What conditions affects HgA1c levels?
Conditions that change the life span of red blood cells, such as recent blood loss, iron deficiency anemia, sickle cell disease, erythropoietin treatment, hemodialysis, transfusion, kidney failure, or liver disease can change A1C levels.
Normal 4-5.6%, Impaired fasting glucose 5.7-6.4%; Diabetes: 6.5 and above. Diagnosing DM2 can be done with 1) Random blood sugar>200, 2) fasting blood sugar is 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests, 3) Oral glucose tolerance test >200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher after two hours.
Name one of two tests commonly used to screen for prostate cancer

DRE(Digital Rectal exam) and PSA(Prostate specific antigen) test
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) had previously concluded that the potential risks of PSA screening in healthy men outweigh the potential benefits. The latest USPSTF final recommendation statement on prostate cancer screening states that men between 55 and 69 should discuss the pros and cons of PSA screening with their clinician before making a decision about screening. Men who are 70 and older should not have routine PSA screenings for prostate cancer.
A key issue is the typical course of prostate cancer. Prostate cancer usually progresses slowly over many years. Therefore, a man may have prostate cancer that never causes symptoms or becomes a medical problem during his lifetime
At what age are women screened for cervical cancer?
21-29 years old pap screen q3 yrs
30-65yo pap every 5 years AND HPV
OR
30-65yo pap every 3 years
If hysterectomy (non-cancerous) no role for pap
*AFP, USPTF, ACOG
The vaccine that all newborns are given at birth.
Hepatitis B: monovalent HepB vaccine only
Routine series: 3-dose series at 0, 1-2, 6-18 months (use monovalent HepB vaccine for doses administered before age 6 weeks)
Infants who did not receive a birth dose should begin the series as soon as feasible.
- Mother is HBsAg-negative: 1 dose within 24 hours of birth for all medically stable infants > 2000 grams. Infants <2000 grams: administer 1 dose at chronological age 1 month or hospital discharge.
- Mother is HBsAg-positive: administer HepB vaccine and 0.5mL of hepatitis immune globulin (HBIG) (at separate anatomic site) within 12 hours of birth, regardless of birth weight. For infants <2000grams, administer 3 additional doses of vaccine (total 4 doses beginning at age 1 month)
The two vaccines that prevent this painful rash that usually presents in a dermatomal distribution.
Two vaccines are licensed and recommended to prevent shingles in the U.S.. Zoster vaccine live (ZVL, Zostavax) has been in use since 2006. Recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV, Shingrix), has been in use since 2017 and is recommended by ACIP as the preferred shingles vaccine.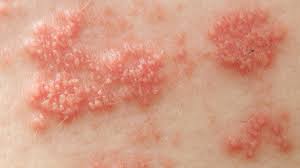
What age is it recommended to screen for lipid profile in males with low CVD risk?
It is recommended that men get lipid screening >35 y/o or >25 y/o if high CVD risk (HTN, DM, Cigarette smoking, family hx of premature CHD)
At what age does the USPSTF recommend screening for Colorectal cancer is no longer needed?
The American Cancer society recommends that adults age 45 to 75 be screened for colorectal cancer every 10 years (previously age 50). Additionally, anyone with a first-degree relative with CRC or advanced adenoma diagnosed before age 60 or two first-degree relatives diagnosed at any age are supposed to be tested at age 40 or 10 years before the age of diagnosis of the youngest relative who had the disease.
Options:
Colonoscopy q10 yrs
Fecal occult blood test annual
Fecal immunochemical test annually
Flex sigmoidoscopy q5 yrs
CT colonography q5 yrs
Multitargeted stool DNA test q3 yrs with FIT
Women are screened for Osteoporosis with _____ starting at age _____.
The USPSTF recommends screening for osteoporosis with bone measurement or DEXA testing to prevent osteoporotic fractures in women 65 years and older.
<65yo if increased fx risk (WHO FRAX fx risk assessment tool)
No USPSTF guidelines for re-screening (2-4 yrs between)
UPSTF does not recommend screening men
*Men >70yoNat’l Osteoporosis Foundation
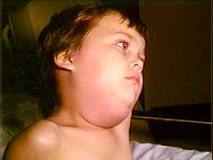
This disease typically starts with fever, headache, muscle aches, tiredness, and loss of appetite. Then, most people will have swelling of their salivary glands. This is what causes the puffy cheeks and a tender, swollen jaw.
Mumps, given with measles and rubella vaccine: minimum age 12 months for routine vaccination.
MMR is given as a 2 dose series at 12-15 months, 4-6 years
Dose 2 may be administered as early as 4 weeks after dose 1
CDC recommends this vaccine for all children younger than 2 years old, all adults 65 years or older, and people 2 through 64 years old with certain medical conditions.
Pneumococcal vaccination
Age 65 years or older (immunocompetent): 1 dose PCV 13 if perviously did not receive PCV 13, followed by 1 dose PPSV 23 at least 1 year after PCV 13 and at least 5 years after last dose PPSV23.
- Previously received PPSV23 but not PCV13 at age 65 years or older: 1 dose PCV13 at least 1 year after PPSV23.
- When both PCV 13 and PPSV23 are indicated, administer PCV13 first (PCV13 and PPSV23 should not be administered during same visit).
- Immunocompromising conditions (congential or acquired immunodeficiency [including B- and T-lymphocyte deficiency, complement deficiencies, phagocytic disorders, HIV infection], chronic renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, leukemia, lymphoma, Hodgkin disease, generalized malignancy, iatrogenic immunosuppression (eg drug or radiation therapy), solid organ transplant, multiple myeloma, or anatomical asplenia (including sickle cell disease and other hemoglobinopathies).
What age is it recommended to get lipid screening in females with increased CVD risk?
It is recommended that women get lipid screening >45 y/o or >30 y/o if high CVD risk(HTN, DM, Cigarette smoking, family hx of premature CHD)
What is one Protective factor against Breast cancer?
Breastfeeding and Multiparity
Pregnancy and breastfeeding reduce the overall number of menstrual cycles in a woman’s lifetime, and this appears to reduce future breast cancer risk. Women who have never had a full-term pregnancy, or had their first full-term pregnancy after age 30, have an increased risk of breast cancer. Estrogen levels may remain lower while a woman is breast-feeding. Women who breastfed have a lower risk of breast cancer than women who have had children but did not breastfeed.
Name this supplement that all women of child-bearing age should take to prevent ______.
Folic acid for the prevention of Neural tube defects
The USPSTF recommends that all women who are planning or capable of pregnancy take a daily supplement containing 0.4 to 0.8mg (400 to 800 micrograms of folic acid).
Women who have a personal or family history of a pregnancy affected by a neural tube defect are at increased risk of having an affected pregnancy. However, most cases occur in the absence of any personal or family history.
All 11 to 12 year olds should get this conjugate vaccine, with a booster dose at 16 years old.
Meningococcal vaccine
There are 2 types of meningococcal vaccines available in the United States:
- Meningococcal conjugate or MenACWY vaccines (Menactra® and Menveo®)
- Serogroup B meningococcal or MenB vaccines (Bexsero® and Trumenba®)
The CDC recommends that everyone 6 months of age and older get this vaccine each year.
Flu vaccine
Routine vaccination: Persons ate 6 months or older: 1 dose IIV, RIV or LAIV appropriate for age and health status annually.
What two periods in life is it recommended for children to get lipid screening?
It is recommended that children get lipid screening before puberty(ages 9-11) and after puberty(ages 17-21). Please note: For young adults who have not been screened as children, we obtain a baseline lipid profile at the time of initiation of care with an adult primary care practitioner to screen for familial hyperlipidemia and to assess cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk
Name at least 3 Risk factors for Breast cancer
Risk factors for breast cancer include:
Older age
Personal hx of breast cancer
family hx of breast cancer in a first degree relative
early menstruation
starting menopause at a later age
nulliparity
HRT
radiation therapy to chest
obesity
drinking
alcohol
When is screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria with urine culture performed for pregnant women?
The USPSTF recommends screening for asymptomatic bacteriuria with urine culture for pregnant women at 12 to 16 weeks gestation or at the first prenatal visit, if later.
The virus can cause severe watery diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal pain.
Rotavirus: minimum age 6 weeks
Rotarix: 2 dose series at 2 and 4 months
RotaTeq: 3-dose series at 2, 4, and 6 months.
The only recommended screening test for lung cancer is _____, starting at age ______.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends yearly lung cancer screening with LDCT for people who—
- Have a history of heavy smoking, and
- Smoke now or have quit within the past 15 years, and
- Are between 55 and 80 years old.
Heavy smoking means a smoking history of 30 pack years or more. A pack year is smoking an average of one pack of cigarettes per day for one year. For example, a person could have a 30 pack-year history by smoking one pack a day for 30 years or two packs a day for 15 years.
How often does the USPSTF recommend screening for abnormal blood glucose in overweight or obese people as part of the CV risk assessment?
The USPSTF recommends screening for abnormal blood glucose as part of cardiovascular risk assessment in adults aged 40 to 70 years who are overweight or obese every 3 years.
A fasting plasma glucose value <100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) or A1C <5.7 percent should be considered normal. We suggest retesting at three-year intervals.
For those with borderline results (fasting plasma glucose 100 to 125 mg/dL or A1C 5.7 to 6.4 percent), we suggest follow-up every one to two years.
The diagnosis of diabetes is confirmed if two consecutive A1C levels are ≥6.5 percent, two consecutive fasting plasma glucose levels are ≥126 mg/dL(7.0 mmol/L), or if both the A1C and fasting plasma glucose are above their diagnostic thresholds.
If A1C and fasting plasma glucose are discordant, the test that is diagnostic of diabetes should be repeated to confirm the diagnosis.
For Every 1000 women who have a screening
mammogram, how many are actually diagnosed
with breast cancer?
5 in every 1000 women who have a screening mammogram are diagnosed with breast cancer.
Once more, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has issued an update to its 2009 breast cancer screening guidelines, reaffirming that women 50 to 74 years of age are most likely to benefit from mammography, optimally performed once every 2 years.
The guidelines diverge from those of issued by the American Cancer Society (ACS), National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), and other groups in the recommended age ranges and the frequency of recommended screenings. The ACS and NCCN guidelines recommend that women start mammography in their 40s, and both call for annual screening until a woman has a less than 10 year life expectancy.
While some have suggested that screening be initiated at an earlier age if a first-degree relative had premenopausal breast cancer, there are no high-quality data supporting this approach in the absence of a known genetic syndrome. Many experts suggest that in women at moderate risk, the decision to undergo supplemental screening (with either magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] or ultrasound in addition to mammography) should be determined after a discussion with the patient regarding personal preferences.
Up to what age can females receive the HPV vaccine?
Females and males through age 45 years according to the FDA.
- Age 15 years or older at initial vaccination: 3 dose series HPV vaccine at 0, 1-2, 6 months (minimum intervals): repeat dose if administered too soon.
- Age 9 through 14 years at initial vaccination and received 1 dose, or 2 doses less than 5 months apart: 1 dose HPV vaccine
- Age 9 through 14 years at initial vaccination and received 2 doses at least 5 months apart: HPV vaccination complete, no additional dose needed.
This disease typically begins with a mild to moderate fever, often accompanied by a persistent cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis and sore throat. Acute illness and rash. The rash consists of small red spots, some of which are slightly raised.
Measles : given in MMR vaccine at 12-15 months, 4-6 years as 2 dose series.
Measles typically begins with
- high fever (may spike to more than 104°),
- cough,
- runny nose (coryza),
- red, watery eyes
- 2-3 days after symptoms begin: Koplik spots
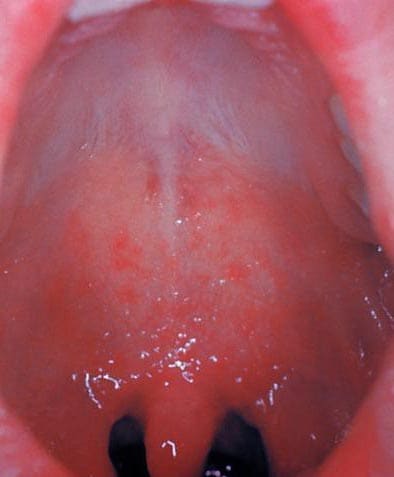
- Three to five days after symptoms begin, a rash breaks out. It usually begins as flat red spots that appear on the face at the hairline and spread downward to the neck, trunk, arms, legs, and feet.
-
The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen for HIV infection starting at age ____ to 65 years.
The USPSTF recommends that clinicians screen for HIV infection in adolescents and adults aged 15 to 65 years. Younger adolescents and older adults who are at increased risk of infection should also be screened.
.ashx)