Melting and boiling
Temperature
Nuclear reactions focus mainly on this part of the atom.
The nucleus
Why is carbon so ideal for organic life?
4 valence electrons
Ability to single, double, triple bond
Small and light
A pH range of 0-7 is normal for a(n) ________.
Acid
________ is the state of matter where atoms constantly slide past each other, but are still confined to a space.
Liquids
This is an endothermic or exothermic reaction?
Endothermic (more energy ending than when you started)
How many protons would an isotope of Carbon-14 have?
6
What does the prefix in an organic molecule's name tell you?
The number of carbon atoms
What is the difference between a saturated and supersaturated solution?
Exceeds proportion of solute:solubility in solution at a given temperature.
Describe the relationship between kinetic energy (movement) and intermolecular forces (what holds atoms together)
They are inversely related
What are the 3 types of modes of heat transfer?
Convection
Conduction
Radiation
Name the 3 types of radioactive decay.
Alpha, beta, gamma
Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes differ because of...
What are the variables in the Ideal Gas Law?
PV = nRT
Pressure, volume, number of moles, temperature
Which of these letters DOES NOT represent a phase change occurring?

A, C, E
The measure of disorder in a system
Example: H2O (s) --> H2O (g)
Entropy!
500g of radioative Carbon-14 undergoes 5 half-life decays. How much is left?
15g
What is the name of an atom that gives an organic molecule its structure?

According to Boyle's Law, as pressure increases, volume _______.
Name some exothermic phase changes (energy exits the system)
Freezing, Condensation, Deposition
If the product side of a thermokinetic system experiences stress, Le Chateleier's principle suggests that the equilibrium will shift to the ...
Reactants
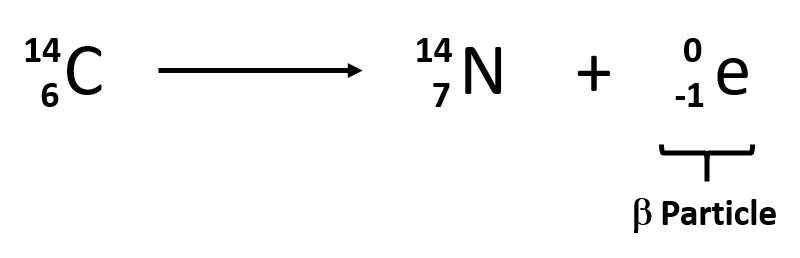
Name the particle (in isotope notation) that pops off of a beta decay.
Draw a molecule of butene
(4 carbons, double bonds)

Titrations are important for scientists studying acids and bases. Why?
Determine the exact neutralization needed for an acid-base reaction.
Acid + base --> salt + H2O