The shape of DNA.
The shape of RNA.
What is a double helix?
What is a single helix?
Individuals fighting for limited resources
What is Competition?
The central dogma of life.
What is DNA-> RNA -> Ribosome -> Protein?
Species change over time.
What is evolution?
Traits that become more common in a population.
What are advantageous traits.
The backbone of DNA.
The "rungs" of the ladder.
What are the sugar and phosphate groups?
What are the nitrogen bases?
Producing more offspring than will survive
What is Overproduction?
Using the letter "B" what would the genotype be for the following:
Heterozygous, homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant
Heterozygous: Bb
Homozygous R: bb
Homozygous D: BB
The type of anatomy that has similar structure but may have different functions.
Adaptations that affect the physical features of an organism
What are structural adaptations?
The complementary base pairs for RNA
Adenine - Uracil
Thymine - Adenine
Guanine - Cytosine
Individuals pass on their traits to their offspring.
What is Inheritance?
The location of transcription in a cell.
The location of translation in the cell.
What is the nucleus?
What is the ribosome?
The thing that biochemistry (DNA/RNA) looks for in sequencing in related species.
What are the similarities and differences?
The variable a scientist manipulates.
The variable the scientist measures.
The variables that do not change in the experiment.
What is the independent variable?
What is the dependent variable?
What are the control variables?
The complementary base pairs for DNA.
Adenine - Thymine ; Guanine - Cytosine
Differences within the same species that helps the population survive environmental changes.
What is Variation?
Straight hair is dominant over curly hair. Use the letter "h" to represent the alleles.
Draw a punnett square; cross a homozygous recessive mom with a heterozygous dad.
What are the possible genotypes along with what phenotype that genotype would show.
h h
H Hh Hh
h hh hh
Genotypes: Hh - straight hair or hh - curly hair
Percentages: Hh - 50% hh - 50%

The type of evidence for evolution being shown. (This is an armadillo by the way)
What are fossils?
A process of change by which an organism or species becomes better suited to its environment.
What is an Adaptation?
Difference between pyrimidines and purines & which bases are which.
Pyrimidines are smaller with only 1 carbon ring (cytosine and thymine)
Purines are larger with 2 carbon rings (adenine and guanine)
The rock pocket mouse population changing over time from light to dark to better suit the environment.
What is Shift in population?
Transcribe the following DNA code into mRNA, then translate it into protein using the codon chart:
TAC GTA ATG CCC AAG ATC
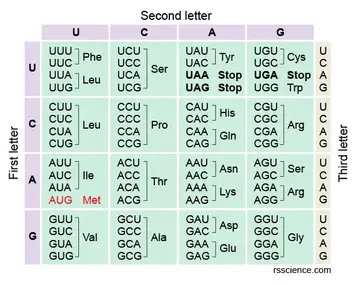
mRNA: AUG CAU UAC GGG UUC UAG
protein: Met - His - Tyr - Gly - Phe - Stop
The type of anatomy that has different structures but the same function.
What are analogous structures?
The axis that shows the Independent variable.
What is the x axis?