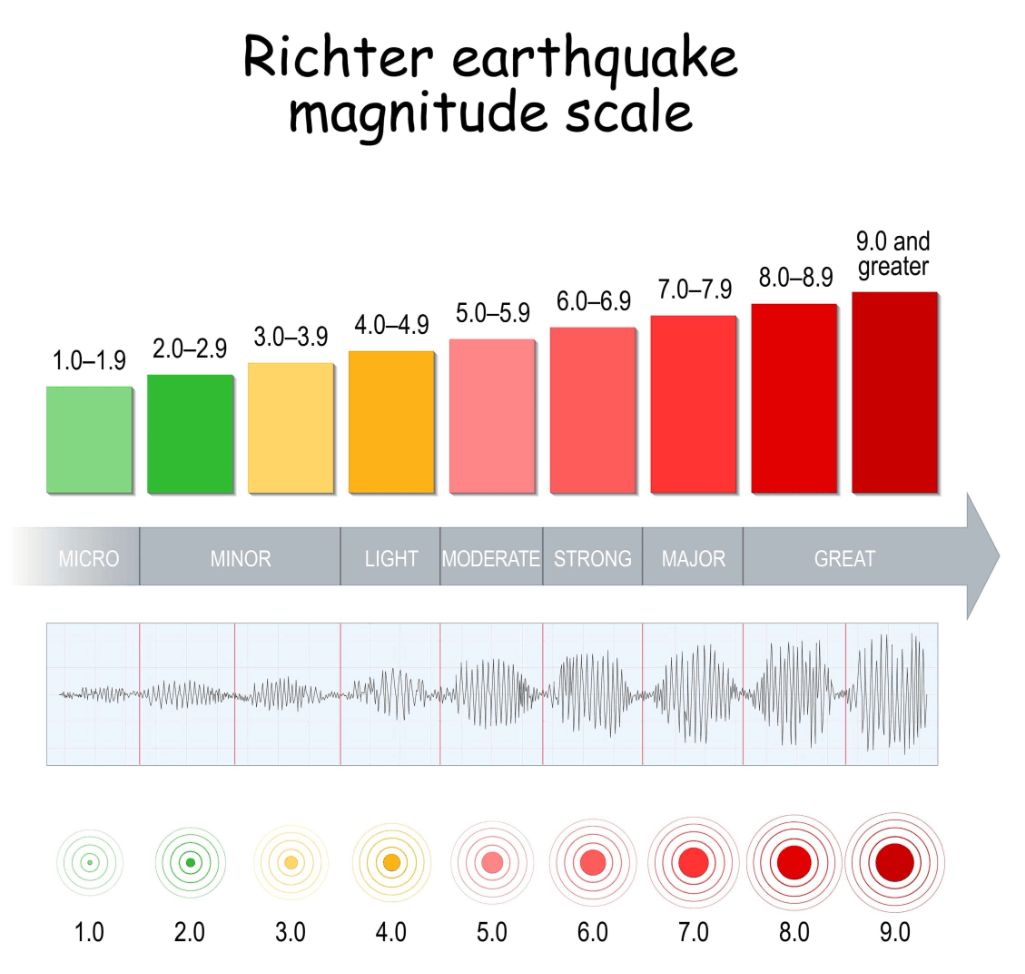
Name the scale that measures the magnitude, or size, of an earthquake.
Here in Washington, what plate cause most of our earthquakes?
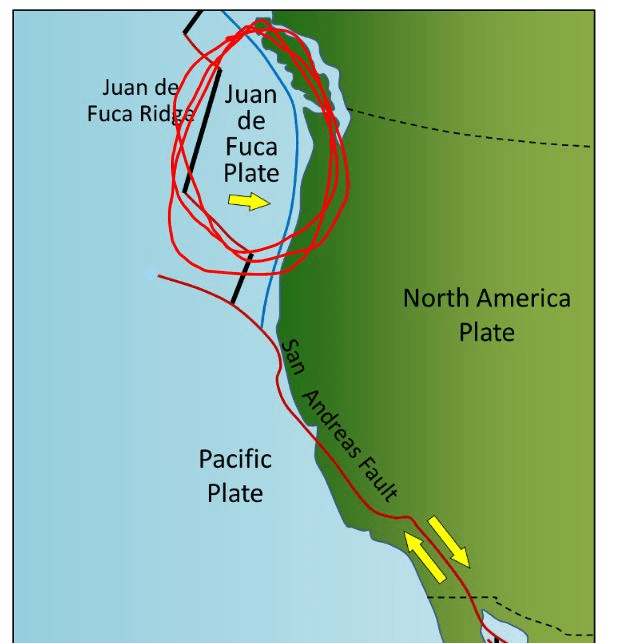
Name the process when part of the ocean floor sinks beneath another and back into the mantle - this process has helped form volcanoes!
Subduction
At what type of boundary is crust neither created nor destroyed?
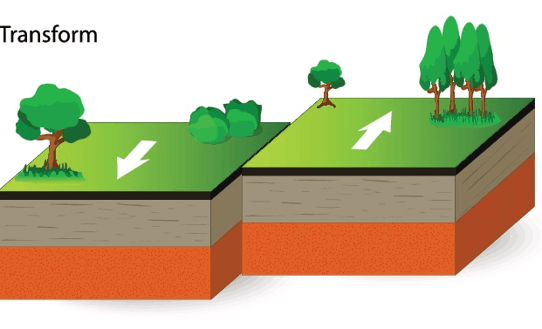
Name the 3 types of faults!
Normal, Reverse, Strike-Slip
Name the type of seismic waves that vibrate side to side and shake structures violently.
S Waves, or Secondary Waves
On a seismograph, what part resists motion during an earthquake?