lining: closely apposed cells, acts as a cover
glandular: invagination or aggregation of cells that forms a solid tissue structure
types of epithelium and their function
surface attached to basement membrane
basilar
bone is composed of
primary extracellular matrix and cells
osteocytes are connected by
canaliculi
This tissue provides structural and mechanical support for other tissues as well as meditates the exchange of waste and nutrients between circulation and other tissues
connective tissue
surface farthest from basement membrane
apical
True or false, Collagen fibers are inelastic
true
squamous, cuboidal, columnar and urothelium
the type of epithelium that lines the bladder
urothelium
bones can can only grow in layers and not from within which is known as
appositionally
the layer on the inside surface of trabecular bone
endosteum
synthesize collagen and ground substance of the extracellular matrix
fibroblasts
The words tight, gap, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes are used to describe
the 4 types of cellular connections epithelium make.
represent an adaptive immune response in tissue
Leukocytes
the type of glands release chemical substances directly into the bloodstream or tissues of the body
endocrine glands
These glands release chemical substances through ducts to outside the body or onto another surface within the body
exocrine
osteoblasts come from
mesenchymal stem cells in periosteum
the histological appearance of this bone is dense regular/parallel collagen arrangement; few osteocytes; osteoblasts lining surface
lamellar bone
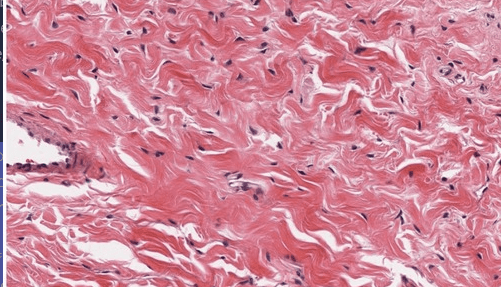
attaches bones to bones and muscles to bones and also found in the dermis of the skin - appears to be closely packed collagen fibers with interspersed fibroblasts and fibrocytes
dense fibrous connective tissue
these two components make up all connective tissue
cells and extracellular matrix
phagocytose foreign material in the tissue layer
Marcophages
simple squamous epithelium known as serosa or mesothelium cover
internal organs
this simple squamous epithelium lines blood vessels
endothelium
these are bone destroying cells that are responsible for reabsorbing inorganic material from bones and bone maintenance
Osteoclasts
These are the two coverings of bones
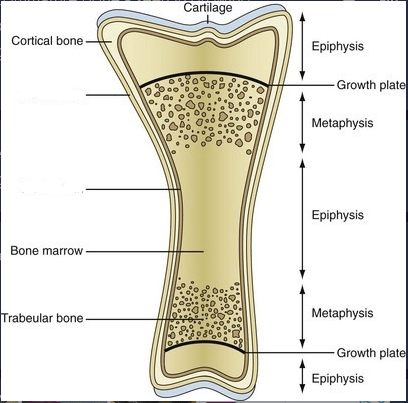
periosteum and endosteum
release large amounts of histamine and enzymes in response to antigen recognition
Mast Cells
this determines the permeability of collagen
amount of ground substance
The microscopic appearance of connective tissue can be divided into two forms:
fibrous or embryonic
Epithelial cells that do not produce and secrete extracellular products - acts as a covering - seen in skin, urinary bladder, esophagus
non-glandular function
Flattened, wider than they are tall - two types (endothelium and mesothelium) - can be found in blood vessels or on the outside of the organs
simple squamous epithelium
process in which the bone changes shape - seen during time of disease and development - two step process (resorption and production)
modeling
process in which "old" bone is replaced by new bone - bone does not change shape - allows bone turnover at osseous envelopes while still maintaining its shape - happens in the same four step sequence
remodeling
Type III collagen is found in
reticular fibers, healing wounds, smooth muscle and fetal skin
cells in the uppermost layer of stratified squamous epithelium lose their nuclei and organelles and leave behind the keratin; forms a waterproof barrier
the process of cornification
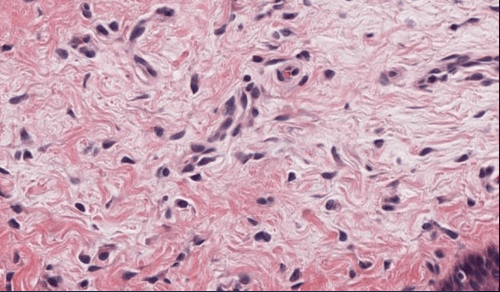
Tissue that binds epithelia to underlying tissues and holds organs in place - representing a network of type I collagen and reticulin fibers with interspersed ground substance, cells, and blood vessels
loose connective tissue
the four ways to classify epithelium
number of layers of the cells, shape of the cells at the free surface, function of the epithelium (glandular vs non-glandular), surface modifications
this represents what type of epithelium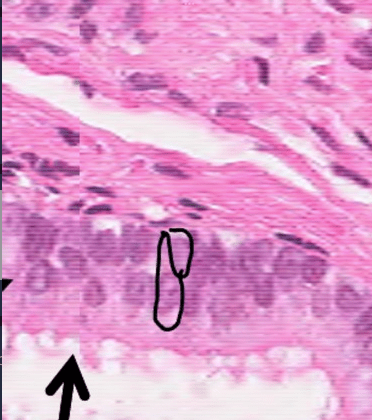
psuedostratified columnar
The two mechanisms by which bones grow
Membranous ossification and endochondral ossification
These are known as:
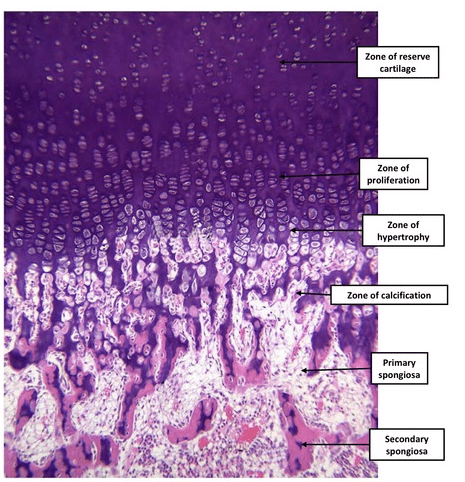
Zones of Physis
________ form supporting frameworks for the liver, lymphoid organs, capillary endothelia and muscle fibers.
reticular fibers
the gelatinous substance responsible for determining the permeability of connective to solutes an proteins
Ground Substance
connective tissue is comprised of these four cells
Fibroblasts, macrophages, leukocytes, adipose cells