what is the pH of a 0.2 M solution of HC2H2O2Cl (Ka = 1.4 x 10-3)
approximation NOT valid
successive:
pH= 1.8
CH3NH2 is a weak base. In a 0.05 M solution, 7.3% of the base is ionized. What is its Kb?
7.3 = x/0.05 x 100
x = .00365
2.87 x 10-4
calculate the pH at 25 degrees C of a 0.30 M solution of acetic acid (Ka = 2.9 x 10-7)
x2/0.3-x = 2.9 x 10-7
approx method
check validity
answer = 3.53
Which of the following are basic when in an aqueous solution?:
1. NaF
2. NaCl
3. NaBr
1 ONLY, because F- is CB of HF, which is weak acid
REMEMBER: for anions, only CB of weak acids act basic, not of strong acids
What is [CO3]2-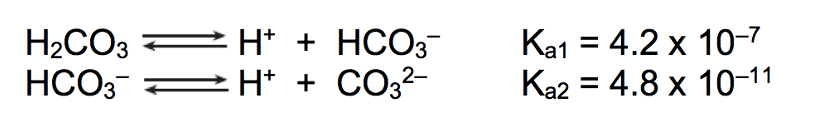
What is the pH of a 0.1 M solution of CH3COOH (Ka = 3.1 x 10-2)? Stop at 3 approximations even if numbers don't match perfectly.
approximation is not valid.
max = 3 approximations
0.042 = x
- log (.042) = 1.38
write out all the equations for pOH, pH, pKa, pKb, Ka, Kb on the whiteboard. whoever gets most gets the points!
check individually
What is the pH of a 0.002M solution of HC2H2O2Cl (Ka = 4.5 x 10-7)
4.5 x 10-7 = x2/(0.002 - x)
0.002 >= 400 (Ka)
pH = 4.523
Write out 3 salts that when in aqueous solution, are:
(a) acidic
(b) basic
(c) neutral
individual! pull up rules on slide.
You have a 0.10 M H2CO3 solution. What is the concentration of all species?
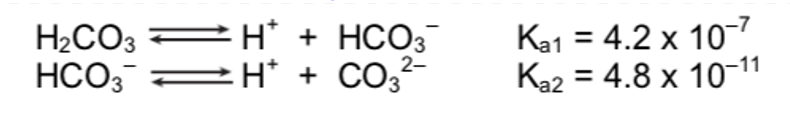
4.2 x 10-7 = x2/(0.1-x)
[2.05 x 10-4] = H+ = HCO3-
[CO32-] = 4.8 x 10-11
Write out the two equations used to determine if an approximation is valid.
[A] initial >= (400) Ka
x/initial x 100 < 5
Select all of the following that are TRUE:
I. As Ka of a solution gets larger, Kb must get smaller.
II. The conjugate base of a strong acid is a strong conjugate base.
III. The conjugate base of a weak acid is a weak conjugate base.
IV. At all temperatures: Ka x Kb = Kw
V. If an acid has a low ionization, it is strong.
I, III, IV
Rank these acids from weakest to strongest: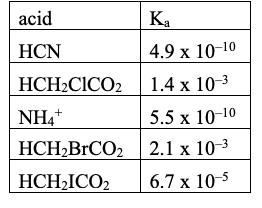
From smallest Ka to largest Ka (weakest to strongest)
Predict in each pair which will be more acidic when in aqueous solution:
1. Al(H2O)3+ or Al(H2O)7+
2. HCl or HF
3. HI or Fe(H2O)3+
1. Al(H2O)7+
2. HF
3. Fe(H2O)3+ because HI is neutral
What are the concentrations of all species (S2-, H+, and HS-), if H2S = 0.2M?
S2- = 1.3 x 10-14
HS- and H+= 1.4 x 10-4
BONUS: write out the rules for cations and anions of aqueous salt solutions being basic vs acidic vs neutral.

Rank from weakest to strongest CONJUGATE BASE: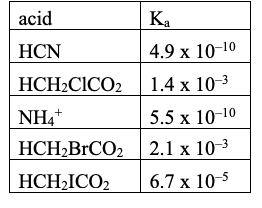
largest to smallest Ka value will be weakest to strongest conjugate base.
What is the pH of a 0.2 M HCl solution?
- log (0.2) = 0.7
Predict if an aqueous solution of each of the following would be acidic, basic, or neutral:
1. KBr
2. NH4I
3. SrBr2
4. Ba(CH3COO)2
1. neutral
2. NH4 = acidic
3. neutral (Sr is group 2)
4. basic (CH3COO is CB of acetic acid)
I. CaCl2
II. AlCl3
III. NH4Cl
IV. LiCl
II and III