This is a ________ fault. (Esta es una falla ________.)
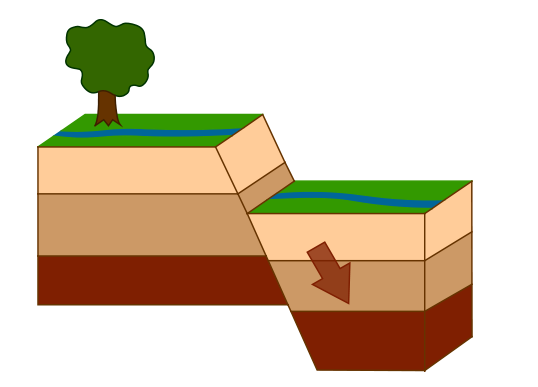
What is a normal fault?
¿Qué es una falla normal?
These are the two types of seismic waves.
Estos son los dos tipos de ondas sísmicas.
What are primary waves and secondary waves?
OR
What are P-waves and S-waves?
¿Qué son las ondas primarias y las ondas secundarias? O ¿Qué son las ondas P y las ondas S?
There tends to be little volcanic activity at which type of tectonic plate boundary?
¿En qué tipo de límite de placa tectónica tiende a haber poca actividad volcánica?
What is a transform boundary?
OR what is a fault?
¿Qué es un límite de transformación? O ¿qué es una falla?
Name the two types of volcanic glass we discussed in class. (No partial credit.)
Nombra los dos tipos de vidrio volcánico que comentamos en clase. (Sin crédito parcial).
What are obsidian and pumice?
¿Qué son la obsidiana y la piedra pómez?
Flood basalts & shield volcanoes have this relative amount of volatiles.
Los basaltos de inundación y los volcanes en escudo tienen esta cantidad relativa de volátiles.
What is low?
¿Qué es bajo?
Compressional waves describe the movement of this kind of seismic wave.
Las ondas de compresión describen el movimiento de este tipo de ondas sísmicas.
What are P-Waves?
OR what are primary waves?
¿Qué son las ondas P? O ¿qué son las ondas primarias?
This is what you should do (for yourself) when you know a tsunami is approaching.
Esto es lo que debes hacer (por ti mismo) cuando sabes que se acerca un tsunami.
What is get to higher ground?
¿Qué es llegar a un terreno más alto?
Hawaiian and Icelandic types of effusive eruptions have this relative level of water content.
Los tipos de erupciones efusivas hawaianas e islandesas tienen este nivel relativo de contenido de agua.
What is low?
¿Qué es bajo?
Big pyroclastic fragments that are solid, white, and airborne, coming from volcanic eruptions, are called this name.
Con este nombre se denominan grandes fragmentos piroclásticos sólidos, blancos y suspendidos en el aire, procedentes de erupciones volcánicas.
What are blocks?
¿Qué son los bloques?
The slowest lava flow & not much volatility will make this volcanic landform, usually inside a crater.
El flujo de lava más lento y no mucha volatilidad formarán este relieve volcánico, generalmente dentro de un cráter.
What is a lava dome?
¿Qué es una cúpula de lava?
This is a ________ fault. (Esta es una falla ________.)
What is a reverse fault?
¿Qué es una falla inversa?
This is the actual physical location that an earthquake starts underground.
Esta es la ubicación física real donde comienza un terremoto bajo tierra.
What is the focus?
¿Cuál es el enfoque?
Name the Three Vs of Volcanology. (No partial credit, but can be in any order.)
Nombra las tres V de la vulcanología. (No hay crédito parcial, pero puede ser en cualquier orden).
What are viscosity, volatiles, and volume?
¿Qué son la viscosidad, los volátiles y el volumen?
Name the three types of lava we discussed in class. (Partial credit is allowed.)
Nombra los tres tipos de lava que discutimos en clase. (Se permite crédito parcial).
What are pahoehoe (pronounced "pah-HOY-HOY"), a'a (pronounced "ah-ah"), and pillow lava?
¿Qué son pahoehoe (pronunciado "pah-HOY-HOY"), a'a (pronunciado "ah-ah") y almohada de lava?
High viscosity & a high level of volatiles will result in this kind of volcanic landform.
Una alta viscosidad y un alto nivel de volátiles darán como resultado este tipo de relieve volcánico.
What is a caldera?
¿Qué es una caldera?
The Mercalli scale is a rating of this quality.
La escala Mercalli es una calificación de esta calidad.
What is earthquake damage (in a given region)?
¿Qué es el daño por terremoto (en una región determinada)?
This is the general type of fault least likely to trigger a tsunami. (It's still possible, just not as likely as the other two general types of faults.)
Este es el tipo general de falla que tiene menos probabilidades de provocar un tsunami. (Aún es posible, pero no tan probable como los otros dos tipos generales de fallas).
What is a strike-slip fault?
¿Qué es una falla de deslizamiento?
A Plinian eruption has this level of viscosity.
Una erupción pliniana tiene este nivel de viscosidad.
What is high?
¿Qué es alto?
Pyroclastic air-fall fragments that are the size of flour particles or sand grains can be referred to as this.
Se puede denominar así a los fragmentos piroclásticos de caída de aire que tienen el tamaño de partículas de harina o granos de arena.
What is ash?
¿Qué es la ceniza?
Medium viscosity & medium volatiles, plus a large volume of eruption material, give you this type of volcanic landform.
La viscosidad media y los volátiles medios, además de un grande volumen de material de erupción, le dan este tipo de relieve volcánico.
What is a stratovolcano?
OR what is a composite volcano?
¿Qué es un estratovolcán? O ¿qué es un volcán compuesto?
This is how much more intense an 8.0 magnitude earthquake is compared to a 4.0 earthquake on the Richter scale.
Así de intenso es un terremoto de magnitud 8,0 en comparación con un terremoto de 4,0 en la escala de Richter.
What is 10,000 times more?
OR
What is 104 times more?
¿Qué es 10.000 veces más?
O ¿Cuánto es 104 veces más?
The following factors can influence how much damage an earthquake causes: intensity, duration of vibrations, how structures are built, and... this.
Los siguientes factores pueden influir en el daño que causa un terremoto: intensidad, duración de las vibraciones, cómo se construyen las estructuras y... esto.
What is what material structures are built upon/on/in?
¿Sobre qué material se construyen las estructuras?
This can be reduced to help generate magma and fuel volcanic eruption.
Esto se puede reducir para ayudar a generar magma y alimentar la erupción volcánica.
What is pressure?
¿Qué es la presión?
This is the key difference between volcanic tuff & volcanic breccia.
Esta es la diferencia clave entre toba volcánica y brecha volcánica.
What is texture?
OR What is types of sediments involved?
OR What is tuff is smooth and/or rounded?
OR What is breccia is coarse and/or angular?
¿Qué es la textura?
O ¿Cuáles son los tipos de sedimentos involucrados?
O ¿Qué es la toba lisa y/o redondeada?
O ¿Qué es la brecha gruesa y/o angular?
Low-to-medium viscosity, plus medium-to-high volatiles, but a small volume of eruption material... and you wind up with this volcanic landform.
Viscosidad baja a media, además de volátiles medios a altos, pero un pequeño volumen de material de erupción... y terminas con esta forma de relieve volcánica.
What is a scoria cone?
OR what is a cinder cone?
¿Qué es un cono de escoria? O ¿qué es un cono de ceniza?