The process when organisms with favorable traits are more likely to survive and have offspring which leads to a change in the population.
What is natural selection?
This type of reproductive isolation occurs when two species have different mating times.
What is temporal isolation?
Two words that can be used to categorize plants
What are autotrophs and producers?
The process when water vapor turns into clouds.
What is Condensation?
This biome is known for having low precipitation and high temperatures.
What is Desert?
This type of selection is illustrated on the graph

What is disruptive selection?
What is geographic or ecological isolation?
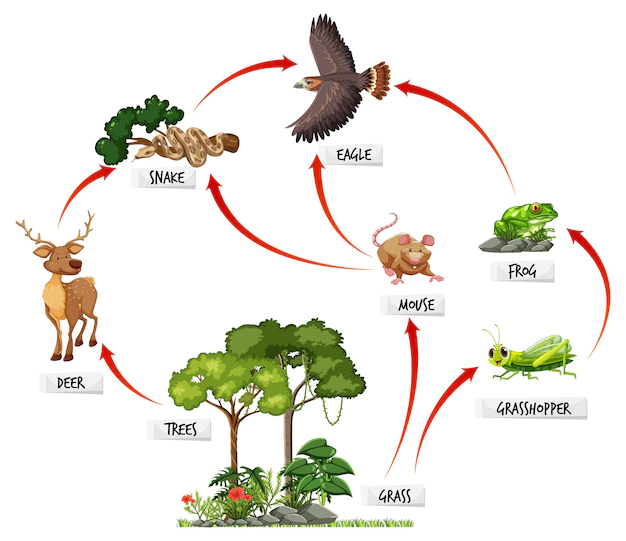 This is the 3rd order heterotroph in this food web.
This is the 3rd order heterotroph in this food web.
What is Eagle?
The process where fossil fuel is converted into carbon dioxide
What is combustion?
This biome is known for having high precipitation and high heat.
What is Tropical Rainforest?
An example of this type of selection occurs when dark colored rabbits are better able to camouflage and hide from predators than light colored ones.
What is directional selection?
This type of speciation occurs when two species are in the same location but have different mating habits.
What is sympatric speciation?
When a producer generates 35,000 joules of energy, the secondary consumer receives that many joules of energy.
What is 350 joules of energy?
An example of this is when a species of rabbits were introduced to Australia and began to outcompete with the native species for food and became overpopulated.
What is an invasive specie?
This biome is threatened by the converting of its land to farmland.
What is Temperate Grassland? *best answer
or
What is Tropical Rainforest *second best
This type of evolution occurs when an organism from one population moves to a new population and brings its genes with it.
What is Gene Flow?
An example of this type of speciation is when some flowers are exposed to sunlight while others within the population are covered by shade. Overtime, they can no longer mate.
What is parapatric speciation?
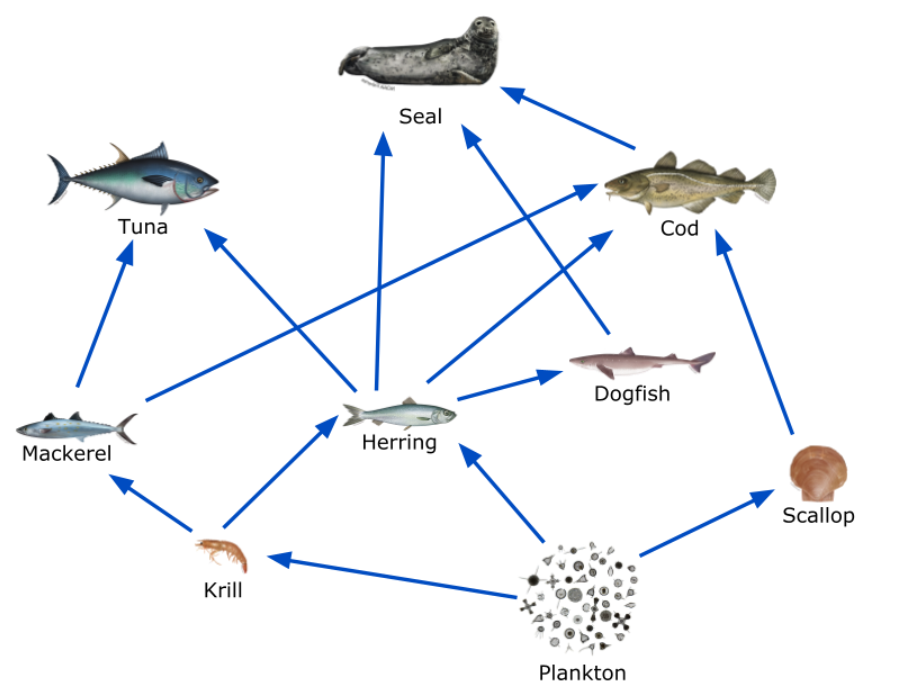 The three primary consumers in this picture.
The three primary consumers in this picture.
What are krill, herring and scallop?
Type of factors that include competition for food, spread of disease, and predators.
What are density dependent factors?
This biome is threatened by over frequent wildfires due to climate change.
What is Temperate Woodlands and Shrublands
or What is Chaparral?
This type of evolution occurs when the population size gets drastically reduced by chance (possibly due to natural disaster)
What is Genetic Drift?
or
What is Bottleneck Effect?
This type of speciation can also be known as the Founder's Effect
What is peripatric speciation?
What is 400,000 Joules of energy?
Two ways that allow for nitrogen fixation.
What are nitrogen-fixing bacteria and lightning?
This biome is categorized by their long, cold winter and short, mild summers.
What is Taiga?
or
What is Boreal Forest?
or
What is Coniferous Forest?