These are the pyrimidine bases
uracil, thymine, cytosine
The most frequent “driver” mutations in melanoma affect these three intrinsic factors
cell cycle control, pro-growth pathways, and telomerase
Breslow thickness is generally measured in this manner
distance from the superficial epidermal granular cell layer to the deepest intradermal tumor cells
These are the ABCDE criteria
asymmetry, borders, color, diameter, evolving
Dabrafenib and Trametinib taken together is indicated for this specific diagnosis
stage 3 melanoma (V600E OR V600K BRAF mutation)
DNA glycosylase is involved in the first step of this type of DNA repair
base excision repair
Presence of this is why depth is the most important factor in prognosis of melanoma
adjacent lymphatics
A potentially metastatic cancer is initially localized just inferior to the fossa ovalis (leg). In theory, the sentinel lymph node would be this.
deep inguinal lymph node

About 10% to 15% of melanomas are inherited in this fashion with variable penetrance
autosomal dominant
In FDG-PET/CT, this is injected into the patient's tissues and shows discrepancies between healthy and diseased tissue
fluorodeoxyglucose
Pyrimidine dimers are generally repaired by this mechanism
nucleotide excision repair
The majority of lesions (melanoma) are greater than this specific measurement at diagnosis
10 mm
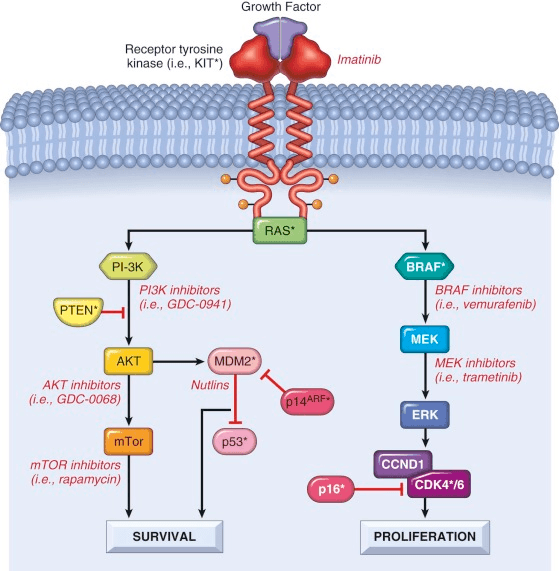
Imatinib is responsible for targeting this component of cell signaling as related to the pathogenesis of melanoma
dimerization of RTK
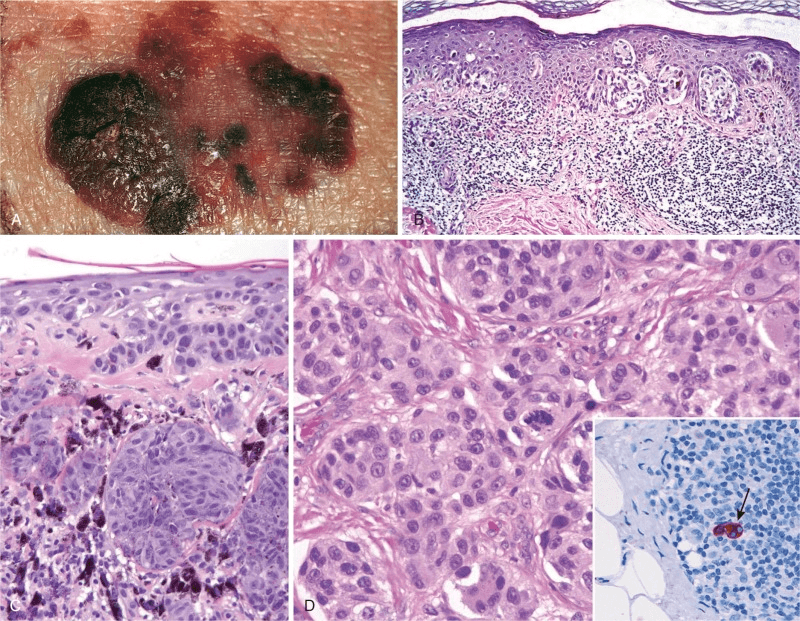
In D, the sentinel lymph node indicated has most likely stained with this stain. Bonus: what does it stand for?
HMB-45 (human melanoma black)
A left axillary lymphadenectomy is indicated for a tumor that has metastasized to the inferior-most and ventral axillary lymph node. This node is..
pectoral (anterior) lymph node

The most common etiology of thymine dimers is due to exposure to this agent
ultraviolet light
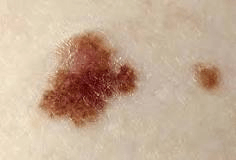
These specific lesions often serve as precursors to melanoma
dysplastic nevi
Dabrafenib's mechanism of action is this
blocks BRAF in V600E (+) mutated melanoma

A radiograph of your patient is taken, and based off of the radiograph, you determine that his condition is in this stage
Cancer, stage II/III
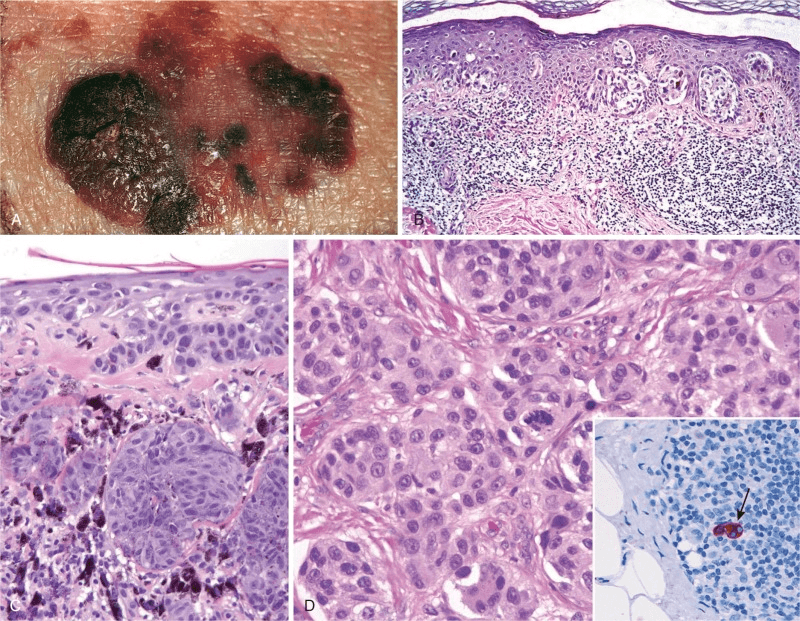
How do B & C differ in this melanoma lesion? (Think 'growth')
B = single cell growth, inflammation of underlying dermis (radial)
C = aggregates of cells (vertical)
photolyase
Melanoma cells are differentiated from regular melanocytes or melanocytic nevi by these morphologic features
larger, irregular contours, clumped chromatin, and eosinophilia
The normal role of tyrosinase is this
catalyzes rate-limiting steps of melanogenesis (recent target for melanogenesis inhibitors)
A tumor is found to be between 3 and 7 cm (but less than 5 cm). It involves nearby lymph nodes on the ipislateral side of the body, and has spread to localized regions adjacent to the lymph nodes. The classification is this.
T2aN1M1
The TERT promoter mutations present in melanoma create new binding sites for Ets family transcription factors, which are known to be up-regulated by this signaling, providing a "link" between these two oncogenic events
BRAF