Select all of the following that are true of reversible reactions:
I. Most reactions are reversible.
II. Reversible reactions can proceed both forwards and backwards, but not both at once.
III. Reversible reactions can proceed both forwards and backwards simultaneously.
IV. Reversible reactions stop once they reach equilibrium.
I and III
The reaction below started with 2.17 M of A and 0.2 M of B:
4A(aq) --> 3B(aq) + C(aq)
At equilibrium, the concentration of A is 1.3 M. Determine Kc for this rxn.
ICE table!!!
In the lab, you take concentration measurements as this reaction proceeds. At equilibrium, [H2] = 0.03M, [I2] = 0.5M, and [HI] = 1.2M. What is the Kc value? SHOW YOUR WORK.
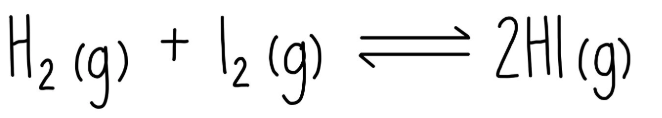
[1.2]^2/[.03][0.5] = 96
Two chemical reactions have two very different Kc values: Kc = 522 and Kc = 0.0052. What can you say about the equilibrium of both of these equations compared to each other?
Kc=522: products are favored (rxn goes almost to completion)
Kc = 0.0052: reactants are favored
BONUS!! Write a series of reactions and their Kc values, created entirely by you (you can use A, B, C as your reactants instead of actual compounds). Then:
a. Find the Kc value for one of your equations if it was multiplied by 8.
b. Find the Kc value for one of your equations if it was quartered.
c. Find the Kp value at 298.15 K, assuming all reactants are gaseous.
Check each individually!
Select all of the following that are FALSE of reversible reactions:
I. These reactions proceed simultaneously in both the forward and backward direction.
II. These reactions go until reaching equilibrium and then halt.
III. Chemical equilibrium are dynamic, and do not stop.
IV. Concentrations of reactants and products keep changing, and do not stop at equilibrium.
V. Molarity is constant for reactants and products throughout the reaction.
I, III
If Kc = 4.5 at 300 degrees C, what will the concentrations be at equilibrium if we start with 0.12M of both H2(g) and I2(g).

(2x)^2 / (0.12 -x)^2 = 4.5
x = 0.0617
H2 = 0.058
I2 = 0.058
HI = 0.1234
Write Kp for the following reactions:
a. Zn(g) + H2SO4(g) --> ZnSO4(g) + H2(g)
b. Na2SO3(g) + 2HCl(g) --> 2NaCl(g) + H2O(g) + SO2(g)
Kp = PH2PZnSO4 / PZnPH2SO4
Kp = PSO2PH2OPNaCl2/ PHCl2PNa2SO3
The equilibrium constant of the below reaction is 3.4 at 280 degrees celsius. Predict the direction the reaction will proceed in if concentrations of CH4(g), Cl2(s), CCl4(aq), and HCl(g) are 0.002M, 1.2 x 10-3M, 0.89 M, and 0.063 M, respectively.
CH4(g) + 4Cl2(s) --> CCl4(aq) + 4HCl(g)
Calculate Qc: 7.01 x 10-3M.
Qc < Kc.
Therefore, the rxn will proceed in the forward direction to establish equilibrium.
For the below rxn, Kc = 1.3.
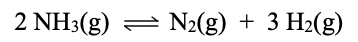
Calculate Kc for 6H2(g) + 2N2(g) --> 4NH3(g).
Reversed and multiplied by 2.
Kc = 0.59
If Kc = 0.4 and Qc = 1.3, which of the following are true of the reaction:
I. It will proceed in the forward direction forever.
II. It will proceed in the forward reaction until reaching equilibrium.
III. It will proceed in the backward reaction until reaching equilibrium.
IV. It has reached equilibrium.
V. Kc = Qc.
III only.
(this is not an ice table equation, sorry!)
The equilibrium constant Kc is 5.43.
2A(aq) + B(aq) --> 2C(aq)
At equilibrium, the concentrations of A and C are 0.56M and 0.29M, respectively. Determine the equilibrium concentration of B.
x = 1.456 M
The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction:
Na2SO3(g) + 2HCl(g) --> 2NaCl(g) + H2O(g) + SO2(g)
is 2.21 x 10-4 at 25 degrees C. What is the value for Kp at this temp?
delta n = moles gaseous products - moles gaseous reactants
4 - 3 = 1
T = 298.15 K
Kp = Kc (RT)n gas
(Kp) = (2.21 x 10-4)(.0821)(298.15)^1
Kp = 5.41 x 10-3
`The equilibrium concentrations for this equation are [NH3] = 0.56M, [N2] = 0.005M, [H2] = 1.3M. Calculate Kp at 298.15 K. 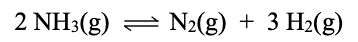
First calculate Kc, then calculate Kp.
Kc = .062
Kp = 37.15
MAKE SURE (RT)^delta n
Given the below info, calculate the Kc of 2NO2(g) --> N2(g) + 2O2(g).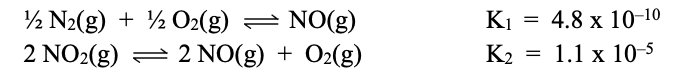
Add equations together to get to the final. you must multiply the top by two and reverse it.
(4.34 x 1018) x (1.1 x 10-5)
= 4.77 x 1013
2A(g) + B(g) --> 3C(g) + D(g)
Select all of the following that are true of the above reaction at equilibrium:
I. The molarities of A, B, C, and D will be equivalent.
II. The rate of the forward rxn equals the rate of the backward rxn.
III. The concentration of A,B,C, and D are constant.
IV. Kc = Qc
V. The reaction constant Q is constant.
II, III, IV.
The reaction below started with 4.67 M of A and 2.54 M of B:
2A(aq) --> B(aq) + C(aq)
At equilibrium, the concentration of A is 2.01 M. Determine Kc for this rxn.
ICE table
[B] = 3.87
[C] = 1.33
[A] = 2.01
Put into Kc equation!
= 1.27
Zn(g) + H2SO4(g) --> ZnSO4(g) + 3H2(g)
Kp = 0.0461 at 298.15 K.
What is the Kc at this temperature?
0.0461 = Kc (.0821)(298.15) ^2
7.694 x 10-5
If Kc is 2.3, predict direction of reaction if [NH3] = 3.1 x 10-4, [N2] = 0.02, and [H2] = 0.86.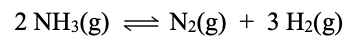
Qc = 132373
Qc >>>> Kc
Rxn will proceed in the reverse direction to reach equilibrium.
2A + 3B --> 6C | Kc= 2.3 x 10-2
B + 2C --> 5D | Kc= 1.18 x 10-6
Determine the Kc value for the following equations:
a. 6C --> 3B + 2A
b. 1/2B + C --> 5/2D
c. 2A + 4B --> 4C + 5D
a. 1/ (2.3 x 10-2) = 43.48
b. (1.18 x 10-6) 1/2 = 1.086 x 10-3
c. ADDED! (2.3 x 10-2) x (1.18 x 10-6) = 2.71 x 10-8
Select all of the following that are true of Qc and Kc:
I. Qc = Kc at equilibrium.
II. Kc and Qc have the same equations.
III. If Qc < Kc, Reverse rxn will be favored.
IV. If Qc = Kc, rate of the forward rxn is favored.
I, II
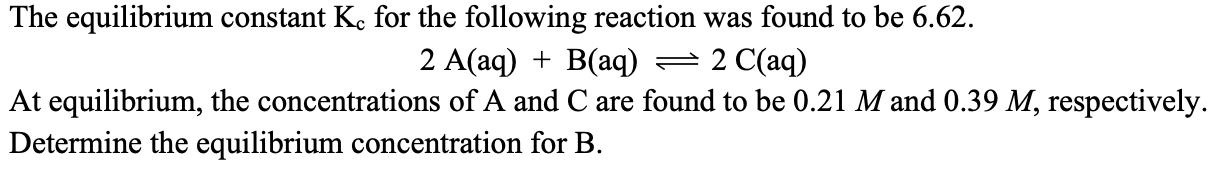
0.52
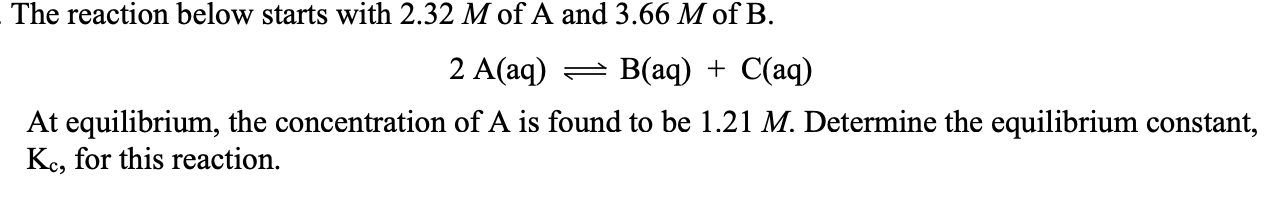
1.60
Hint: use approx. method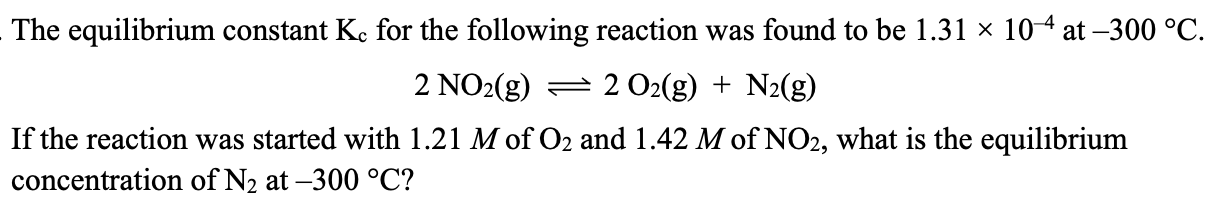
1.8 x 10^-4
BONUS: go to whiteboard and write out as much content as you know from this Exam's content. Team with the most written wins the points!
:)