This bone forms the roof of the shoulder and articulates with the clavicle at the AC joint
Scapula (acromion)

This artery is a direct continuation of the subclavian artery after it passes the first rib.
Axillary artery

The supraspinatus initiates the first _ degrees of shoulder abduction
15 degrees

What root levels and peripheral nerve innervates the biceps brachii?
Musculocutaneous, C5-6
This is a condition of the shoulder characterized by functional loss of both passive and active shoulder motion commonly associated with diabetes, and thyroid disease.
adhesive capsulitis
This bony landmark of the humerus serves as the attachment for the supraspinatous tendon.
Greater tuberosity
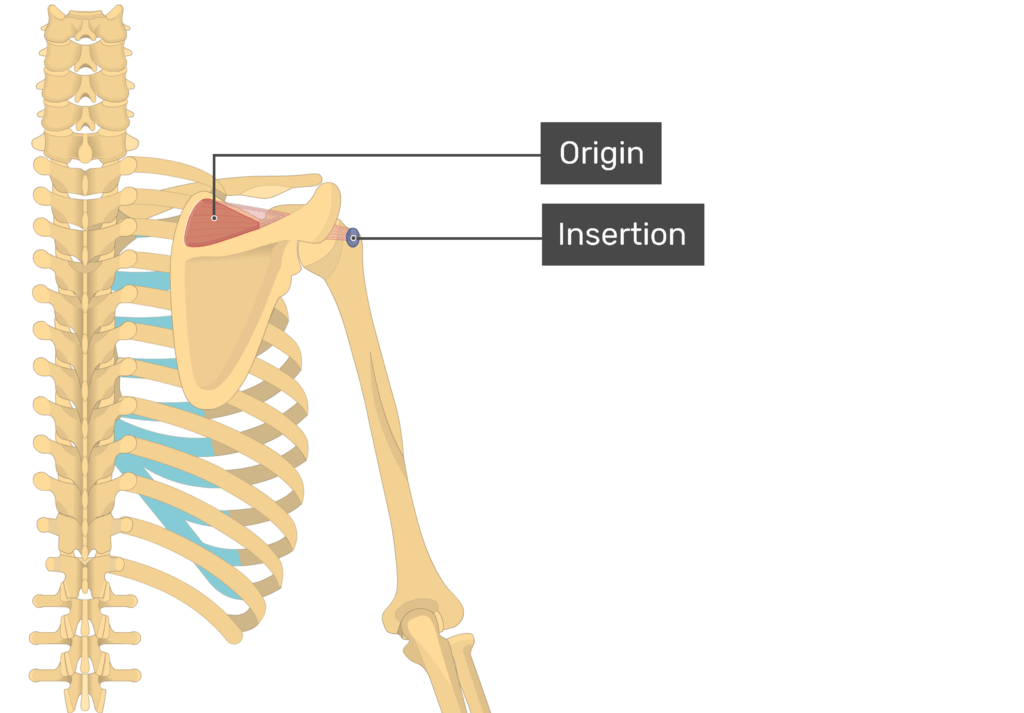
This artery supplies the deltoid and teres minor muscles and travels with the axillary nerve, passing through the quadrangular space.
Posterior circumflex humeral artery
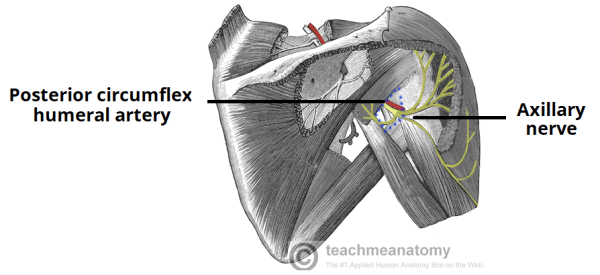
This muscle is the primary internal rotator of the shoulder and inserts on the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.
Subscapularis
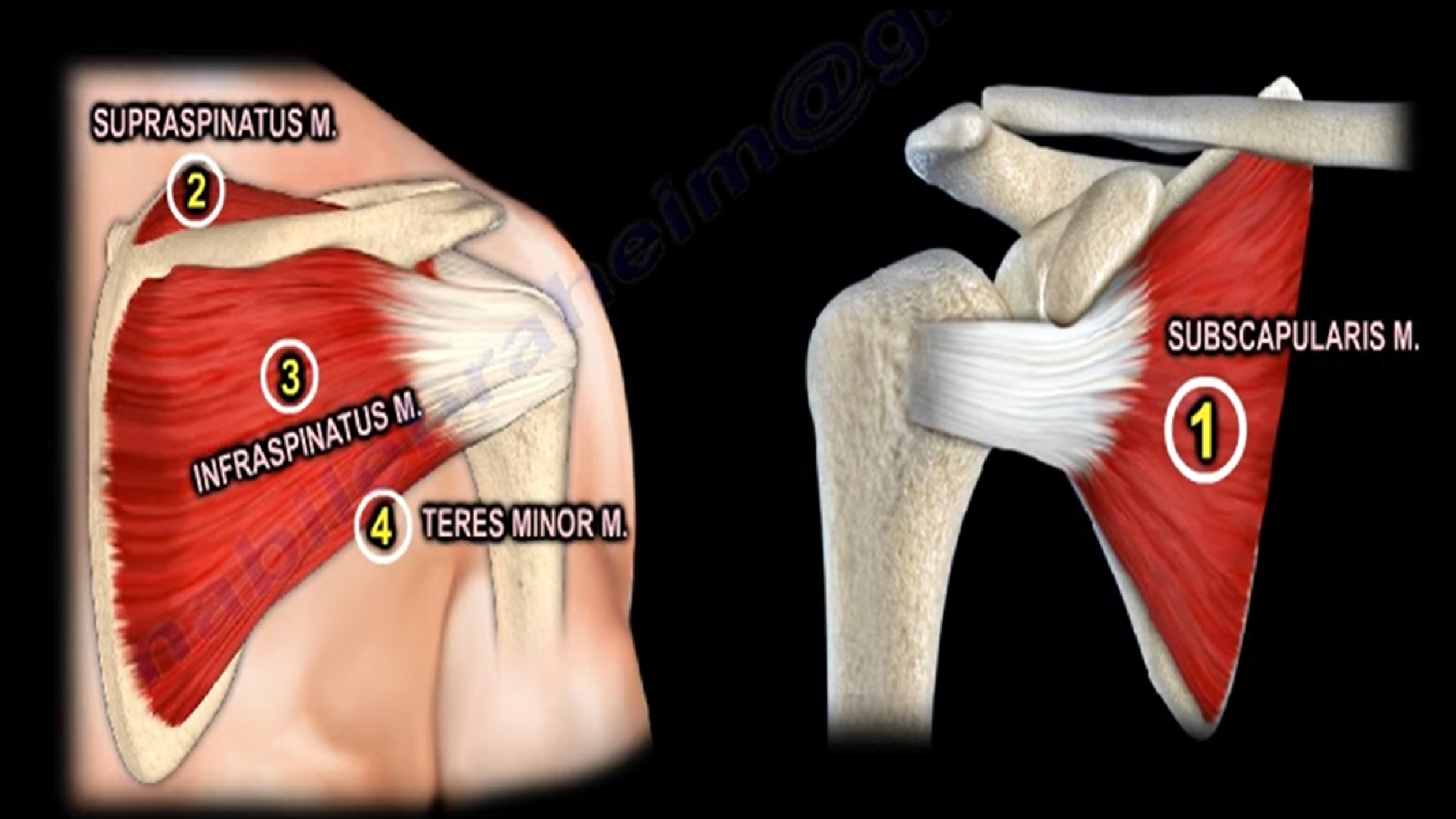
What pre-plexus muscle carries only C5 innervation? (note, some sources like PMR Recap say C4-5)
Rhomboids via the dorsal scapular nerve
A _ (injury) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and biceps tendonitis.
SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear)
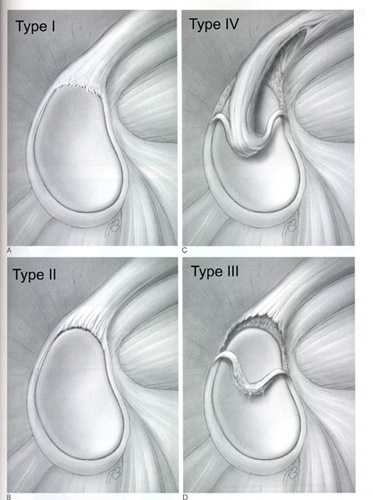
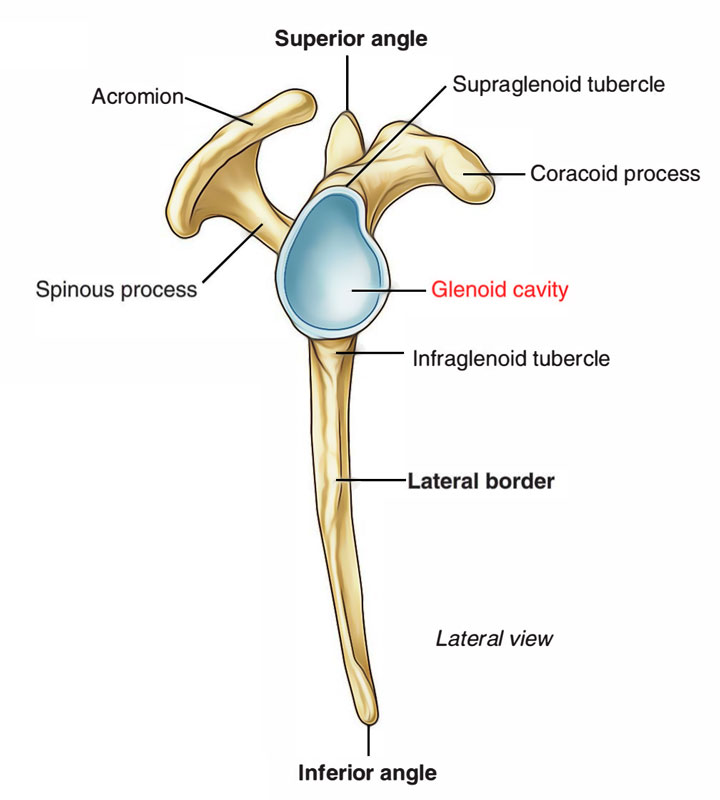
This shallow socket of the scapular articulates with the humeral head and is deepened by fibrocartilage
Glenoid (glenoid fossa/cavity)
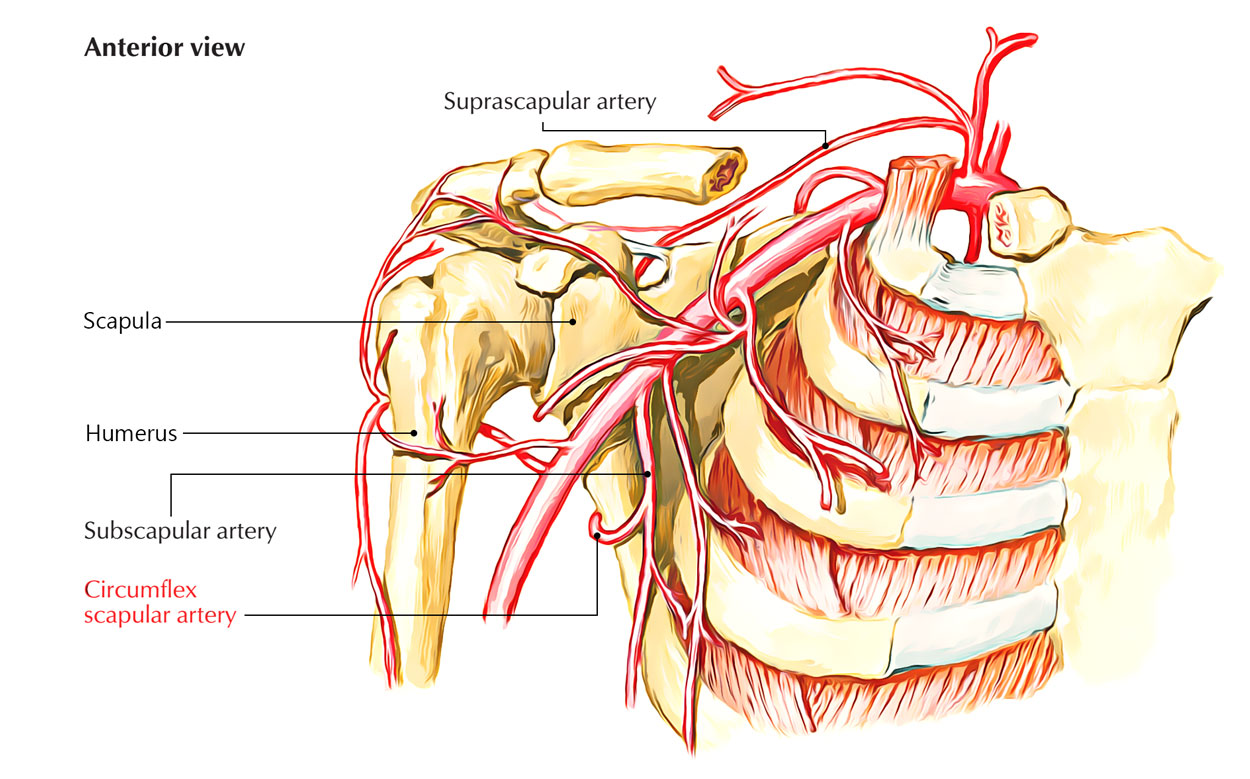
This branch of the axillary artery contributes to the scapular anastomosis and passes through the quadrangular space
Circumflex scapular artery
This muscle assists in adduction and internal rotation and forms the inferior border of the quadrangular space.
Teres major

What anatomical landmark does the suprascapular nerve pass through prior to innervating the infraspinatus?
Spinoglenoid notch
A patient presents with sudden severe shoulder pain followed by resolution of pain but the development of progressive weakness. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Brachial Neuritis aka Parsonage Turner Syndrome
This process of the scapular provides attachment for the short head of the biceps and coracobrachialis
Coracoid process
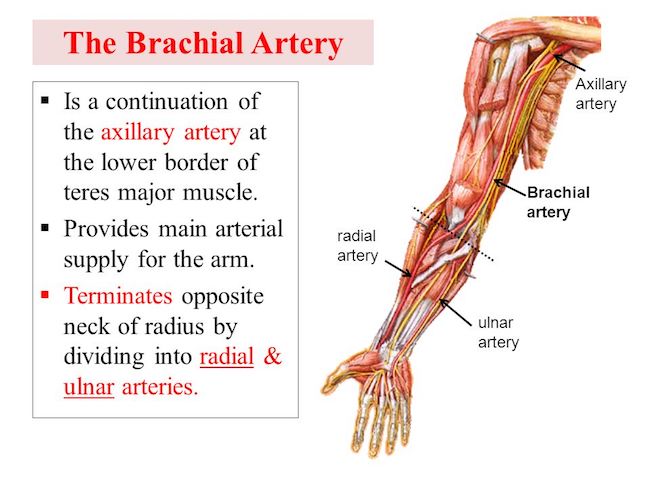
This artery originates from the axillary artery and begins at the inferior border of the teres major muscle.
Brachial artery
An injury to this muscle leads to medial scapular winging
Serratus anterior

What is the innervation pathway of the supraspinatus? Need to know: Root(s) -> trunk -> cord -? peripheral nerve
C5-6 -> upper trunk -> lateral cord -? suprascapular nerve
This is the most common cause of shoulder pain which occurs as a result of compression of the rotator cuff muscles by superior structures (AC joint, acromion, coraco-acromial ligament) leading to inflammation and development of bursitis.
Subacromial impingement
This anatomical neck fracture of the humerus places the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex artery at greatest risk.
Surgical neck of the humerus
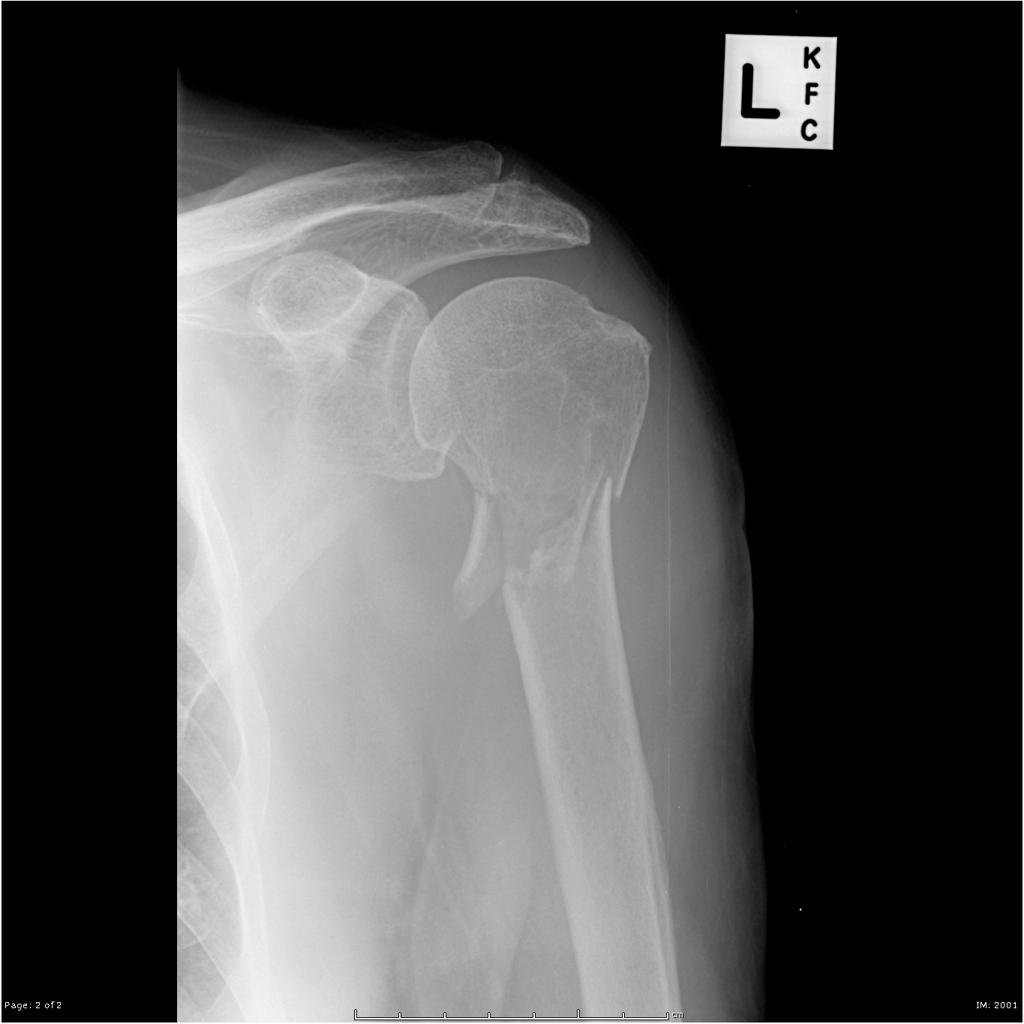
In a surgical neck fracture of the humerus, what artery is at greatest risk for injury?
posterior circumflex artery
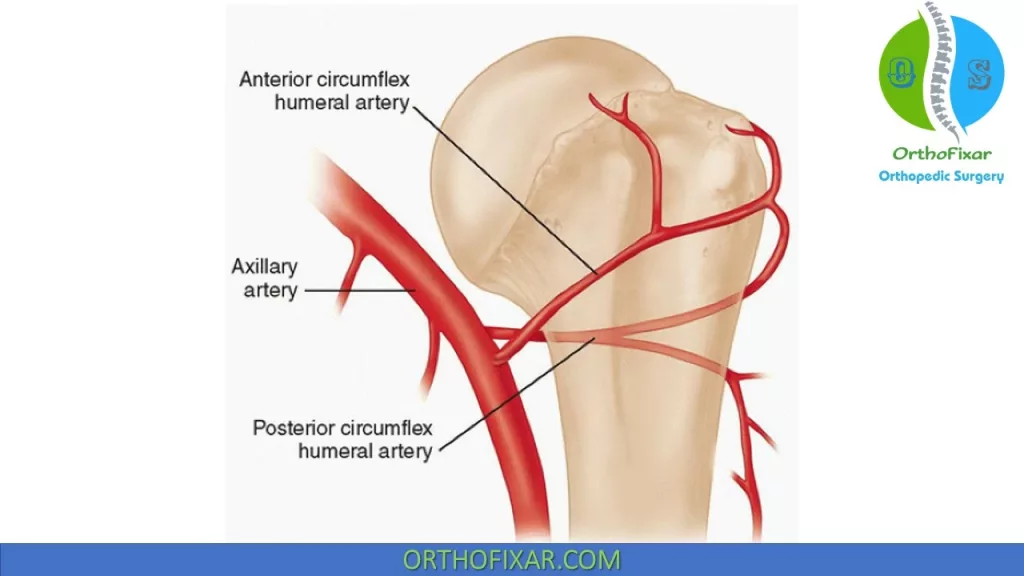
An injury to this muscle can lead to lateral scapular winging (will accept 2 different answers)
trapezius or rhomboid muscles

What is the innervation pathway of the deltoid? Need to know: Root(s) -> trunk -> cord -? peripheral nerve
C5-6 -> upper trunk -> posterior cord -? axillary nerve
What is a bankart lesion?
Strictly speaking, a "Bankart lesion" refers to an injury of the labrum and associated glenohumeral capsule/ligaments. The term "bony Bankart" (contrasted with a "soft Bankart" or "fibrous Bankart") is often used to refer to fracture of the adjacent anteroinferior glenoid, an injury which also commonly occurs in the setting of anterior glenohumeral dislocation.
