Part of the eye which helps focus on objects with its clear and flexible parts.
What is the lens?
Rods are associated with what 2 functions.
What is black and white and peripheral vision?
Fovea at the center of the retina is associated with this function.
What is color?
Theory suggests how colors are perceived after the initial detection by the retina and fovea. Colors are paired in opposing pairs: blue, yellow; red-green etc.
What is opponent process theory?
Back of the eye in which cones and rods (photoreceptors) turn light into neural signals.
What is the retina?
If a stimulus activates the edge of the retina where rods are, this cannot be seen.
What is color?
Concentrated at the center of the fovea are these parts which help with color.
What are cones?
Explains how light stimulates one of three cones (blue, green, red) and allow the sensation of all colors ROYGBIV 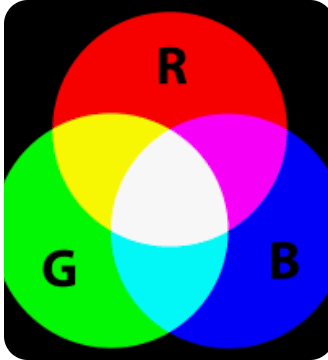
What is trichromatic theory? Young-Helmholtz theory?
The part of the eye which is at the center of the retina.
What is the fovea?
3 colors associated with the retina (fovea)
What are red, green, blue?
The small portion of radiation in the universe that can be seen.
What is visible light?
Red is associated with this type of wave.
What is long frequency?
In order for case studies to be generalizable to a target population this needs to be done.
What is random sampling?
White part, or "shell" of the eye.
What is sclera?
What is an experiment?
2 dimensions associated with light waves.
What is length and amplitude?
Blue is associated with this type of wave.
What is short frequency?
This is necessary for studies on vision and memory to be replicated by other psychologist and scientist; in other words the use of precise and quantifiable language.
What is operational definitions?
The colored sphincter part of your eye which controls amount of light entering the eye.
What is the Iris?
A study which looks at 2 age groups to analyze how photoreceptors of firefighters (young and old) are impacted by exposure to smoke and heat.
What is a cross-sectional study?
Frequency of a light wave helps in sensing this aspcet of sight.
What is color? What is hue?
The intensity of color is determined by this.
What is amplitude?
What is random assignment?
Front of the eye, acts like a windshield and protector of the eye.
What is the Cornea?
What is longitudinal study?
Amplitude of a wave is associated with sensing this of color.
What is brightness?
Dull or not so bright colors have this type of amplitude.
What is low amplitude?
Part of the eye in which light enters through a hole.
What is the Pupil?
What is negative correlation?
Bright neon intense colors are associated with this type of wave.
What is high amplitude?