This step is when you observe and ask...
Step (1) Question or observation
How many mls in a L?
1000 mls in = 1 L
Use this to Measure DISTANCE
Ruler, Tape measure, Meter Stick


Types of Data: numbers, times, distances.
(qualitative. OR quantitative)
QuaNtitative Data
At ALL together and DIVIDE by the number.
A+B+C / 3= average
This step you discuss your data, hypothesis, errors and mistakes.
Step (6) Conclusion and sharing
What unit measure TEMPERATURE?
Celsius degrees 34 Co
What is this called? Used to measure mass

Triple Beam Balance
What is it called when you look at data and graphs to see relationships.
(ie. The biggest / smallest, fastest / slowest, difference between)
Analysis / Analyze Data.
Why do we SHARE results?
So scientists can se our results, try the experiments and test our theories.
Putting collected data into tables and a graph happens in this step.
Step (5) Results
The amount of SPACE inside or AMOUNT something can hold.
Volume
A Graduated Cyclinder is used to measure _____ in ___ units?

Volume (of liquids) in mls.
Control Variables
Everything else is KEPT the SAME.
Try to do about 4-5 trials. This reduces errors and we can calculate an average.
In this step you list the materials needed and write a step-by-step procedure.
Step (4) Experiment. (materials & procedures)
Amount of matter in an object.
Mass
Measures amount of heat
Thermometer
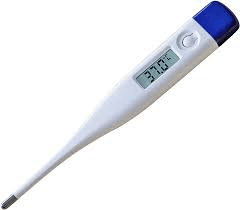
Dependent Variable
What is MEASURED?
Scientist given credit for discovering GRAVITY
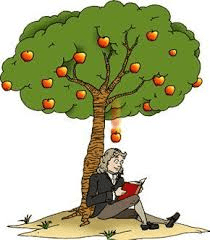
Newton
YOUR educated guess. (If.......then......)
Step (3) Hypothesis
Write the difference between VOLUME and MASS.
Convert
7954m = ________km
437ml = ________L
7.954 km
0.437 L
Independent Variable
What is CHANGED?
Do you know what INFERENCE means? (To make a inference is to...)
make a guess.