What is the ideal imaging modality for evaluation of the acute scrotum in adults and children?
Ultrasound
The epididymis is ___________ to the testicle
parallel
AKA Vas deferens
Ductus Deferens
The testes migrate through the _________________ into the scrotal sac.
inguinal canal
AKA for head of the epididymis
Globus major
AKA Cremasteric artery
External Spermatic Artery
AKA tail of Epididymis
AKA Testicular Artery
Internal Spermatic Artery
AKA for calcifications
Scrotal Pearls
Endodermal sinus tumors
Form wedge-shaped compartments that contain the _________________
Septa; seminiferous tubules
Pediatric testes are _______________ and measure ~ _______ with uniform low-to-medium echogenicity.
ovoid; 1 cm
Attention to appropriate color Doppler settings is needed because detection of ________________ is critical
Slow flow
Thick fibrous connective tissue capsule that surrounds the testicle
tunica albuginea
From age 8 to puberty the testes are about ___________
4 cm
What kind of echotexture does a normal testis have?
Homogeneous medium level echo texture
Forms the support for the entering and exiting testicular vessels and ducts
Mediastinum
The thin hypoechoic ring of fibrous tissue surrounding the testis giving it an encapsulated appearance
Tunica Vaginalis
This is where sperm become concentrated and other fluids are reabsorbed
Rete testis
Largest part of Epididymis
Head
What two things should be performed when evaluating for varicoceles?
1. Valsalva
2. scanning in upright position
What are the 2 layers of the tunica vaginalis?
1. Visceral (touching organ)
2. Parietal (not touching organ)
Which layer of the tunica vaginalis lines the scrotal chamber?
Outer (Parietal)
The epididymis is where the _________________ converge to form a single convoluted duct called the _______________
efferent ductules; ductus epididymis
_________________ is a useful adjunct to color Doppler in low flow states, but it is more sensitive to _______________
Power Doppler; motion artifacts
Carry the seminal fluid from the rete testis to the epididymis
efferent ductules
As the tail of the epididymis courses cephalad it becomes known as the ________________
vas deferens
Supports the testes in the scrotal sac and has a thin film of serous fluid between its layers
Tunica vaginalis
Primary function of the spermatic cord
facilitate passage for semen through the vas deferens
Attached to the posterior wall of the testis preventing each testis from rotation within the scrotum
Tunica Vaginalis
The seminiferous tubules course centrally to form these 20-30 larger ducts
Tubuli recti
Normal measurements of the Epididymis:
__________ Head
__________ Tail
__________ Body
Head 5-12 mm
Tail 2-5 mm
Body 2-4 mm
The division of the 2 scrotal chambers
Scrotal Raphe
Runs through the abdominal region down to the testicles
Spermatic cord
Venous drainage of the scrotum occurs through the veins of this
Pampiniform Plexus
The tunica albuginea is continuous posteriorly and divides the testis into _____________
~ 250 lobules
The right testicular vein drains into this
IVC
______ length
______ width
______ AP
Ovoid; 3-5 cm length; 2-4 cm width; 3 cm AP
Layer of smooth muscle fibers that live beneath the scrotal skin and divides the scrotum into 2 chambers
Dartos muscle
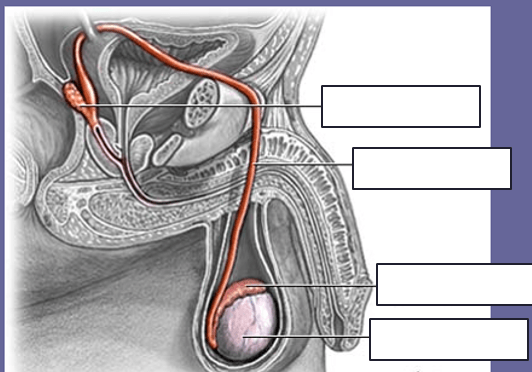
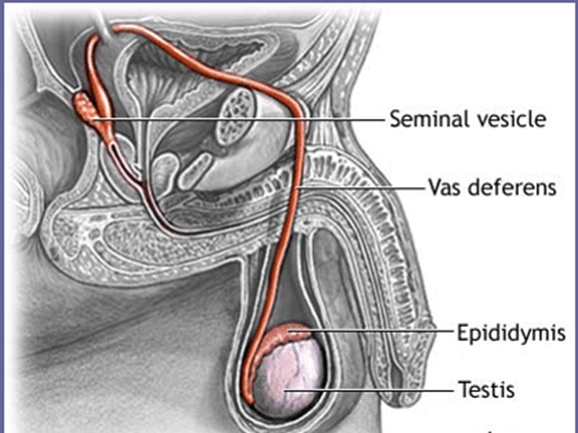
The left testicular vein drains into this
Left Renal Vein
Where does the pampiniform plexus terminate?
into the testicular vein
Intrascrotal masses can be detected with a sensitivity of _____
nearly 100%
Testicular cyst
The deferential vein drains into this
Manual detorsion involves rotating the painful testicle outward like this
opening a book
Normal scrotal skin measures __________ in thickness
2-8 mm
Sign for Varicocele
"Bag of Worms"
The Cremasteric vein drains into this
Tributaries of the epigastric veins
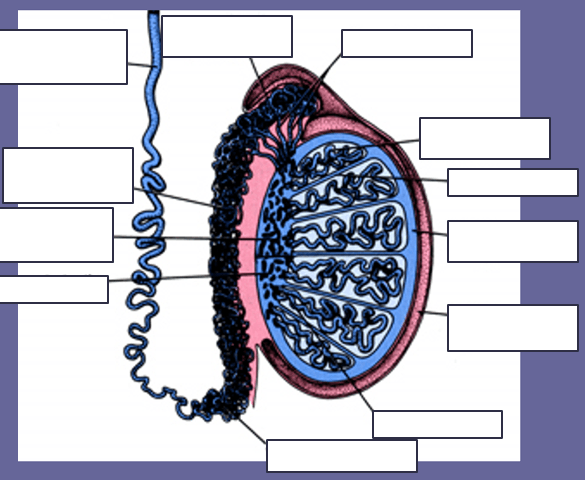
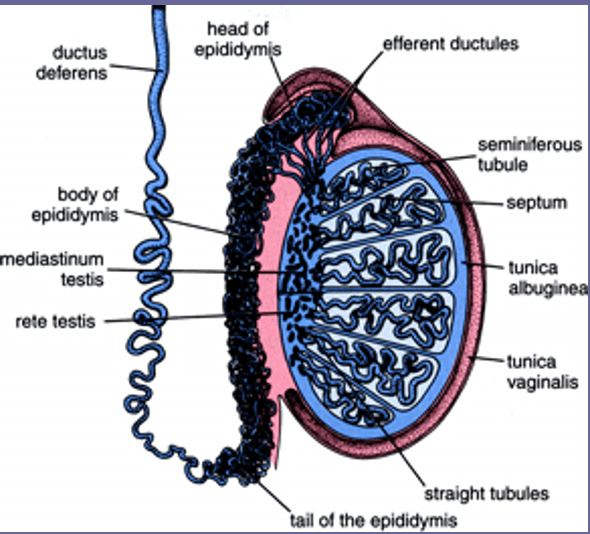
Usually a complication of epididymo-orchitis; present with enlarged testicle containing a fluid-filled mass with hypoechoic or mixed echogenic areas
Abscess
Over half of the testicular ruptures occur during what
sporting events
The second most cause of testicular rupture is
An initial infarct looks like what?
focal or diffuse hypoechoic testicle
sperm granuloma
Benign cysts that are well circumscribed and of germ cell origin; mostly 20s and 40s; painless testicular nodule filled with flaky, cheesy, white keratin
Epidermoid cysts
Testicle decreases in size and areas of increased echogenicity (fibrosis and calcs)
One of the most common genitourinary anomalies in male infants
cyryptorchidism
Where do the testicles form?
Increased blood flow
hyperemia
Approximately 90% of rupture testicles can be saved if surgery is performed within the first _________ hours
72
Epididymal cysts are found where in the epididymis
head
40 year old male, asymptomatic, palpable mass on testicle seen on the periphery of the testicle
tunica albuginea cyst
cyst that is more common than epidydimal cysts
Spermatocele
Testicular cancer or mass
This is seen as an enlarged and hypoechoic testicle with increased blood flow
orchitis
Undescended testicle or hidden testicle
Chryptorchidism
May be seen within the parenchyma of the testicle, on the surface, or freely located within hydrocele; testicular microlithiasis could be seen with this
prior case of epididymis
mass that develops as a result of the body's immune reaction to sperm leaking from the cut of end of the vas
Sperm Granuloma
Most common extratesticular tumor
Benign adenomatoid tumor
Most common cause of painless scrotal swelling
hydrocele
Typically, the testicle is attached to the tunica vaginalis; without this attachment or a higher attachment than normal, the testicle can rotate freely on the spermatic cord, which is called this
Bell Clapper Deformity
Rare and usually involve the epididymis; commonly in 20-50 year old pts; generally unilateral, solitary and well defined rarely over 5 cm
extratesticular tumors
Abnormal collection of serous fluid between the layers of the tunica vaginalis
Hydrocele
Most malignant testicular neoplasms appear
Hypoechoic compared to rest of testicle
Most common extratesticular tumor in adults
adenomatoid tumor of the epididymis
Most common condition that causes acute scrotal pain
epididymitis
This requires immediate surgery
Torsion
Torsion most often involves the _________ testicle
left
Typically patients present with the insidious onset of pain, which increases over 1-2 days; fever, dysuria and urethral discharge may also be present
Epididymitis
Testicular salvage rate is 80-100% if surgery is performed within _________ hours of the onset of pain
5-6
A rare gonadal stromal tumor that presents with feminization with gynecomastia; small homogeneous and hypoechoic that are often bilateral
Sertoli
Collection of abnormally dilated, tortuous and elongated veins of the pampiniform plexus located posterior to the testis
Varicoceles
Leydig cell tumor produces ___________________ resulting in _______________
Progesterone; precocious puberty
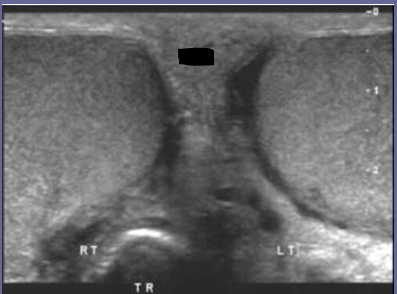 What is this muscle and divider?
What is this muscle and divider?
muscle: dartos
divider: scrotal raphe
caused by direct trauma to the testis or torsion leading to hemorrhagic suffusion or invasion by tumor
hematocele
Alpha fetoprotein and testicular tumor: suspect what type of cancer?
non-seminomatous tumor
Most common correctable cause of male infertility
varicoceles
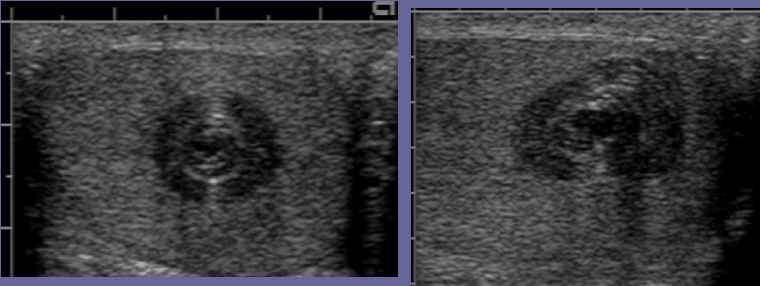
Epidermoid cyst
2 complications of cyrptocrchidism
1. infertility
2. cancer
Epididymitis is usually caused by:
______________ men > 35
______________ men < 35
men > 35 trauma or UTI
men < 35 sexually transmitted diseases
Most common malignant mass of the testicle
seminoma
Most primary malignant tumor of testicle are of ____________ origin
germ cell
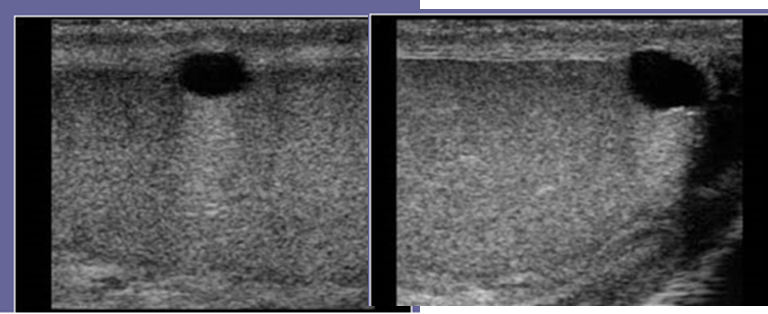
2 types of Varicoceles
1. Primary or idiopathic
2. Secondary
Malignant lymphoma
2 most common causes of acute scrotal pain
1. epididymitic/orchitis
2. torsion of the spermatic cord
Half of bilateral testicular neoplasms are ______________
malignant lymphomas
Sonographically associated with:
1. enlarged hypoechoic epididymis
2. hypoechoic testicle
3. increased blood flow compared to the asymptomatic side
4. reactive hydrocele
5. scrotal wall thickening
Epididymitis
Most malignant testucular neoplasms are more _____________ than normal testicular parenchyma
hypoechoic
Most malignant lymphomas of the testicle are this type
non-Hodgkin's type
What results in failure of testicular descent predisposes the patient to malignancy?
Hormonal deficiency
The yolk sac tumor is what kind of tumor?
Germ cell
Seminomas spread initially where?
Fetal hydrocele has what sign?
Owl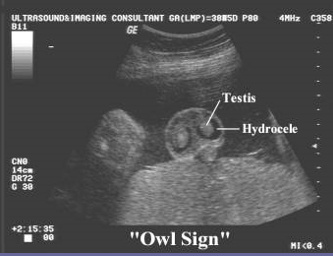
Least common and most lethal form of germ cell tumors
choriocarcinoma
Most common prepubertal testicular tumor
Yolk sac tumor
teratoma
What can be mistaken for the testis?
a Large Lymphnode
Malignant lesions to the scrotal wall are usually of _____________ origin.
epididymal
Malpositioned testes may be located anywhere along the pathway of descent from the ______________ to the ______________
retroperitoneum; scrotum
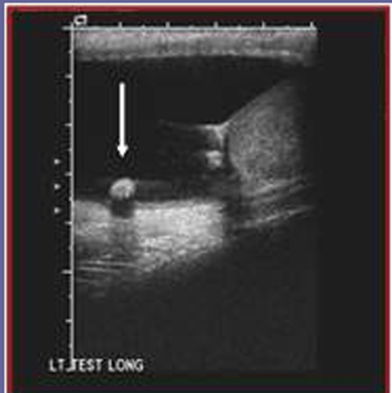
Scrotal Pearls
Cryptorchidism is not associated with this
Hydrocele
This tumor is associated with an increase in beta hCG
Choriocarcinoma
Patients with testicular neoplasms often present with these 2 things.
2. diffuse testicular enlargement
The 2 most common metastatic testicular tumors
1. lymphoma
2. leukemia
What tumor has an incerased level of alpha-fetoprotein?
Yolk sac tumor (germ cell)
Teratomas in children are usually _______ and in adults are usually _________
benign; malignant
Most common malignant paratesticular tumor in infants and children
rhabdomyosarcoma
Microlithiasis
Most common germ cell tumor in adults
Seminoma
The majority of stromal tumors are
Leydig cell
The highest risk factors for testicular cancer is being a _________________ and ______________________ between _____ and ______
White male
males
15
35
___________________ metastasize by hematogenous routes
Choriocarcinomas
Seminomas are commonly confined wihtin the _______________
Tunica albuginea
The term gonadal stromal tumor refers to a neoplasm containing 5 types of cells
2. Sertoli
3. thecal
4. granulosa
5. lutein
5 reasons to have testicular implants
1. undescended testicles
2. torsion of testicle
3. traumatic injury
4. cancer
5. small, deformed, or non-functioning testicle(s)
Flow of semen from testicle out (6)
1. Seminiferous tubules
2. Tubuli recti
3. Rete testis
4. Efferent ductules
5. Ductus epididymis
6. Vas Deferens
Mixed germ cell tumors include what 3 things?
1. teratoma
2. choriocarcinoma
3. yolk sac tumor
3 types of benign cysts
1. tunica albuginea cysts
2. intratesticular cysts
3. epidermoid cysts
4 testicular appendages
1. Appendix testis
2. Appendix Epididymis
3. Vas aberrans
4. Paradidymis
5 things the spermatic cord consists of
1. vas deferens
2. arteries
3. pampiniform plexus of veins
4. lymphatics
5. nerves
3 arteries that bring blood to the testicle
1. testicular
2. deferential
3. cremasteric
What are the waveforms of blood flow to the testis (3):
1. Deferential: HIGH
2. Cremasteric: HIGH
3. Testicular: LOW
Benign intratesticular lesions (3)
1. cysts
2. abscesses
3. calcifications
Extratesticular lesions (6)
1. hydrocele
2. hematocele
3. pyocele
4. varicocele
5. extratesticular tumors
6. scrotal hernia
3 types of epididymal lesions
1. cysts
2. spermatoceles
3. sperm granuloma
4 types of germ cell tumors of the testicle
1. seminoma
2. teratoma
3. choriocarcinoma
4. mixed tumors
3 layers of a teratoma
1. endoderm
2. mesoderm
3. ectoderm
What 3 distal metastases may be the initial presentation of choriocarcinoma
2. liver
3. brain