Define the difference between a heterogenous and homogenous mixture. Mention the distribution of particles.
Heterogenous: Particles are not evenly distributed
Homogenous: Particles are evenly distributed
The difference between atoms and ions is . . .
That atoms are neutral and ions are positively or negatively charged
Groups and families: Which are rows and which are columns?
Groups: Columns
Rows: Families
An element has 12 protons. Which element is it?
Magnesium
The respective number of electrons that can be contained within the first, second and third energy levels
2, 8, 8
Ionic compounds are a combination of a positive ____________ and a negative ______________
Metal, nonmetal
Give the compound name of this formula: P6Cl4
Hexaphosphorus tetrachloride
Define the difference between the two kinds of pure substance
Elements are made up of same atoms
Compounds are made up of same particles which consist of a few atoms in a fixed ratio
A positively charged ion is called a ________________ and a negatively charged ion is called a ________________
Cation, anion
Find the chemical symbol, atomic number and atomic mass of Rhodium respectively. Round all numbers.
Rh, 45, 103
An element has 8 protons, 6 neutrons and 12 electrons. Its atomic mass is . . .
What element does this Bohr model represent?
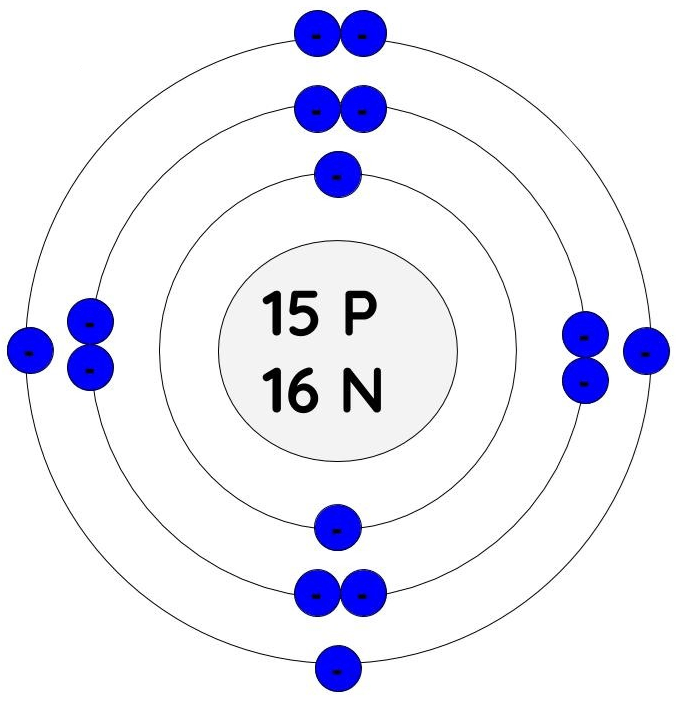
Phosphorus
T or F: The compound name for OsCl4 is Osmium tetrachloride if the charge of Osmium is 4+
False, that is not how ionic compounds are written. The correct compound name is Osmium (IV) chloride.
Give the formula of this compound name: Nonasilicon trioxide
Si9O3
When a mixture does not mix well and settles into distinct phases, it is called a/an _______________. Give an example.
Mechanical mixture (water and sand or oil, etc.)
The atomic number is equal to ________________
# of protons
Name 6 of the noble gases
Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon (and oganesson)
Why are noble gases non-reactive?
They have full valence shells so they are stable
What is the charge of this atom/ion?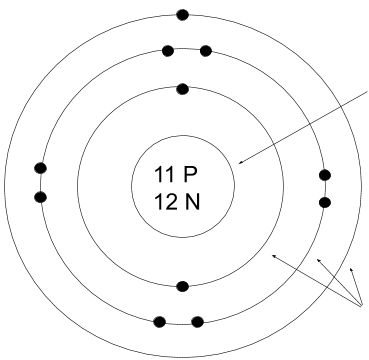
Neutral, no charge
Give the formula of this compound name: Potassium nitride
K3N
Give the formula for diarsenic trioxide
As2O3
What is a suspension?
The particles blend fairly well and appear homogenous when mixed, but will always settle back into distinct phases
The atomic mass is equal to ________________
# of protons + #of neutrons
Of the alkali metals, which is the most reactive?
Francium
An element has 8 protons, 7 neutrons and 10 electrons. What is its charge?
-2
How many electrons would be in the (hypothetical) valence shell of aluminum (III)?
10 electrons total, so 8 valence electrons
Give the formula of this compound name: Barium phosphide
Ba3P2
Give the compound name for the formula K2CrO4
Potassium chromate
An element is a semiconductor used in your phone. What group of elements does it belong to?
Metalloids
The outermost energy level is the ________________ and contains ________________
Valence shell, valence electrons
What kind of elements are found along the staircase? Name three elements that belong to this grouping.
Metalloids: Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic, Antimony, Tellurium, Polonium, Astatine
The charge of an element is +7. It has 23 protons. How many electrons does it have?
16 electrons
Neutrons = 126
Electrons = 83
Atomic mass = 209
How many protons?
83 protons
Sulfur (II) and Scandium (III) form a compound. What is its formula and name?
Scandium sulfide, Sc2S3
Write the chemical formula for chromium (III) permanganate
Cr(MnO4)3