process by which our senses (sight, sound, smell, taste, touch) become less sensitive to a constant stimulus over time
is this sensory adaptation or transduction?
sensory adaptation (ex: When you enter a room with a strong perfume, the smell initially seems very strong, but after a few minutes, you no longer notice it.)
*transduction 
_____________ occurs when the visual image focuses in front of the retina, causing difficulty seeing distant objects
_____________ occurs when the image focuses behind the retina, leading to difficulty seeing close objects
nearsightedness (myopia) occurs when the visual image focuses in front of the retina, causing difficulty seeing distant objects
farsightedness (hyperopia) occurs when the image focuses behind the retina, leading to difficulty seeing close objects
process of sound transduction
soundwaves enter through the ear drum (part of outer ear) then go to
outer ear -> middle ear -> inner ear
What is the difference between a supertaster, a medium taster, and a nontaster?
a supertaster experiences tastes with greater intensity, a medium taster has an average ability to sense flavors, and a nontaster has less taste perception than a medium taster.
The brain’s natural painkiller
endorphins
This is a neurological condition where stimulation of one sense (like seeing) triggers experiences in another sense (like associating colors).
Which is the correct answer:
a. sensory adaptation
b. sensory interaction
c. synesthesia
c. synesthesia
ex: associating colors with academic subjects like english (yellow), math (blue), and science (green) can be an example of synesthesia
___________ are highly sensitive to light, enabling vision in dim conditions and peripheral vision, while ___________ enable color vision and sharp, detailed vision in bright light.
Rods are highly sensitive to light, enabling vision in dim conditions and peripheral vision, while cones enable color vision and sharp, detailed vision in bright light.
____________ occurs when sound waves are unable to travel through the outer and middle ear, while ____________ happens due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve pathways
conductive hearing loss (less common) occurs when sound waves are unable to travel through the outer and middle ear, while sensorineural hearing loss (more common) happens due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve pathways
The taste buds on your tongue are housed inside visible bumps called _________
papillae
When your brain creates pain after the amputation of a limb
phantom limb sensation
What are these all examples of?
- Vision: The lowest level of light the human eye can detect.
- Hearing: The lowest level of tone the human ear can detect.
- Smell: The smallest amount of odor a person can detect.
- Taste: The minimum concentration of a substance that can be tasted.
- Touch: The smallest amount of pressure a person can feel.
absolute threshold = is the point at which a stimulus is strong enough to be detected by a person's senses.
example: you might not be able to hear someone whispering from 20 feet away, but if that person speaks to a normal voice, it may reach your absolute threshold
Which part of the eye is the adjustable opening in the eye that allows light to enter through?
The Pupil -The adjustable opening in the eye that allows light to enter through
The Iris -A ring of muscle tissue that controls the dilation or constriction of our pupil based on light intensity
The Cornea-The clear protective layer of the eye that ultimately protects the Pupil
The Lens-The structure behind the pupil that changes its shape in order to help us focus on the images in front of us
The Fovea-The holding zone for the Eye’s “cones” to detect specific color and daylight
The Retina-The holding zone for the Eye’s “rods” to detect dark matter and peripheral vision
Blind Spot-The part of the Eye that contains no visual receptors.
Optic Nerve- Carries messages and neural impulses from your Eye to your Brain.
which is amplitude, which is pitch, and which is frequency?
a. The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time, Determines the pitch we experience, Measured in hertz
b. The height of sound waves, Determines their perceived loudness
c. The degree of highness or lowness of a tone, Low frequency = low _____, high frequency = high ____
a = frequency (The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time, Determines the pitch we experience, Measured in hertz)
b = amplitude (The height of sound waves, Determines their perceived loudness)
c = pitch (The degree of highness or lowness of a tone, Low frequency = low pitch, high frequency = high pitch)
receives and processes smell information from the olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity, acting as the first stage of olfactory processing
a. olfactory bulb
b. olfactory epithelium
c. olfactory cortex
olfactory bulb
The theory that the spinal cord contains a neurological “gate” that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain. The “gate” is opened by the activity of pain signals traveling up small nerve fibers and is closed by activity in larger fibers or by information coming from the brain
gate control theory
Which of the following best illustrates Weber´s Law?
(a) A person can easily hear a faint whisper in a quiet room, but struggles to hear it in a noisy room.
(b) A person notices a 50-cent increase in the price of a candy bar more readily than a 50-cent increase in the price of a car.
(c) A person's sensitivity to a constant stimulus decreases over time.
(d) A person's ability to detect a light stimulus is influenced by their expectations.
(e) A person's perception of a stimulus is influenced by their current emotional state.
(b) A person notices a 50-cent increase in the price of a candy bar more readily than a 50-cent increase in the price of a car.
**Weber´s law states that the larger the original stimulus, the larger the change needed to notice a difference.
a theory of color vision that suggests the human eye has three types of cones, each sensitive to different wavelengths of light (red, green, and blue). These cones work together to create our perception of any color
trichromatic theory

Hyrum is at a concert when a flute player hits a very high note at the end of a song. Which of the following best explains why the pitch of the note sounds so high?
A) It has a long wavelength and high frequency.
B) It has a short wavelength and high frequency.
C) It has a long wavelength and low frequency.
D) It has a large amplitude.
B) It has a short wavelength and high frequency.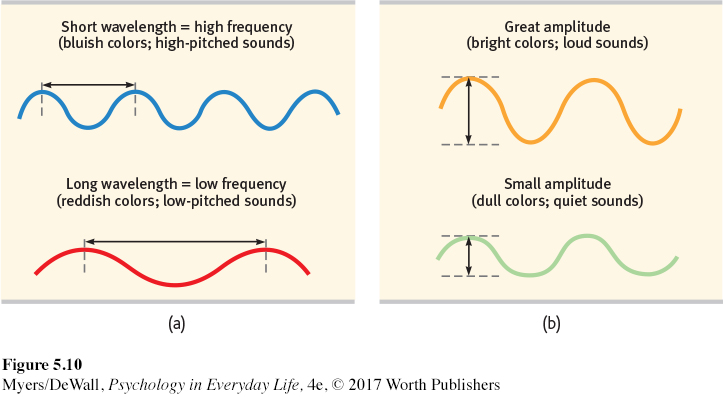
Name the different types of taste
Sweet-Energy Source
Salty-Sodium is essential to physiological processes
Sour-Potentially a toxic acid
Bitter-Potentially poisons
Umami-Proteins that grow and repair tissue
Oleogustus-Fats for energy, insulation, and cell growth
both kinesthetic sense and vestibular sense are crucial for body movement and spatial orientation.
which focuses on sensing the body's position and movement? which primarily contributes to balance and spatial orientation, using structures in the inner ear?
kinestetic sense: focuses on sensing the body's position and movement
vestibular sense: primarily contributes to balance and spatial orientation, using structures in the inner ear
What is the difference between the difference threshold (also known as the just noticeable difference) and Weber´s law?
- The difference threshold (just noticeable difference) is the minimum detectable change (ex: noticing the difference between two weights, two sounds, or two lights)
- Weber's Law describes how that minimum detectable change relates to the original stimulus intensity (ex: it is easier to notice a small increase in weight when you are lifting with 10 pounds compared to lifting with 100 pounds)
A classic example is afterimages, where staring at a color and then looking at a blank surface causes the perception of the opposite color. For example, staring at a yellow dot and then looking away will result in a blue afterimage
opponent-process theory: we perceive color in terms of opposing pairs (red/green, blue/yellow, black/white), with only one color of each pair being perceived at a time
What parts make up the outer ear?
What parts make up the middle ear?
What parts make up the inner ear?
outer ear: pinna and ear canal
middle ear: eardrum, hammer, anvil, and stirrup
inner ear: cochlea
Odor is smelt & received by our Olfactory Receptor, then moves into the →___________ then → processed through our ______________ reaching our brain’s Limbic System to determine our memory, learning, and emotions.
Odor is smelt & received by our Olfactory Receptor, then moves into the →_OLFACTORY BULBS___ then → processed through our _OLFACTORY CELLS/SMELL CORTEX reaching our brain’s Limbic System to determine our memory, learning, and emotions.
Certain spots of our skin are especially sensitive to:
1. pressure
2. warmth
3. cold
4. pain