What is the purpose of the shoulder girdle?
Are there any joints that are more mobile than the shoulder (glenohumeral joint)?
What joints makes up the shoulder?
What bones makes up the shoulder girdle?
What bones make up the shoulder joint?
The purpose of the shoulder girdle and the entire upper extremity is to allow the hand to be placed in various positions to accomplish the multitude of tasks it is capable of performing.
The shoulder (glenohumeral joint) is the most mobile joint in the body. However, motion happens in other joints to allow this to happen.
Sternoclavicular (SC) Joint
Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint
Glenohumeral (GH) Joint
Scapulothoracic Joint
Shoulder Girdle: scapula and clavicle
Shoulder Joint: scapula and humerus
SCAPULOHUMERAL RHYTHM
Describes what?
What happens at the first 30 degrees of motion?
For every __ degrees of shoulder flexion/abduction scapula upwardly rotates __ degree.
Further describes movement relationship between shoulder girdle and shoulder joint (scapula and humerus)
First 30 degrees: Just shoulder joint (GH) motion
After that,
for every 2 degrees of shoulder flexion/abduction
scapula upwardly rotates 1 degree
This 2:1 ratio => Scapulohumeral rhythm
ADLS STANDS FOR?
Activities fundamental for what?
examples?
What are some AD?Ls which may be affected by a shoulder joint or shoulder girdle injury?
Basic tasks “concerned with daily self-care”
• Activities oriented toward taking care of one’s own body
• Activities fundamental to living in a social world; they enable basic survival and
well-being, such as bathing, toileting, dressing and eating
SHOULDER COMPLEX!
Please list all the anatomical structures involved :)
Scapula
Clavicle
Sternum
Humerus
Rib cage
SC Joint
AC Joint
GH Joint
ST articulation
MUSCLES OF THE SHOULDER GIRDLE
Muscles with greater vertical line of pull will perform what of the scapula?
Muscles with greater horizontal line of pull will perform what of the scapula?
5 muscles primarily responsible for moving the scapula...
Muscles with greater vertical line of pull will perform elevation, depression of scapula
Muscles with greater horizontal line of pull will perform protraction, retraction of scapula
5 muscles primarily responsible for moving the scapula:
Trapezius
Upper, middle, lower
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboids
Major and minor
Serratus Anterior
Pectoralis Minor
• Which rehabilitation professional handles these the most?
• How are ADLs handled differently in different settings? in-patient vs out-patient
• Hospital
• Home Health
• SNF
• Outpatient orthopedics
1.Occupational therapist
• Hospital- special equipment
• Home Health-Focus on exactly how they do things
• SNF- Sometimes you work with people 3 hours a day, low level actives.
• Outpatient orthopedics
SHOULDER
GIRDLE
MOTIONS
List them all please :)
What 2 joints allow for these motions of the shoulder girdle?
AC and SC joints allow the following
motions of the shoulder girdle:
Elevation/ Depression
Protraction/ Retraction
Upward & Downward rotation
Anterior and posterior tilt
IADS
Stands for?
Often requires what?
examples?
• Instrumental Activities of Daily Living
• Activities to support daily life within the home and community that often require more complex interactions than those used in ADLs
• financial management
• housekeeping
• shopping for groceries
• making phone calls
• taking medication
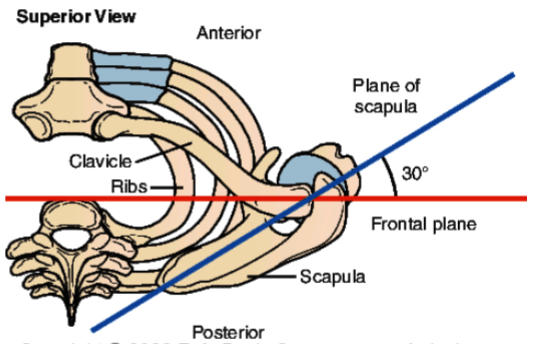
PLANE OF THE SCAPULA
What is a scaption?
Scaption:
Movements of the shoulder joint that occur in the scapular plane
~30 degrees forward from frontal plane
ADLS AND IADLS
Older adults experience ADL and IADL disabilities through what two pathways?
Performance in ADL and IADLs indicate and predict what?
• Older adults experience ADL and IADL disabilities through two pathways:
1) a catastrophic event, such as a hip fracture
2) progressive decline in the brain functions
• Successful performance in ADL and IADLs are significant health indicators that can predict mild cognitive impairments, dementia, and mortality in older adults
SCAPULA
What shape is this bone?
How does the scapula attach to the trunk?
Slightly ______ and glides over the ______
rib cage posteriorly
In resting position the scapula is located between what ribs?
What angle is the reference point to describe scapular movement?
When the scapula moves this changes the position of what fossa?
Triangular shaped bone
Attaches to the trunk indirectly through
ligamentous attachment -> clavicle ->sternum
Slightly concave and glides over the convex
rib cage posteriorly.
In the resting position, located between the
2nd and 7th ribs with 2-3 inches between its
medial border and the spinous processes of T/S
Spine of scapula ~T3,4
Inferior angle is the reference point when
describing scapular movement
When scapula moves, this changes position
of glenoid fossa
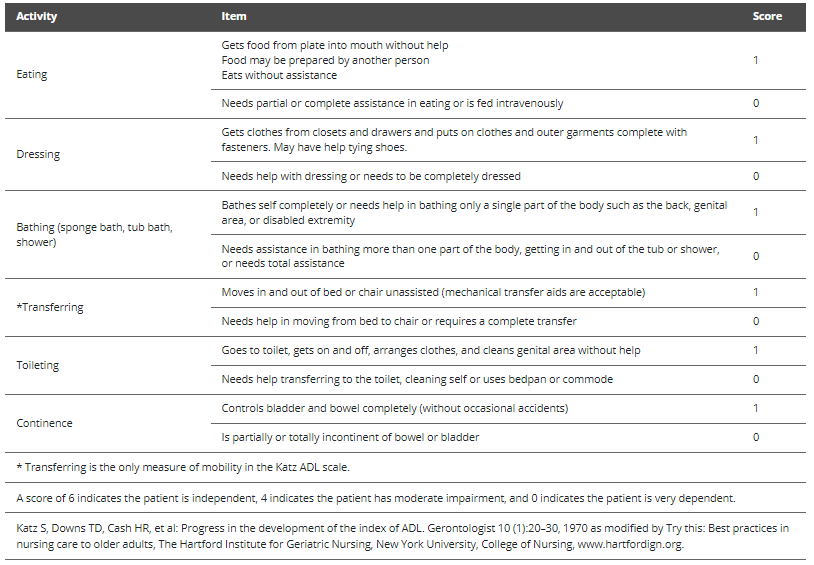
KATZ INDEX OF ADL
6=?
4=?
0=?
Example of one type of measure to assess basic ADL function
• A score of:
• 6 = patient is independent
• 4 = patient has moderate impairment
• 0 = indicates the patient is very dependent
SCAPULAR WINGING
What direction does the medial border of the scapula move?
Movement occurs in what plane? what axis?
Medial border of scapula moves posteriorly, away from thoracic cage.
Movement occurs within horizontal plane about a vertical axis.
OUTCOME ASSESSMENT AND
INFORMATION SET (OASIS)
Primarily used in what setting?
Comprehensive screening tool reflecting what?
• Primarily used in home health setting
• Comprehensive screening tool reflecting quality of life concerns
• Includes ADL, self-performance, disease diagnosis, and activity pursuits
• Assesses
• Socioeconomic factors
• Living arrangement
• Cognition
• Nutritional status
• Medication management
• Judgement for safety in home
CLAVICLE
What shape is this bone?
Connects to the UE to the axial skeleton via what joint?
Also attaches the scapula to what joint?
S-shaped bone
Connects upper extremity to the axial skeleton at the SC joint
Also attaches to the scapula at the AC joint
MINIMUM DATA SET (MDS)
Used at what kind of facility?
Assesses what?
MINIMUM DATA SET (MDS)
• Comprehensive screening tool reflecting quality of life concerns in a skilled nursing facility (SNF)
• Includes ADL, self-performance, disease diagnosis, and activity pursuits
• Assesses psychometric variables
• Depression
• Cognition
• Problem solving
• Learning
STERNUM
Bone shape?
Located in the midline of the .....
At its superior end it attaches to clavicle via what joint?
It also attaches to what cartilage of the rib?
What are the 3 parts of the sternum?
Flat bone
Located in the midline of the anterior thorax
At its superior end it is attached to the clavicle at the SC joint
Attaches to the costal cartilages of the ribs at the body
3 parts:
Manubrium
Body
Xiphoid process
THE INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF
FUNCTIONING, DISABILITY AND HEALTH
(ICF)
A framework for describing what?
What does the ICF provide?
ICF recognizes the role of what factors in the creation of disability? As well as the relevance of the effects of what?
• A framework for describing and organizing information on functioning and disability.
• It provides a standard language and a conceptual basis for the definition and measurement of health and disability.
• The ICF integrates the major models of disability.
• It recognizes the role of environmental factors in the creation of disability, as well as the relevance of associated health conditions and their effects.
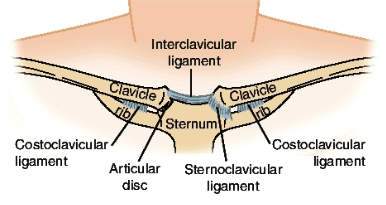
STERNOCLAVICULAR JOINT
How many ligaments?
Joint disk have a double attachment (like a double hinge door) that allows for what?
Synovial joint = Joint capsule
3 ligaments
Joint’s disk has a double attachment much like that of a double hinge door that can swing in 2 directions.
Minimal motion at SC joint contributes to large motion of shoulder girdle.
ARTHROKINEMATIC
&
OSTEOKINEMATIC
CHARACTERISTICS

SC JOINT-LIGAMENTS
3 ligaments...
One connects the clavicle to the sternum..
One connects the inferior clavicle to the superior costal cartilage of the first rib...
One connects the superior sternal ends of the clavicles.
Sternoclavicular:
Connects the
clavicle to the
sternum both ant.
& post.
Costoclavicular:
Connects inferior
clavicle to superior
costal cartilage of
1st rib
Interclavicular:
Connects superior
sternal ends of the
clavicles.
ACROMIOCLAVICULAR (AC) JOINT
What 2 structures make up this joint?
What kind of joint is this?
Movement of AC joint accompany WHAT JOINT to increase ROM of scapula, mostly upward rotation?
Articulation of acromion process of
the scapula and the lateral end of
clavicle
Plane synovial joint
Movement of AC joint accompany SC
joint to increase ROM of scapula,
mostly upward rotation
AC JOINT LIGAMENTS
Connects what to what?
What kind of joint?
How many planes of motion?
Weak joint capsule reinforced by what 2 accessory
ligaments?
Acromioclavicular Ligament:
Connects the acromion process of the scapula with the lateral end of the clavicle.
Plane-shaped synovial joint
3 planes of motion
Weak joint capsule reinforced by 2 accessory
ligaments.....
AC JOINT – ACCESSORY LIGAMENTS
The coracoclavicular ligament connects what to what?
The Coracoacromial ligament connects what to what?
Coracoclavicular:
Connects inferior surface of
lateral end of clavicle to the
superior surface of the
coracoid process.
Coracoacromial:
Forms an arch over the
head of the humerus.
Attaches on the superior
lateral coracoid process to
inferior surface of the
acromial process.
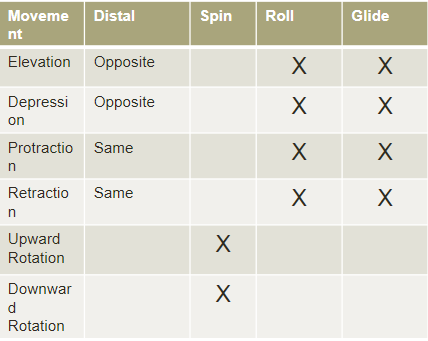
COMPANION MOTIONS SHOULDER JOINT & SHOULDER GIRDLE
What are the linear movements?
What are the angular movements?
Which can happen without the humorous moving?
Linear movements (elevation/depression, protraction/retraction):
Can occur without shoulder joint (humerus) motion
Angular movements (upward/downward rotation, anterior/posterior
tilt):
Motions must accompany shoulder joint motions
With shoulder flexion and abduction, one must have upward rotation of scapula