What is science?
Science is the study of the world around us.
What is matter?
*Also has volume*
Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass.
What are physical properties of matter?
(Definition)
Physical properties of matter are characteristics of matter that can be observed or measured without changing it.
What is the Atomic Theory?
The Atomic Theory:
Atoms are the smallest unit of an element
All matter is made up of Atoms
What are the 2 types of changes in Matter?
Physical changes
Chemical changes
What are Pure Substances?
Pure substances:
Elements
Substances made of only one type of atom
Cannot be separated by any physical or chemical process
What are acids?
Acids are chemical substances that:
taste sour
some can dissolve metals
Corrosive
Turns Blue litmus paper red
What are the three parts of the cell theory?
1. All organisms are made of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic unit and function of all living things
3. Cells come from pre-existing cells
What organelles does only the animal cell have?
Animal cells have a small vacuole and centrioles.
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use light energy, water, and carbon dioxide to make sugar (glucose) and oxygen.
What is cellular respiration?
The process by which cells use sugar, (glucose) and oxygen to produce energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
What is the Carbon Cycle?
The process by which carbon travels from the atmosphere into organisms and the Earth and then back into the atmosphere.
What are celestial bodies?
Natural objects outside the Earth (objects in space)
What is gravity?
Gravity - a force that pulls objects towards each other
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
(Travels in waves)
The Electromagnetic Spectrum refers to the many types of radiation released from stars including our Sun.
What are the 2 main methods of studying the world around us?
The 2 main methods are Observation and Expiermentation.
What are the states of matter?
The states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
What are the physical properties of matter?
*these physical properties are independent of sample size*
The physical properties of matter include: Melting point, boiling point, freezing point, density, magnetism, solubility, and conductivity.
What are the three subatomic particles the atoms are made up with?
Also say their charges
The three subatomic particles are…
Protons (+)
Neutrons (no charge)
Electrons (-)
What is a physical change?
*Physical Changes can go back to its original form*
Physical change is when a substance changes form but it is still the same substance.
True or False
Atoms make up the element, but are not chemically combined.
True
What are some examples of acids?
*Also known as stomach juice*
Examples:
Hydrochloric acid (HCI) in gastric juice
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Carbonic acid in soft drink (H2CO3)
What does multicellular mean?
What does unicellular mean?
Multicellular means two or more cells
Unicellular or single cell well means one cell
What organelles does only the plant cell have?
The plant cells have a large central vacuole, tonoplast, chloroplast, plasmodesmata, and a cell wall.
*Person only needs to say the ones that are italic*
What do plants use as food?
Plants use sugar, (glucose) as food and release oxygen.
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Mitochondria or Mitochondrion
What are carbon reservoirs?
Places on Earth where carbon is stored
What are the celestial bodies smallest to largest?
1. Comets
2. Asteroids
3. Nebula
4. Dwarf Planets
5. Moon
6. Planets
7. Stars
8. Solar system
9. Galaxies
10. Universes
What are the 2 factors that affect gravity?
Mass and Distance
What are the types of Electromagnetic radiation from the Sun?
1. Gamma
2. X - Ray
3. Ultra-Violet
4. Visible Light
5. Infrared
6. Mircowaves
7. Radio
What is Observation?
Observation is watching, listening, touching, testing, or smelling to gain information.
What is mass?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
What is the melting point, boiling point, and freezing point of water?
Melting point = 0 degrees Celsius
Boiling point = 100 degrees Celsius
Freezing point = 0 degrees Celsius
How have theories like the Atomic Theory changed over time?
Theories like the Atomic Theory has changed over time as new technologies have become available along with new discoveries.
What are three examples of physical change?
three examples of physical change are…
mixing, breaking and melting
others answers could be…
*boiling, freezing, phase changing, folding, chopping, cutting, shreddin, and dissolving*
What is an Element?
Element = made of one type of atom and is a pure substance
What are bases?
Bases are substances that:
taste bitter
slippery to the touch
turns red litmus paper blue
What does part two of the cell theory demonstrate?
*Part 2 = cells are the basic unit and function of all living things*
Part two of the cell theory demonstrates the function of the cells and how it helps maintain homeostasis.
What organelles does both the animal cell and plant cell have?
Both the plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, peroxisme, mitochondrion, ribosomes, a rough endoplasmic reticulum, a nucleus, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, a Golgi apparatus, lysosome, and a cell membrane.
*The subject only needs to say 5 things.*
Where in the cell does photosynthesis take place?
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells.
What is the equation for Cellular Respiration?
Sugar (glucose) + Oxygen = Energy + Water + Carbon Dioxide
What are some examples of carbon reservoirs?
Atmosphere - gases such as Carbon Dioxide
Organisms - Carbon is released when one organism eats or breaks down another
Plants - during photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Water - carbon dioxide dissolves in water
Rocks and Soil - contains minerals such as calcium carbonate
Fossil Fuels - burning releases carbon dioxide and methane gases
*Only need to name 3*
What are Comets?
What are Asteroids?
A comet is an object made of ice, gas, and dust.
Asteroids are rocks that orbit the sun. (rocks in space)
True or False
The larger the object, the more gravitational pull.
The farther the object the less gravitational pull.
True
What are the parts of waves?
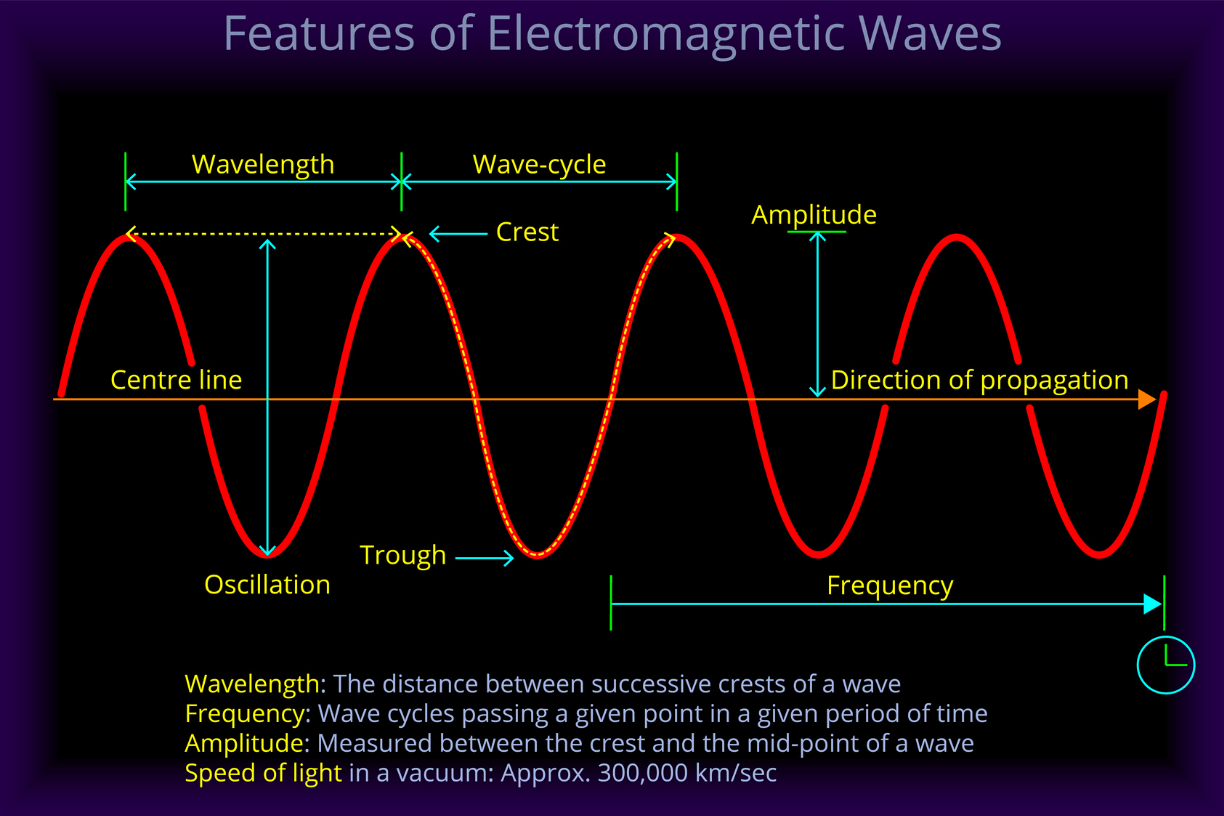
Crest - Top of the wave
Trough - Bottom of the wave
What is Experimentation?
*Helps to establish scientific laws and theories*
*Also known as an controlled experiment*
Experimentation is when you are using the scientific method with different variables.
What is weight?
Weight is how much gravity is pulling on an object.
What are the properties of matter that are dependent on sample size?
The properties of matter our mass and volume.
Why does the nucleus of an atom have a positive charge?
The nucleus of an atom has a positive charge because of the protons.
What are some evidence of physical changes?
*You only need to say 3 types*
Evidence of physical changes are…
Changes shape
Changes form
Changes size
Changes phase/state of matter
Mixing two solids
What is a compound?
*cannot be easily separated*
Compounds are two or more different elements that are chemically bonded together.
What are some examples of bases?
Examples of bases:
Soap
Washing Powder
Coffee
Baking Soda
What is the process do cells come from other cells?
Cells come from pre-existing cells through a process called cell division.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus
- controls all action of the cell
- contains DNA (genetic materials)
- found in both plant and animal cells
What does Chlorophyll do?
Chlorophyll
- Absorbs light and starts the whole process of photosynthesis
- Gives plants its green color
What are the ingredients for Cellular Respiration?
Sugar (glucose) and oxygen
What are the effects of too much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide traps heat on earth causing the "greenhouse effect," which is warming up the earth (global warming).
What is a Nebula?
What are Dwarf Planets?
A nebula is a cloud of gas and dust in outer space (visible in the night sky).
Dwarf Planets is an object resemblinv a small planet but does not meet the criteria to be classified as a planet.
What are the 2 ways distances are measured in space?
Astronomical Units and Light Years
What are the properties of waves?
Wavelength - measures the length of the wave
Frequency - How many waves passes a certain point per second
What is a Scientific Theory?
A scientific theory is an explanation or idea about what happens in nature to repeated experiments, but changes over time with new evidence, new data or new discoveries with advancement of technology.
What does density measure?
Density measures how closely packed particles are in an object.
What is magnetism?
*Magnets only attract metals such as iron, cobalt, and nickel*
Magnetism is the attraction or repulsion between two objects.
Why do the electrons remain in orbit around the nucleus?
The electrons remain in orbit around the nucleus because the nucleus has a positive charge in the electrons have a negative charge.
What is a chemical change?
*Chemical changes cannot go back to its original form*
A chemical change is when a substance combines with another to form a new substance.
True or False
When atoms combine, they form different substance with different properties from the original atom.
True
What is litmus paper?
Litmus paper is used to indicate whether a substance is a acid or a base.
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the process by which an organism maintains a stable internal environment.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane
- Controls what enters and leaves the cell
- protects/supports the cell
- Maintains homeostasis
- Both plant and animal cell
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
Light + Water + Carbon Dioxide = Sugar and Oxygen
What are the products of Cellular Respiration?
Water, Carbon Dioxide, and energy
What does global warming lead to?
- melting ice caps
- acid rain
- increase ocean levels
- warmer ocean
- warmer temperature
- Stronger storms
- Flooding
*Only need to name at least 3*
What is a moon?
What are stars?
A moon is a natural satelite that revolves around a planet.
A star is a large ball of burning gas in space, mainly made of hydrogen and helium.
What are Astronomical Units?
Astronomical Units represent the distance from the earth to the sun.
True or False
The longer the wavelength, the less harmful the wave (radiation) is.
The shorter the wavelength the more harmful the wave (radiation) is.
True
What are some examples of a scientific theory?
Some examples are…
The Atomic Theory
The Theory of Evolution
The Big Bang Theory
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
What is density?
*Density is independent of sample size*
(meaning: it does not matter how big or small and object the density will be the same)
Density is a physical property of matter.
What is conductivity?
Conductivity is the rate at which heat and electricity pass through a material.
Why are models essential for the Atomic Theory?
Models are essential for the atomic theory because we cannot see atoms we use models to teach and learn about atoms.
What are three examples of chemical change?
three examples of chemical change are…
sour milk, rotting, and digesting
others answers could be…
*baking, cooking, rusting, oxidation, burning, combustion, and reacting with an acid*
What type of changes in matter are compounds?
Chemical changes because they form new substances that cannot go back to the original.
What is the pH scale used for?
The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a substance is.
What are some homeostasis examples?
Stable blood sugar level (70-99)
Stable blood pressure (120/80)
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall
- Protect and support in plant cells
- Found only in plant cells
What are the ingredients of photosynthesis?
Light energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
What type of energy transfer takes place during cellular respiration?
Chemical to Mechanical (kinetic energy)
What is the effect of too much carbon dioxide in the water?
Too much carbon dioxide dissolved in our water can cause the water to become acidic.
What is a solar system?
What are galaxies?
What is the Universe?
A solar system consists of planets, moons, asteroids, meteroids, and comets in orbit around a star.
Galaxies contains billions of stars, solar systems, gas and dust, held together by gravity.
The Universe contains billions of stars, solar systems, and galaxies.
What is 1 AU?
About 93 million miles or 150 million km.
In the Electromagnetic Spectrum, does the lower frequency mean lower energy or higher energy?
Lower energy
What is Observation also known as?
*It is a Scientfic investigation*
*It is information gained by using your five senses*
Empirical evidence
How do you calculate density?
Density is equal to mass divided by volume.
Units of density are g/mL or g/cm (cubed)
What are the two types of conductivity?
The two types of conductivity are heat or thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity.
What are elements?
Elements are pure substances that are made of one type of atom and are arranged on the periodic table.
What is some evidence of a chemical change?
Evidence of a chemical change:
color change
given off a odor (smell)
tempature change
form gas (bubbling)
releasing light or heat
What is a molecule?
A molecule is two or more atoms bonded together
What is the range in the pH scale?
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14.
What are the two categories of cells?
Prokaryotic
Eukaryotic
What is the function of the Chloroplast?
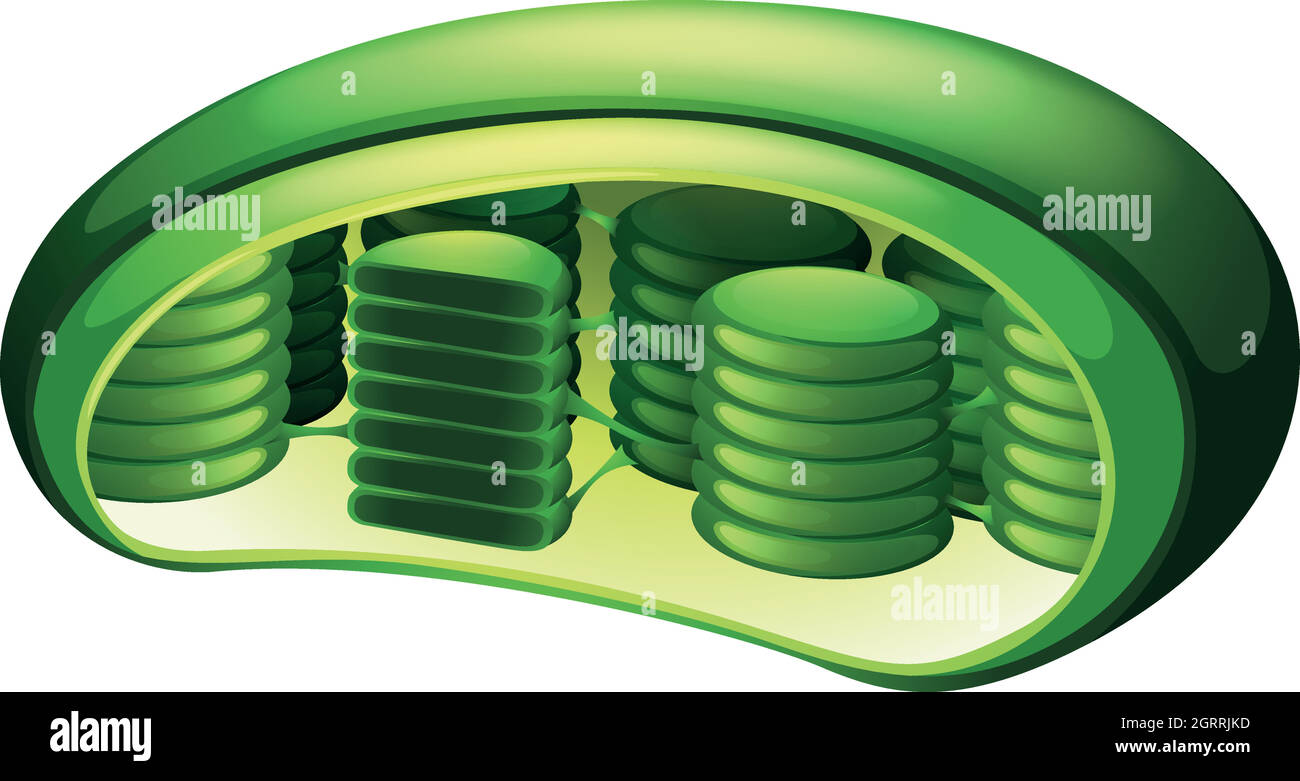
The chloroplast
- Contains chlorophyll and converts light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into sugar and oxygen.
- Found only in plants
What are the products of photosynthesis?
Sugar and oxygen
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
They are opposites of each other.
What is the Law of Conservation of Matter?
Matter cannot be created or destroyed. It can only go from one state of matter to another state of matter.
What are inner planets?
(Terrestial)
Planets closest to the sun and made of mostly rock.
What is a Light Year?
The distance light travels in one year
Which region is the violet region?
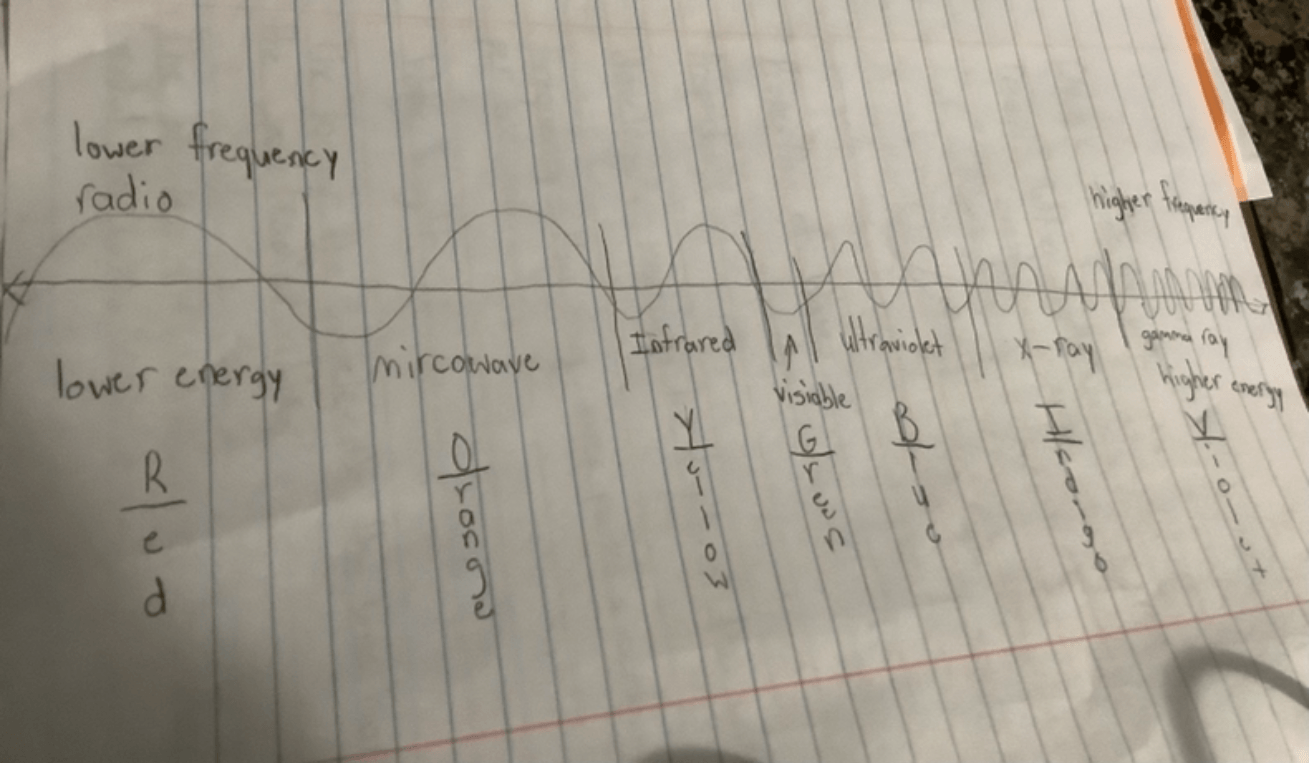
Gamma-ray
That has the highest frequency
What is a Scientific Law?
A scientific law is an explanation about what happens in nature that seems to be true all the time.
What happens if it objects density is one or greater?
what happens if I object density is less than one?
If an object density is one or greater the object will sink.
If an object density is less than one then the object will float.
What are Conductors?
What are Insulators?
Conductors are materials that heat and electricity pass through easily.
Insulators are materials that heat and electricity cannot pass through easily.
How are elements arranged on the periodic table in column/groups/families?
Elements on the periodic table, in column/groups/families are arranged by their similar properties.
True or False
Mass is created during a physical change
False!!!
What type of molecule has the same type of atom?
A molecule of an element
From what number to what number is it acidic on the pH scale?
From 0 to 6 the substance is acidic.
Describe Prokaryotic cells
(prokaryotes)
Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus around the DNA (genetic material), have no cell membrane, and make up unicellular or single celled organisms.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm
- supports and protects the organelles of the cell
- Found in both plant and animal cells
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transferred from one form of energy to another form of energy.
What organisms undergo cellular respiration?
All organisms, both plants, and animals, because they both contain mitochondria.
How does the carbon cycle follow the law of matter?
Carbon is not destroyed it only goes from one state of matter to another state of matter.
What are outer planets?
(Extraterrestrial)
Planets further from the sun, mostly made of gas.
What is the speed of light?
300,000 km/sec
What is visible light?
Visible light is wavelengths that are visible to most human eyes. We are able to see light because of its wavelength.
What are some examples of a scientific law?
Some examples are…
Law of Gravity
Laws of Motion
Law of Conservation of Energy and Matter
Yes or No
In material identification, could density also be used to identify unknown materials?
Yes, density could also be used to identify unknown materials.
What is solubility?
Solubility is when a solid or gas can dissolve in a liquid.
How are elements arranged on the periodic table in periods/rows?
Elements on the periodic table, in periods/rows are arranged by the number of protons.
What does the Law of Conservation of Mass state?
* During any physical or chemical change, the mass stays the same*
It states
“Mass is not created or destroyed during a chemical or physical change”
What type of molecule has the different types of atoms?
A molecule of a compound
What number is neutral on the pH scale?
7 is neutral on the pH scale, it is not a acid or a base.
What is an example of a prokaryotic organism?
(Prokaryotes are organisms that are made up of prokaryotic cells)
Some bacteria
What is the function of the mitochondria?
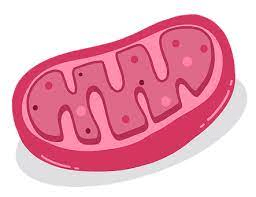
Mitochondria
- Uses sugar and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy for the cell
- Found in both plant and animal cells
What type of energy transfer takes place during Photosynthesis?
Light energy to chemical energy
When do plants undergo cellular respiration?
In the daytime and nighttime
What are some examples on how does the carbon cycle follow the law of matter?
1. In the Atomsphere - Gas
2. In animals - Gas
3. In plants - gas
4. Dissolved in water - liquid
5. In Rock and Soil - Solid
6. Burning fossil fuels - gas
What does terrestrial mean?
Terrestrial means earthlike
What are the properties of stars?
Apparent Magnitude
Absolute Brightness
Color and Tempature
What are the colors of the electromagnetic spectrum?
*please say it in order*
Red, Orange, yellow, Green, blue, indigo, and violet
Say all the steps of the scientific method
Step 1: the problem statement
Step 2: come up with a hypothesis
Step 3: Test your hypothesis or experiment
Step 4:Collect Data
Step 5: Conclusion
Step 6: Communicate your results
How do you calculate Mass?
You can get the mass by, multiplying the density times the volume.
Mass = Density x Volume
If a solid or gas can dissolve in a liquid is it soluble or insoluble?
If a solid or gas cannot dissolve in a liquid is it soluble or insoluble?
If a solid or gas can dissolve in a liquid it is soluble.
If a solid or gas cannot dissolve in a liquid it is insoluble.
True or False
The number of protons equal the number of electron.
True
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass equation?
It states
mass of substance 1 + mass of substance 2 = mass of substance 1 + mass of substance 2
What are mixtures?
*Can be easily separated*
Mixtures are two or more substances that are combined but is not chemically bonded.
From what number to what number is it basic on the pH scale?
From 8 to 14 the substance is basic on the pH scale.
Describe eukaryotic cells
(Eukaryotes)
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus around the DNA (genetic material), have a cell membrane, and makes up multicellular organisms.
What is the function of the vacuoles?
The vacuoles
- stores food, water and waste for the cell
- found large in plant cells
- found small in animal cells
How does the process of Photosynthesis follow the law of conservation of energy?
The light energy wasn't destroyed, it was only transferred to chemical energy.
In the daytime, what do plants mostly release?
Plants undergo both cellular respiration and photosynthesis in the daytime and release mostly oxygen.
How does the Carbon cycle follow the Law of Mass?
The amount of Carbon that it starts with is the amount that it ends with.
What does extraterrestrial mean?
Extraterrestrial means nonearthlike.
What is Apparent Magnitude?
What does Apparent Magnitude depends on?
Apparent Magnitude is how bright a star appears from Earth.
It depends on how bright the star actually is and the distance.
What are the Types of Variables in an Experiment?
The variables are…
The test variable, also known as the independent variable, and it is the different samples being tested.
The outcome variable, also known as the dependent variables, and it is what you are testing for.
The control group, the sample you don’t do anything to.
The constant variables, the factors that are kept the same in the experiment.
Describe each state of matter
(how the particles are arranged, how fast the particles move, the shape and the volume)
Solids: The particles are packed together, they move slow, and the object has a fixed shape and volume.
Liquids: The particles are loosely packed together, they move at regular speed, and the liquid has no fixed shape, but has a fixed volume.
Gas: The particles are very far apart, they move very fast, and they have no fix shape and no fix volume.
What are Solutions?
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures that forms by dissolving a gas or solid into a liquid.
Does the number of protons equal the atomic number?
*On the Periodic table*
The number of protons does equal the atomic number.
What are two examples of mixtures?
Examples: Sugar/Water, Sand/Water, Peanuts/Raisins, and Fruit Salad.
From what number to what number is it very acidic on the pH scale?
From 0 to 3 is very acidic on the pH scale.
What is an example of an eukaryotic organisms?
(Eukaryotes are organisms are made up of eukaryotic cells.)
Plants and Animals (humans)
In the nighttime, what do plants mostly release?
Plants only undergo cellular respiration at night and release carbon dioxide.
Surprise fact!
Mercury doesn't have an atmosphere and has very little or no gravity.
What is Absolute brightness?
What does Absolute brightness depend on?
Absolute brightness is how bright a star actually is.
It depends on the temperature of the star and the size of the star.
What is Repetition?
Repetition is repeating your own experiment over a number of times to see if your results are accurate or correct.
How do you calculate volume?
If you divide mass by density, you’ll get the volume.
Mass/Density = Volume
What is the solvent?
What is the solute?
The solvent is the liquid that the solid or gas that dissolved in.
The solute is the solid or gas that has dissolved in a liquid.
On the periodic table, how do you get the number of neutrons?
By subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass
Atomic mass - atomic number = number of neutrons
What are the two types of mixtures?
Heterogenous Mixture and Homogeneous Mixture
From what number to what number is it slightly acidic on the pH scale?
From 4 to 6 means that the substance is slightly acidic on the pH scale.
What are atoms?
What are molecules/compounds?
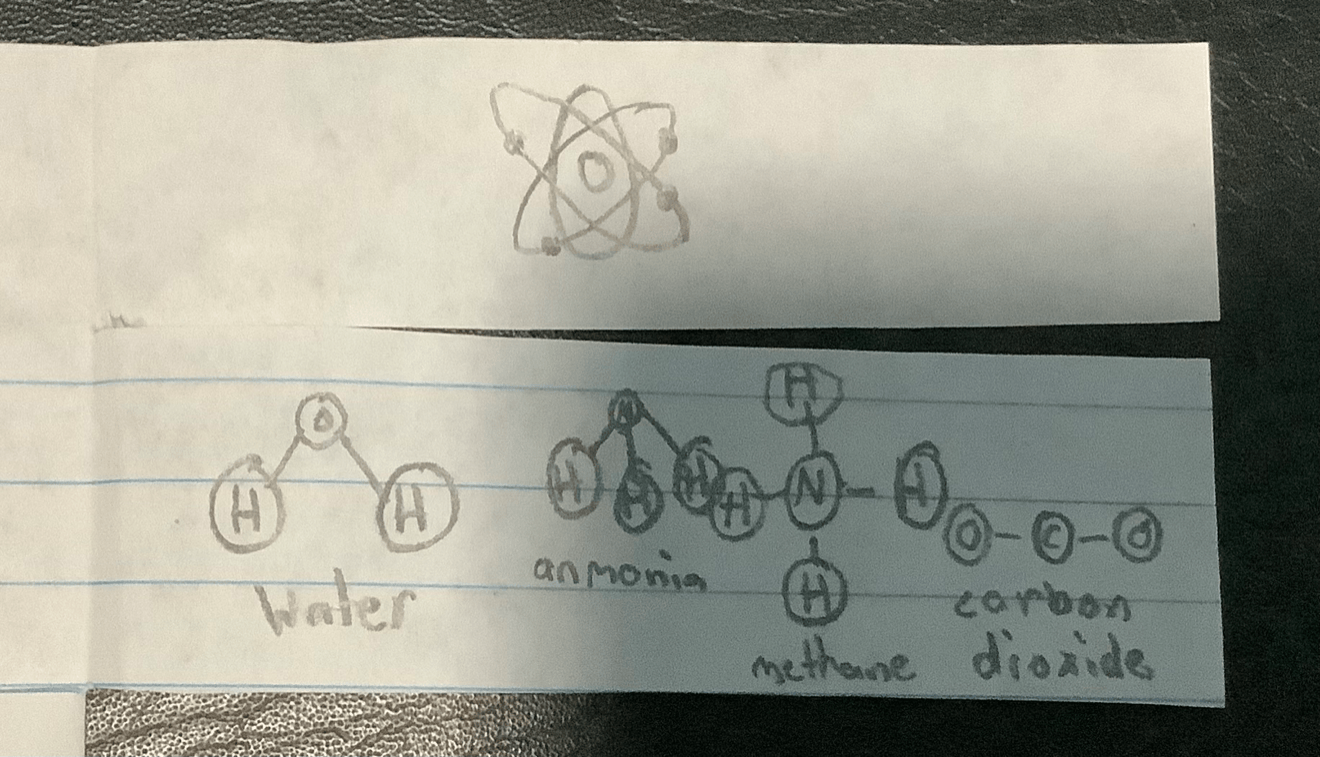
Atoms are the smallest unit of an element.
Molecule/Compounds are a group of atoms bonded together.
About what temperature and what color is the Sun?
What color has the highest temperature?
Which star is the brightest?
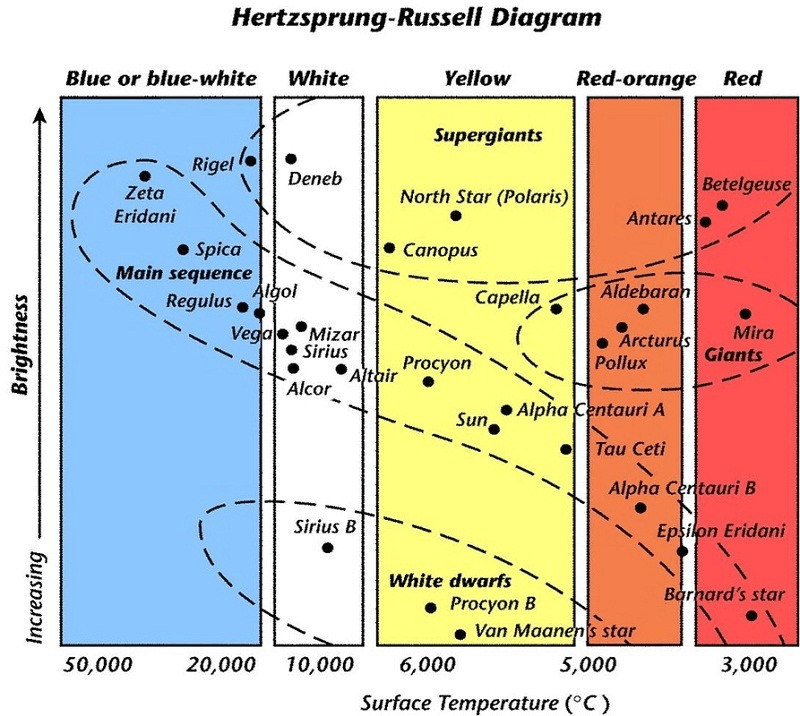
The Sun is yellow and about 5,500 degrees Celcius.
Blue and blue-white are the stars with the highest temperature.
The brightest star is Deneb.
What is Replication?
*If that scientist gets the same results, the more likely your conclusion is correct.
Replication is one another scientist repeats your experiment without changing anything
True or false
If the volume is greater than the mass the objects density will be less than one and the object will float.
True
What is a saturated solution?
A saturated solution is a solution in which no more solute can be dissolved in it.
For numbers, 1 and 2 name the sections on the periodic table.
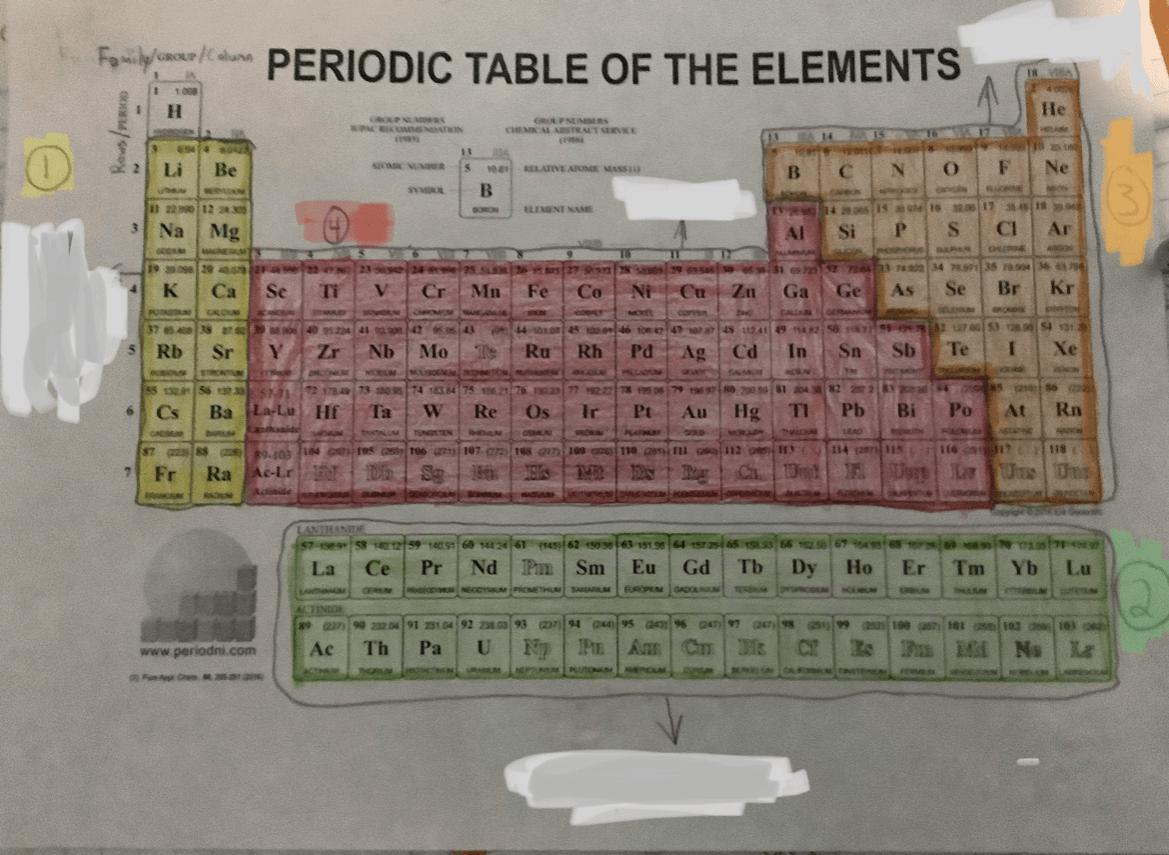
1 = Alkali or Alkaline Metals
2 = Synthetics
What is a homogeneous mixture?
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture of two or more visibly different substances or phases.
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture of two or more substances that have the same appearance throughout.
From what number to what number is it slight basic on the pH scale?
From 8 to 10 that means the substance is slightly basic on the pH scale.
What are organelles?
What are cells?
What are tissues?
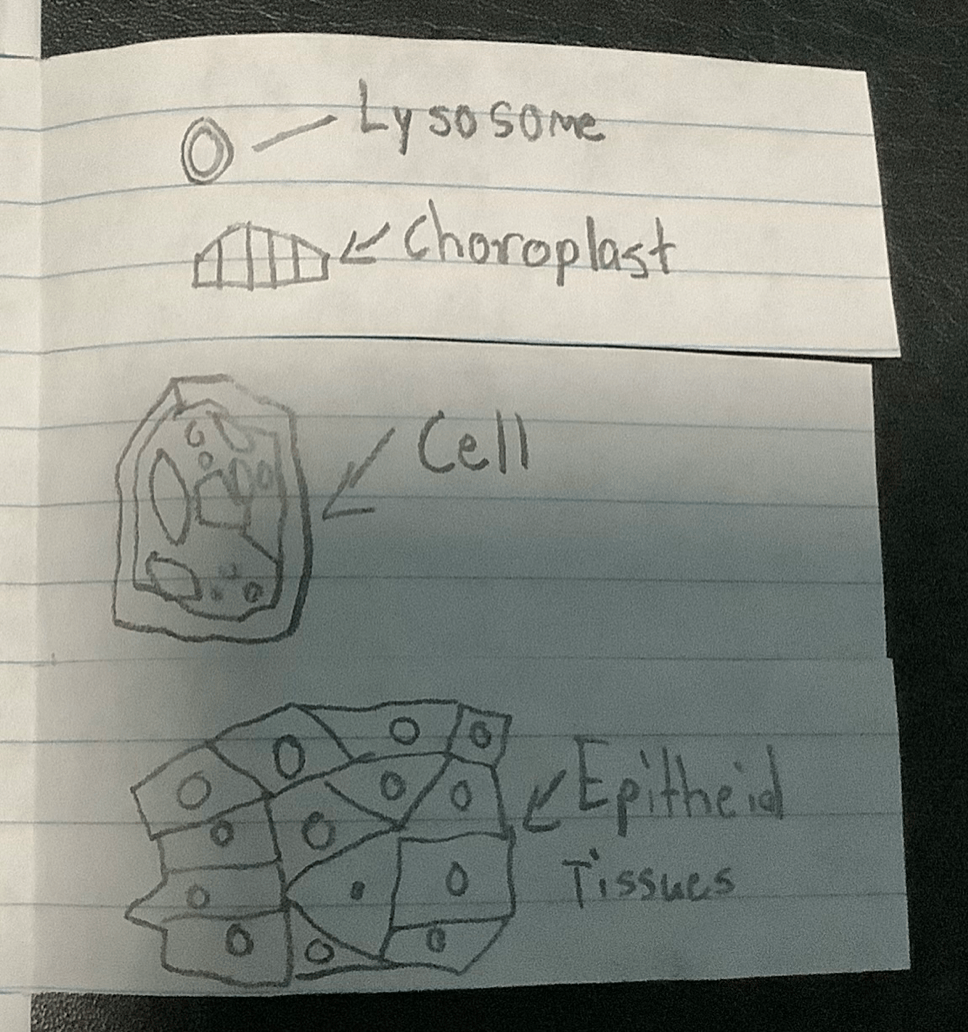
Organelles are parts that make up a cell.
Cells are made of organelles and are the basic unit and function of life.
Tissues are a group of cells working together to do a specific job.
How does the Sun rotate?
The Sun rotates on its own axis about 1.2 miles per second.
From the center it takes 25 days for a full rotation and for the top and bottom it takes 36 days.
What are the benefits and limitation of models?
*Models represent living and no living things better than drawings*
The benefits are…
it helps you to understand more about the concepts
The limitations are…
it is not exactly like the real thing
True or False
*The warmer the temperature the faster the particles move*
True
What is the chemical reaction time?
The chemical reaction time is the warmer the temperature, the faster the reaction time.
For numbers, 3 and 4 name the sections on the periodic table.
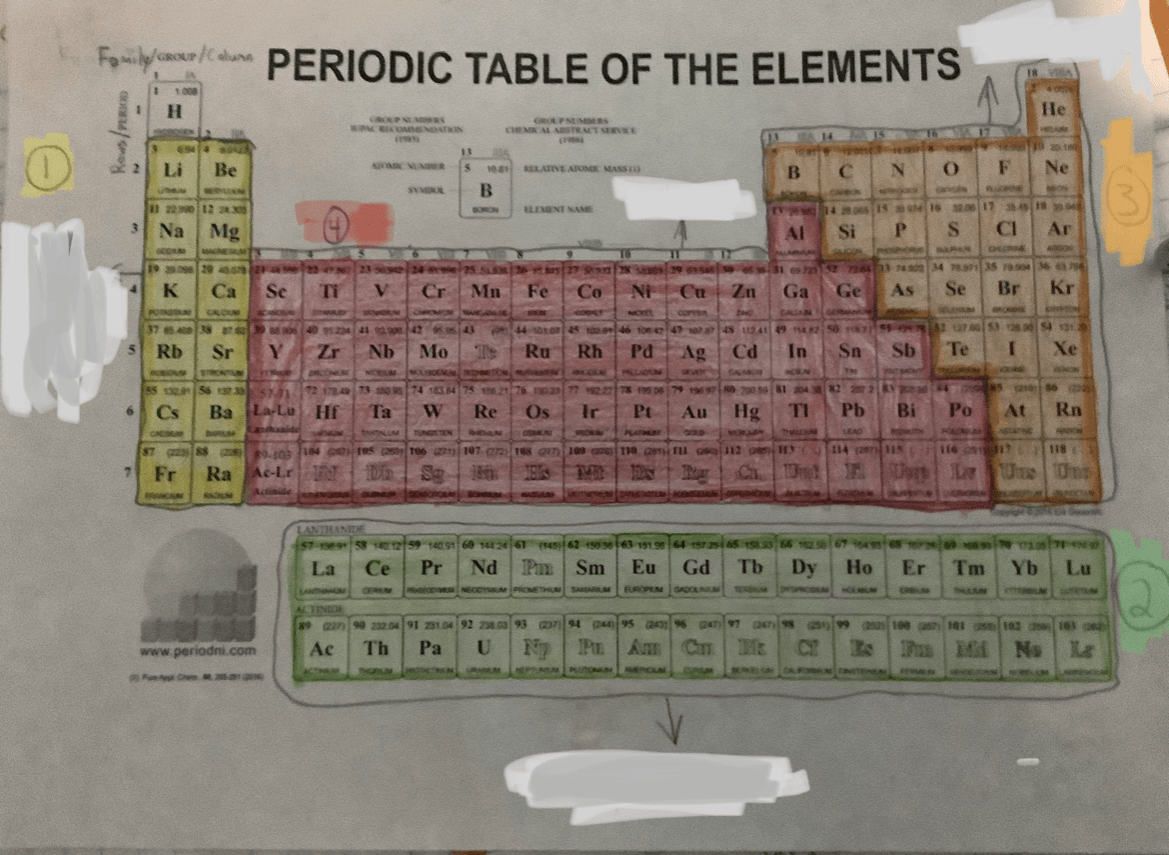
3 = Non Metals
4 = Metals
What types of changes in matter are mixtures?
Physical changes because they do not form new substances and can go back to the original form.
From what number to what number is it very basic on the pH scale?
From 11 to 14 that means the substance is very basic on the pH scale.
What are Organs?
What are organ systems?
What are Organisms?

Organs are a group of tissues working together to do a specific job.
Organ systems are a group of organs working together to do a specific job.
Organisms are all living things.
What are Sunspots?
What is the Convection Zone?
What is prominence?
What are Solar flares?
Sunspots are dark, cooler areas on the surface of the sun called the photosphere.
The Convection Zone is the layer of the Sun where hot gases rise and cooler air sinks.
Prominence is a large, bright, gas feature extending outward from the Sun's surface in a loop shape.
Solar flares are a sudden bursts of high-energy radiation from the Sun's surface.