What state of matter has a definite shape and definite volume?
Solid
Name a way to separate a homogeneous solution
evaporation
What is an element? Give one example from the periodic table.
Element: substance made of only one kind of atom (e.g., oxygen, O).
What is density? Provide a simple definition relating mass and volume.
mass per unit volume; how much matter is packed into a given space.
Is melting ice a chemical or physical change? Explain one reason for your answer.
Physical change: melting ice changes state but does not form a new substance (water remains H2O).
Give one example of a change of state that requires energy to be added.
Examples: melting (solid → liquid) requires energy; evaporation/boiling (liquid → gas) also requires energy.
Which of the following substances is a homogeneous mixture?
Pure water
Dressing
Maple syrup
Sugar crystals
Maple syrup
On the periodic table, where are metals generally located compared to nonmetals? Describe the general trend
Metals are generally on the left and middle; nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table.
If object A has the same volume as object B but object A has more mass, which object is more dense?
Object A is more dense because more mass in the same volume.
List two signs that a chemical change might have happened.
Signs: gas production (bubbles), color change, temperature change, or formation of a precipitate
Rank the kinetic energy of solids, liquids, and gases in order from greatest to least.
gas, liquid, solid
Which of the following is an example how a homogeneous mixture might be depicted?
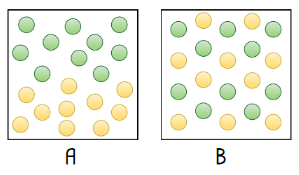
B
Which periodic table correctly identifies metals, metalloids, and nonmetals?
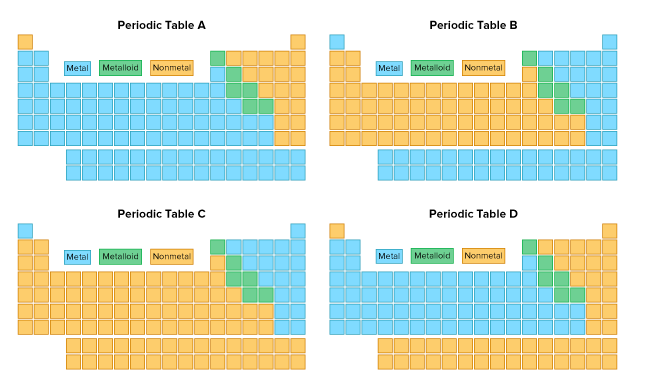
Table A
A solid object has a density of 0.8 g/cm³. If placed in both water and a fluid with a density of 0.6 g/cm3, predict what will happen in each fluid.
In water (density 1 g/cm3 the object will float. In the fluid with a density of 0.6 g/cm3, the object will sink because the object is denser than that fluid.
Burning paper is an example of a chemical change. Explain TWO pieces of evidence you might observe that show a new substance formed.
Evidence: smoke or gas produced; new ash or charred material; change in temperature; and color change
A container holds water at room temperature. The water is slowly heated until it boils. Which sequence correctly describes the changes in particle arrangement and energy?
Particles move faster → particles get closer → particles vibrate in place
Particles gain energy → particles slide past each other → particles move freely
Particles move slower → particles spread apart → particles stop moving
Particles vibrate in place → particles lose energy → particles move freely
Particles gain energy → particles slide past each other → particles move freely
A student mixes together several substances for a science experiment and observes the following:
Sample A is a mixture of sand and iron filings
Sample B is melted silver
Sample C has salt dissolved in water
Identify each as a pure substance, homogeneous mixture or heterogeneous mixture?
Sample A is heterogeneous
Sample B is pure substance
Sample C is homogeneous
Identify which of the following elements is a metal, nonmetal, and metalloid.
Boron ________
Sodium _______
Neon ________
Boron = metalloid
Sodium = metal
Neon = non metal
The following table gives the density of three liquids. What order would the liquids layer in the beaker, and then add water (1.0 g/ml) where appropriate?
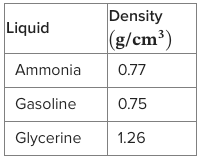
gasoline, ammonia, water, glycerine
Which of the following is NOT a chemical change? Select all that apply.
Metal rusting
Melting ice cream
Burning wood
Decomposing milk
Water evaporating
Sugar dissolving in water
melting ice cream, water evaporating, sugar dissolving in water
The three diagrams below show the three states of matter. Which statement best explains a state? Select two answers.
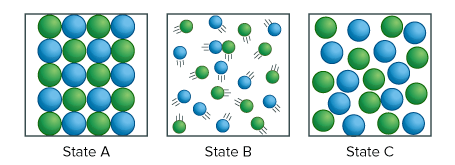
State B is a solid because the particles are evenly spaced.
State C is a liquid because the particles fill the space.
State A is a solid because the particles are evenly packed.
State A is a gas because the particles are evenly packed.
State C is a liquid because the particles fill the space.
State A is a solid because the particles are evenly packed.
Classify the following as a pure substance, heterogeneous mixture or homogeneous mixture.
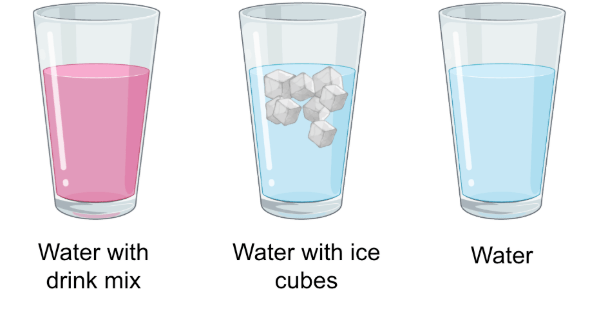
Water with drink mix = homogeneous mixture
Water with ice cubes = heterogeneous mixture
Water = pure substance
Which statements describe the properties of a metalloid? Select two.
They can conduct electricity under certain conditions
They are always brittle
They are good heat conductors
They have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
They can conduct electricity under certain conditions
They have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
As part of a science challenge, a student must place an object into one of two liquids and have it sink. One liquid is glycerin with a density of 1.26 g/ml. The other is rubbing alcohol with a density of 0.79 g/ml. The object has a density of 1.40g/ml. Which liquid should the student place the object in? Explain why.
The student can place the object in either liquid, because it will sink in both. The object is denser than both liquids.
Four students are carrying out different experiments as shown in the table. Which of the students' experiments results in a chemical change?
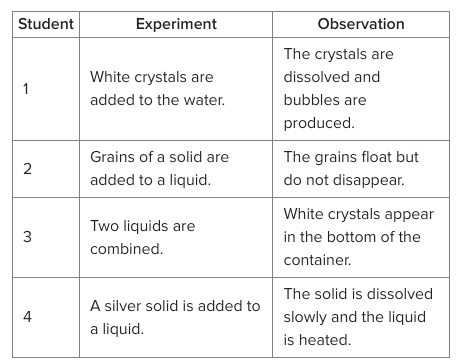
1, 3, and 4