The three subatomic particles that comprise an atom
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons?
What is kinetic energy?
Mass and energy are related, and one can be converted into the other
What is Einstein's principle of mass-energy equivalence?
What is a force?
The three most basic things the universe is made of
What are matter, energy, and intelligence?
This holds everything together and enables any process to happen
What is energy?
A quantum of electromagnetic energy
What is a photon?
The law of conservation of energy
What is "Energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only changed in form"?
The weakest of the four fundamental forces
What is gravity?
The orderly and very mathematical system of rules that objects in nature obey
What are the laws of nature?
Neutrally charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus
What are neutrons?
What are solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric energy, fossil fuels, geothermal energy, and nuclear energy?
On moving objects it always causes heating, which always releases energy into the environment
What is friction?
He said that all objects with mass attract all other objects with mass
Who is Isaac Newton?
The belief that the only way to reach objective knowledge is through modern science
What is scientism?
The zones of residence occupied by electrons in an atom, according to their energies
What are orbitals?
Stored energy due to an object’s location in a gravitational field
What is gravitational potential energy?
A mechanical process whereby energy is transferred from one object to another by a force pushing through a certain distance
What is work?
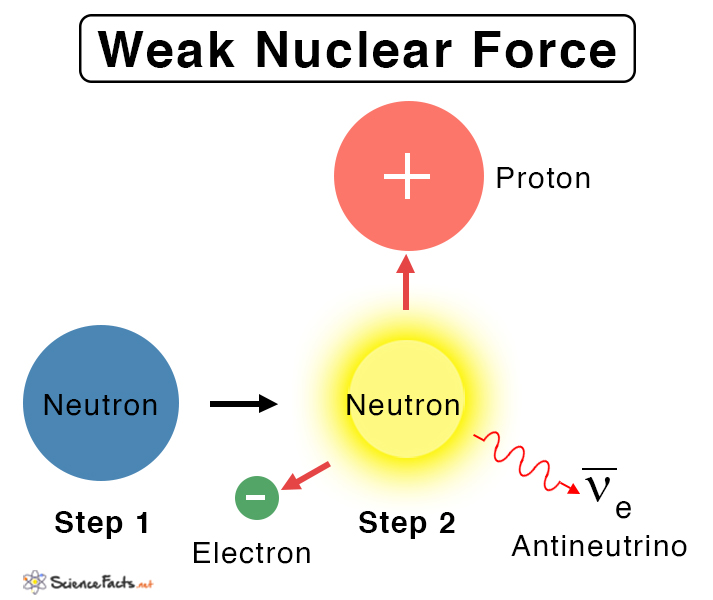
What is the weak nuclear force?
The hierarchically ordered sequence of existence, starting with God and descending to minerals.
What is the Chain of Being?
The atomic model theorized by J.J. Thomson, where negatively charged particles are embedded in a positively charged whole
What is the plum pudding model?

The six regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, in order from highest energy to lowest
What are gamma rays, X-rays, UV radiation, visible light, infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves?

When hot and cold particles in a fluid mix and collide, causing slower, cooler molecules to gain kinetic energy and speed up
What is convection?
The cause of an electric field
What is any charged particle?
A broad term for the study of the natural world and its methods, made possible by the laws of nature and the intelligibility of the universe
What is science?