This is the principle that the processes we observe today occurred throughout Earth's history.
What is "Uniformitarianism?"
These are the three types of plate boundaries.
What are "Divergent, Convergent, & Transform?"
This process occurs when rocks are moved from one location to another.
What is "Erosion?"
These are the three types of rocks.
What are "Igneous, Sedimentary, & Metamorphic?"
This type of variable should be kept the same for every test in the experiment.
What is a "Constant Variable?"
This type(s) of waves have a "Crest & a Trough."
What is a Transverse Wave?
This is a set of steps that explains how to carry out an experiment.
What is a "Procedure?"
These types of plate boundaries are associated with volcanoes.
What are "Divergent & Convergent" plate boundaries?
This process puts materials down.
What is "Deposition?"
These rocks form directly from liquid magma.
What are "Igneous Rocks?"
This part of the scientific method must be testable, specific, and include the words "IF, THEN, & BECAUSE" to receive full credit.
What is a "Hypothesis?"
This type(s) of waves cause the particles to move perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
What is a "Transverse Wave?"
This is a break in Earth's lithosphere where one block of rock moves toward, away from, or past another.
What is a "Fault?"
These are the two types of plates found on Earth.
What are "Oceanic & Continental?"
This type of weathering physically breaks a rock down into smaller pieces without changing its composition.
What is "Mechanical Weathering?"
These are the two types of Metamorphic Rocks.
What are "Contact Metamorphism" and "Regional Metamorphism."
This wave property is shown in the diagram below as the Dotted Red Line from the "Rest Line" to Point A or the "Rest Line" to Point C.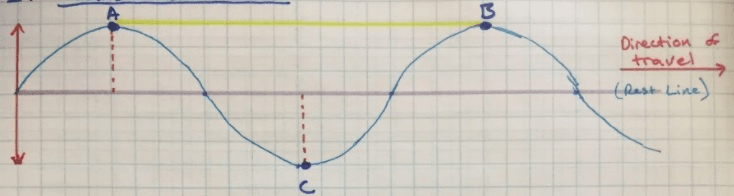
What is the "Amplitude?"
This process breaks down rocks into smaller pieces.
What is "Weathering?"
This type of fault is associated with a transform plate boundary.
What is a "Strike Slip Fault?"
This type of weathering breaks down rocks by dissolving minerals or otherwise changing their composition.
What is "Chemical Weathering?"
These are the two types of igneous rocks.
What are "Intrusive Igneous Rocks" (Plutonic) and "Extrusive Igneous Rocks" (Volcanic).
In a scientific graph, this variable is found along the X-axis.
This wave interaction is shown below. 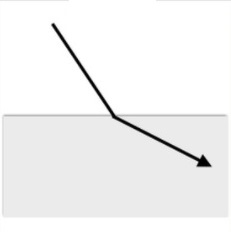
What is Refraction?
This variable is what is measured in the experiment.
What is the "Dependent Variable?"
This type of volcano is associated with a Convergent Plate boundary that contains an Oceanic & Continental Plate.
What is a "Composite (or Strato) Volcano?"
This surface feature is formed when flowing water quickly comes to a stop and deposits the sediment it was carrying.
What is a "Alluvial Fan" or "Delta?"
This type of Igneous Rocks have very large crystals because the rocks cooled very slowly.
What are "Intrusive Igneous Rocks" (Plutonic)?
Why is the reliability of the data an important thing to discuss in your conclusion?
Answers will vary, but may include things like "It explains why your conclusions should be trusted," or "It informs the reader of any issues that may have affected the outcome of the experiment."
This type(s) of waves transfer energy without transferring the matter.
What is "Both Transverse & Longitudinal Waves?"