When the partial pressure of water vapor equals the saturation vapor pressure, this weather condition is at 100%.
What is Relative Humidity?
At what temperature is the Lifting Condensation Level in the image?
What is 2 C?
On a hot day, this process occurs as the sun heats the ground, causing air to become less dense and rise.
What is Convective Lifting?
After many years, compressed layers of snow turn into this dense, crystalline substance that is the basis of a glacier.
What is ice?
These samples extracted from glaciers can contain layers of volcanic ash and trapped air bubbles, which provide a record of Earth's ancient climate.
This is the temperature to which air must be cooled at a constant pressure to reach 100% relative humidity, causing condensation.
What is Dew Point?
Both the dry and moist adiabatic rates describe the cooling of an air parcel as it does this.
What is Rise?
Rain shadows are a product of this lifting mechanism, which forces air up and over a mountain range.
What is Orographic Lifting?
What is a defining characteristic of an ice age? (Are we currently in an ice age?)
What is glacial ice? (Yes)
What type of feedback loop is the ice-albedo feedback?
If the air temperature is 20°C and the dew point is 20°C, what is the relative humidity?
What is 100%?
This high-altitude, wispy cloud is composed of ice crystals and can signal a change in weather.
What are cirrus clouds?
Found often at the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), this mechanism occurs when air flows horizontally inward toward a low-pressure area and is forced upward.
What is convergence?
Where the tradewinds from both hemispheres converge
Once a glacier is formed, this force causes the ice to flow slowly downhill, giving it the nickname "river of ice".
What is gravity?
What are the 3 configurations of orbital parameters that would favor glaciation?
What is...
1) Changes in axial tilt
2) Precession of the equinoxes
3) Changes in orbital eccentricity
When the air temperature goes up, what generally happens to the relative humidity, assuming the amount of moisture stays the same?
What is it decreases?
Compared to the dry adiabatic rate, the moist adiabatic rate cools at this speed.
What is slower?
Which biome would this most likely represent?
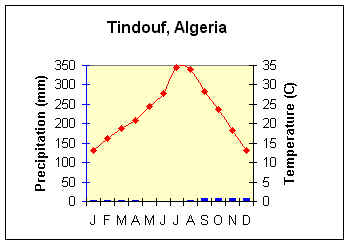
What is a desert?
Who was the Swiss naturalist who came up with the theory of a great ice age in the past?
Who was Louis Agassiz?
What are 2 causes of climate change?
What is..
variation in solar output, release of aerosols (small dust particles from major volcanic eruption), position of landmasses, changes in earths orbital parameters, climate feedbacks
In an unstable atmosphere, a lifted air parcel will continue to do this on its own accord.
During this process, ice crystals grow at the expense of supercooled liquid water droplets because of differences in the saturation vapor pressure over ice versus liquid water.
What is the Bergeron Process?
What latitudinal line will not have any hurricanes due to the absence of the Coriolis effect in this region?
Where are glaciers currently found on earth?
They are found on every continent except Australia.