What color is the plaque on the skin when psoriasis is present?
silver plaques
What are the APC cells located in the skin?
Macrophages, Langerhans Cells, Dendrites
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
Name some non prescription Rx Tx methods for plaque psoriasis
using moisturizers and emollients that clear the plaques and minimize itchiness, avoiding picking scabs, dietary interventions
What are the three dermatophytes?
Trichophyton
Epidermophyton
Describe Nail Pitting
Nail pitting is when small depressions appear on the surface of the nails
What is the purpose of the cytokines in the skin (think specifically for psoriasis)
They increase keratinocyte proliferation
In what part of our skin are langerhans cells present? What is their function? Be specific.
The stratum spinosum. Function is to act as an APC to T-cells
Explain why taking stelara (an immunosuppressant) could potentially help with this individual's plaque psoriasis?
Stelara decreases the activation of T-cells, which are normally over-excited (excrete lots of cytokines) and cause plaque psoriasis
How does humidity affect our ability to cool down when exercising?
It makes sweating less efficient in it's ability to release heat
What does natural history mean?
The natural history of disease is the course a disease takes in individual people from its pathological onset ("inception") until its eventual resolution through complete recovery or death.
What are some possible causes of the immune response that is triggered and results in plaque psoriasis?
Genetics component, Trauma, infection
Define parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis. Are they present in plaque psoriasis?
Parakeratosis- keratinization with retain nuclei in the stratum corneum
Hyperkeratosis-thickening of the stratum corneum due to an abnormal quantity of keratin present
Both are present in plaque psoriasis
What are some other drug alternatives to stelara?
Cimzia
Enbrel
Humira
What type of neurotransmitters and receptors does the sympathetic nervous system act on to cause vasoconstriction and vasodilation?
vasoconstriction: norepinephrine acts on alpha receptors (adrenergic) on smooth muscles
vasodilation: Ach acts on muscarinic (cholinergic) receptors
What are the normal histological findings of plaque psoriasis?
thin stratum basale, thickens in the other layers (mostly in the stratum corneum and stratum spinosum)
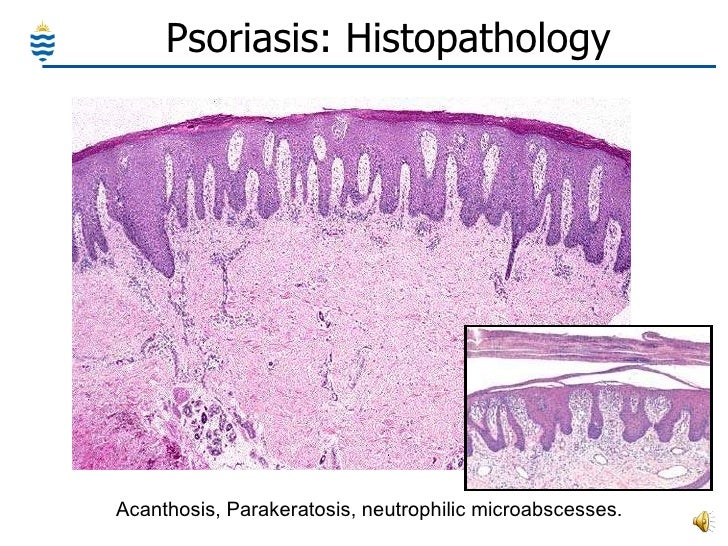
In what layer do neutrophils normally collect in the epidermis?
Stratum Corneum Layer
Describe the difference between a macule, papule, and plaque
Macule: discolored, flat, less than 5mm
Papule-raised, discolored, less than 5mm
plaque-elevated, firm, rough lesion with flat top and surface greater than 5mm
What are the pros and cons of treatment with stelara
cons-increased risk of infection, increase risk for cancer, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, and allergic reactions
Explain the characteristics of local anesthetics that contribute to their functionality.
The aromatic ring makes it lipophilic, allowing it to cross the cell membrane into the cell. It is also a weak base because of the tertiary amine. This allows it to become ionized in the acidic environment within the cell, which activates the drug to bind intracellularly to the ion-gated sodium channel and cause them to close.
If you wanted to run a full thickness biopsy of a plaque, what technique(s) would you use?
excision, punch
What are the interleukins involved in the immuno response that leads to the development of plaque psoriasis?
IL12, IL23, IL17
Describe why the stratum spinosum is named the stratum spinosum. Also, what is the specific type of junction that is present?
Diagram the mechanism of action of Stelara
blocks interleukin 12 and 23, which normally help activate T-cells. It does this by binding to the p-40 subunit of both IL12 and IL 23 so they cannot bind to their receptors.
Explain the mechanism of Azoles and Allylamines. Explain why Azoles are not toxic to humans.
Give an example of azoles and allylamines
Azoles (such as itraconazole) inhibit the synthesis of Ergosterol, which is the lipid that is in the cell membrane of fungus.
Allylamines (such as terbinafine) inhibit squalene epoxidase, which converts squalene to ergosterol. This causes an increase in the amount of squalene inside the cell and it is toxic to the cell.