Static characters do NOT do this in the course of a story, because like you know, they're static!
What is CHANGE?
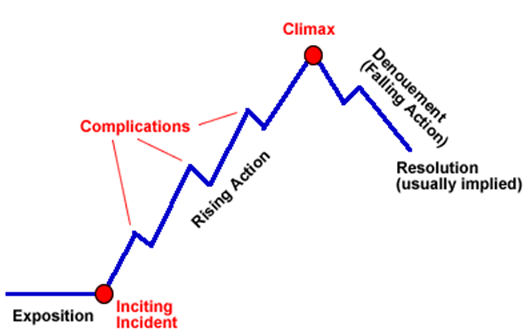
Narration often follows a structure which includes the exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
What is PLOT STRUCTURE?
A logical guess about a story based on story details and the reader's experiences.
What is an INFERENCE?
In a participant point of view, the narrator tells the story using this "person," using pronouns like "I, me, we, us, etc."
What is FIRST PERSON?
This short story term means not only physical location, but historical context and time.
What is setting?
The author makes use of these two devices in the passage--name one.
"The fire burst the house open and let it slam flat down, puffing out skirts of spark and smoke."
What is personification and imagery?
This type of character has several traits and a complex personality; they are generally dynamic.
What is a round character?
The part of the story where we are introduced to the main character(s), conflict, and setting.
What is EXPOSITION?
This literary device is used to represent something deeper and abstract.
What is a symbol?

In this point of view, the narrator "knows all"--they can relate both thoughts and deeds of ALL the characters.
What is third person omniscient?:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/third-person-omniscient-point-of-view-1277125-v4-5b87078946e0fb0025390fa6.png)
The person who tells the story
What is NARRATOR?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY: The author makes use of two devices in this passage:
"At eight-thirty the eggs were shriveled and the toast was like stone."
What is imagery and simile?
This relatively simple type of character generally has only one trait; they are often a stereotype.
What is a FLAT character?
In plot, this is when everything changes for the protagonist - either for good or for bad.
What is the climax?
This literary device does not just appeal to our sense of sight--it can be an appeal to any of the five senses.
What is IMAGERY?
Sometimes a third-person narrator does not enter characters' minds; they only relate what they see and hear.
What is third person limited point of view?
When a reader asks, "What's a universal truth about humans or human nature in this story?" they are attempting to discover this.
What is theme?
Double Jeopardy!
The author makes use of which two devices in this passage: "The fire burned on the stone hearth and the cigar fell away into a mound of quiet ash on its tray. The empty chairs faced each other between the silent walls, and the music played."
What is imagery and personification.
A character in the story who also tells the story
When the source of the problem is within the character.
What is INTERNAL CONFLICT?
When an author exaggerates to emphasize a point or create humor.
What is a HYPERBOLE?
The way the story is told in this passage:
"I ain't gonna let you take that quilt from Maggie," I said. "She's gonna put it to 'everyday' use!"
What is first person point of view?
When we know something that other characters in the story don't know.
Example: Before any of the other characters know, we know that Miss Strangeworth is the author of the nasty letters to townsfolk.
What is dramatic irony?
Language that communicates meaning beyond the literal meanings of words to create effects, emphasize ideas, or evoke emotions.
What is FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE?
Information (STEAL - character's Speech, Thoughts, Effect on others, Actions, or Looks) that an author gives us about a character.
What is INDIRECT characterization?
This word is often the reason that characters do / say the things that they do / say and it's the "why" of a story.
What is MOTIVATION?
When what happens contrasts with what the characters in the story expect.
What is DRAMATIC IRONY?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY:
The most casual point of view that most writers do not use.
What is second person?
A contrast between what the reader expects and what actually happens.
Example: The reader expects the house in "There Will Come Soft Rains" to be able to extinguish the fire.
What is situational irony?
The author utilizes this device to build suspense in the story.
What is FORESHADOWING.