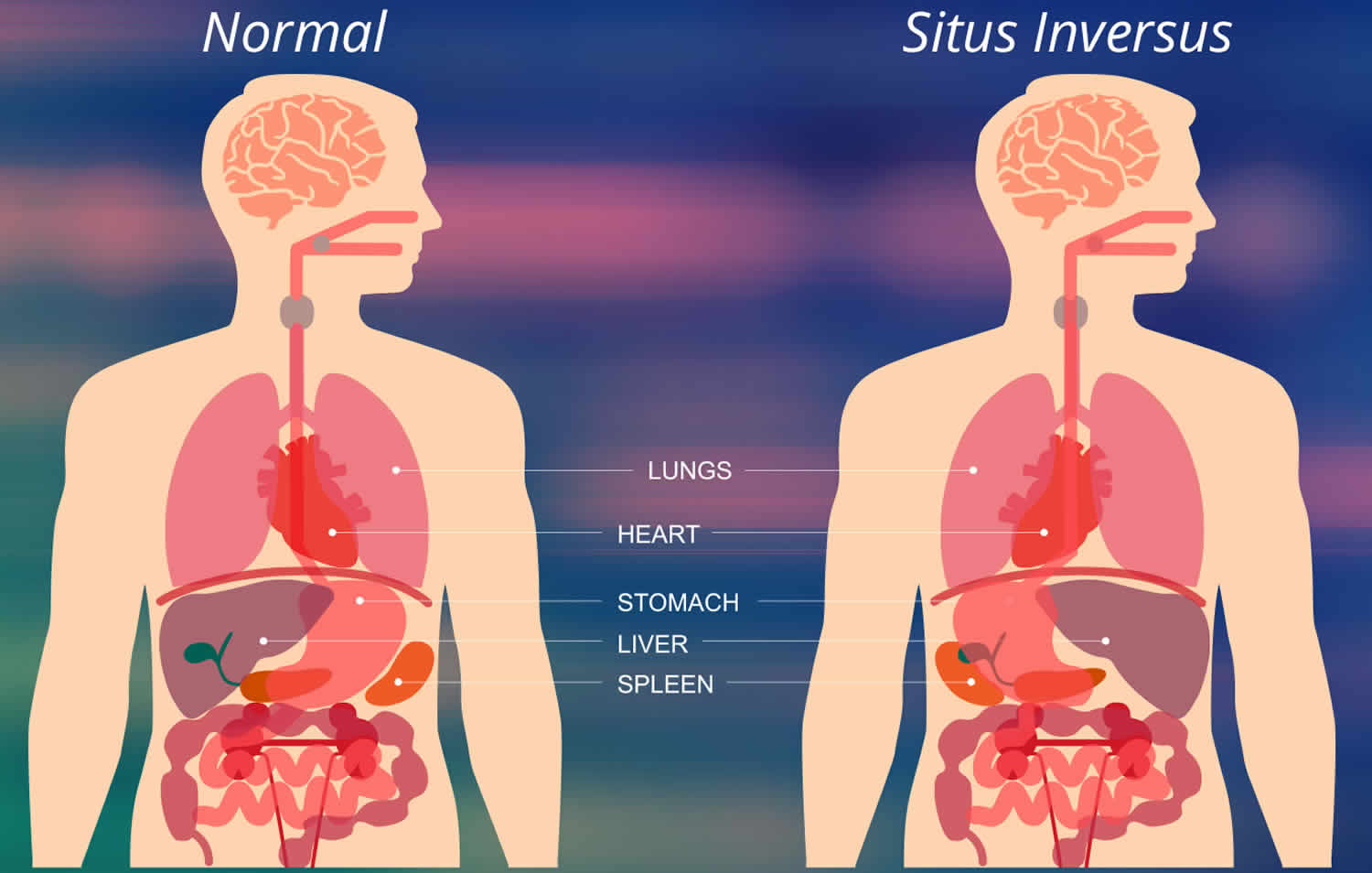
What's the mistake in the Scrubs intro?
They flipped the X Ray.
(Or the patient has situs inversus)
Word referring to the ability of a study to detect a true difference between two treatment groups
Power

Protein that protects the lower airways from damage by elastase
Alpha-1 antitrypsin
People with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency usually develop the first signs and symptoms of lung disease between ages 20 and 50. The earliest symptoms are shortness of breath following mild activity, reduced ability to exercise, and wheezing. Approximately 15 percent of adults with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency develop liver damage (cirrhosis) due to the formation of scar tissue in the liver
Term applied to neuroendocrine tumors originating in the digestive tract
Carcinoid tumor
Recommended treatment of early localized Lyme disease in pregnancy
Amoxicillin or Cefuroxime

Brugada Pattern
pseudo-right bundle branch block and persistent ST segment elevation in leads V1 to V2.
Brugada Pattern:EKG pattern w/o symptoms
Brugada Syndrome: EKG pattern with common symptoms (sudden cardiac arrest, syncope, nocurnal agonal respirations)
Term for number of new cases of disease divided by the population
Incidence


Name this finding
Pleural Plaques
Frequency of colonoscopy in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease
Annually
Condition characterized by fever, hypotension, diffuse erythroderma, and multiple organ involvement
Toxic shock syndrome
"Tumor Plop" is the name for mid-diastolic auscultatory finding associated with what growth?
left atrial myxoma
Benign myxomas are the most common tumors arising in the left atrium. May not metastasize, but may embolize with neurologic symptoms.
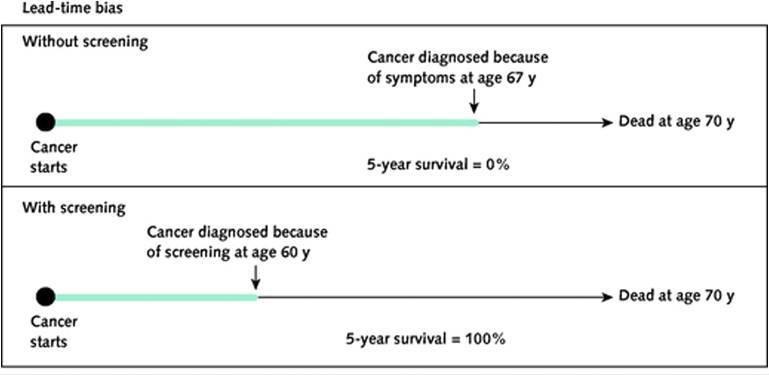
Type of bias due to early detection of disease without change in eventual mortality
Lead time bias
Two highest-risk conditions for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Atopic asthma and cystic fibrosis
Asthmatic patients may develop IgE sensitivity to molds including A. fumigatus. In patients with CF, growth of A. fumigatus hyphae within the bronchial lumen triggers an immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated hypersensitivity response that results in airway inflammation, bronchospasm, and bronchiectasis. Prevalence is about 8.9%
Excluding hepatitis B DNA, three serological markers associated with the early phase of hepatitis B infection
HBsAg, HbeAg, IgM Anti-HBc (accept anti-HBc)
The antibodies and antigen assessed by the 4th generation HIV test
HIV 1 and HIV 2 antibody and HIV p24 antigen (all three required)
Pain radiating to this location is associated with highest likelihood of MI
Right arm or shoulder
A systematic review of 64 published studies and one unpublished study (N not reported) reviewed bedside diagnosis of MI in adults presenting to the emergency department with chest pain unrelated to trauma and unexplained by radiography.1 The diagnosis of acute MI was determined by elevated cardiac isoenzymes and electrocardiography (ECG) changes. Factors that most reliably predicted acute MI were pain radiation to the right arm or shoulder (sensitivity = 15% to 41%; specificity = 94% to 95%; positive likelihood ratio [LR+] = 4.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.9 to 12)
Name of this statistical formula for calculating conditional probability
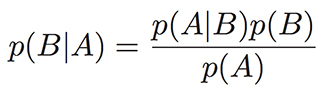
Bayes' Theorem (accept Bayes' Law, Bayes' Rule, Bayesian Analysis)
Conditional probability is the likelihood of an outcome occurring, based on a previous outcome occurring.
Treatment for insomnia involving limiting and then gradually increasing the time in bed for sleep
Sleep restriction
Sleep restriction therapy works by limiting the total time allowed in bed, including naps and other sleep periods outside of bed, in order to increase the drive to sleep [31]. This consolidates sleep and improves sleep efficiency (the percentage of time in bed that the patient is asleep).
Sleep restriction therapy begins by decreasing the time spent in bed to the same amount of time that the patient reports sleeping (usually determined from sleep diaries or logs completed by the patient), but not less than five hours per night (table 4). On a daily basis, the patient reports the amount of sleep obtained the previous night and the amount of time spent in bed. The clinician then computes the sleep efficiency, which is the reported time asleep divided by the reported time in bed. The time in bed is increased by 15 to 30 minutes once the sleep efficiency exceeds 85 percent. This process is repeated until the patient reports improved sleep without residual daytime sleepiness. However, total time in bed for some patients can remain at six hours or less for long periods of time. Naps are not permitted.
The most commonly used ablative therapy for Barrett's esophagus with high grade dysplasia
Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation (accept radiofrequency ablation or RFA)
Clinical syndrome associated with "sandpaper" rash and "strawberry tongue"
Scarlet Fever
Congenital cardiac condition that may cause platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome
Patent foramen ovale
platypnea - SOB worsened by being upright
orthodeoxia - decrease in arterial oxygen tension or arterial hemoglobin desaturaton >5% when patient moves from supine to upright position
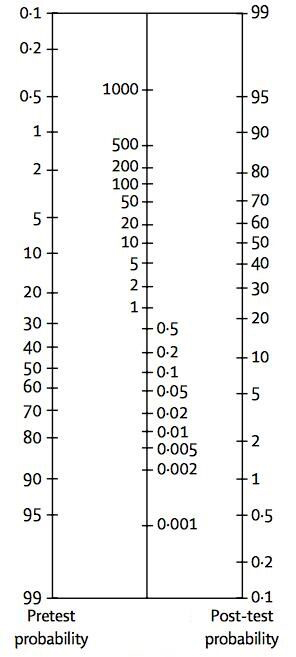
Name this nomogram used to interpret likelihood ratios
Fagan Nomogram
Likelihood ratios (LR) are used to assess two things: 1) the potential utility of a particular diagnostic test, and 2) how likely it is that a patient has a disease or condition. LRs are basically a ratio of the probability that a test result is correct to the probability that the test result is incorrect.
Pleural fluid to serum (PF/S) creatinine ratio greater than 1 is supportive and greater than 1.7 is diagnostic of WHAT diagnosis?
Urinothorax

Urinothorax is the presence of the urine in the pleural space. This condition is very rare and occurs due to unrelieved obstruction of urinary flow.
A 20-year-old female presented 7 days after cesarean section with tachypnea, and generalized abdominal pain. There was absent air entry over the left hemithorax. CT scan showed massive left pleural effusion and a stone obstructing the renal pelvis with hydronephrosis and peri-renal collection. The pleural fluid had high fluid creatinine level suggesting urine collection. Ureteroscopy done and double J catheter inserted.
Imaging study used to evaluate the anatomical and functional changes of the anorectum
Defecography (accept MR defecography or defecating proctogram)
Preferred antibiotic treatment of traveler's diarrhea for travelers to Asia
Azithromycin