A variety of terms are used to describe this methodology: single-subjects design, small n design, n of 1 design.
What is single case research design?
In a simple AB design, the A stands for this potentially misleading word.
What is Baseline?
Self-report data often used with single case designs can introduce this issue to the research.
What is bias?
Single case designs can only have one participant.
Myth! Single case designs can have many participants.
High degrees of this in baseline data can make predictions more difficult.
In single case designs, participants are exposed to different types of these to determine whether
behavior changes. They are often labeled using letters (A denotes baseline, B denotes intervention).
What are conditions?
A withdrawal (reversal) ABA design can have ethical complications for this reason.
Ends with the intervention not in place and participants without support.
A main limitation of single case designs is related to data being collected from one individual, making it difficult to do this.
What is generalize results?
Single subject designs can lack external validity.
Fact! However, so can group research designs.
Using a BAB instead of an ABA design can correct the ethical dilemma associated with this single case design.
What is withdrawal (reversal) design?
The degree that two or more observers provide similar data based on their observation of specified behaviors.
What is interobserver agreement?
This design offers useful information on intervention effectiveness with rapid A-B changes.
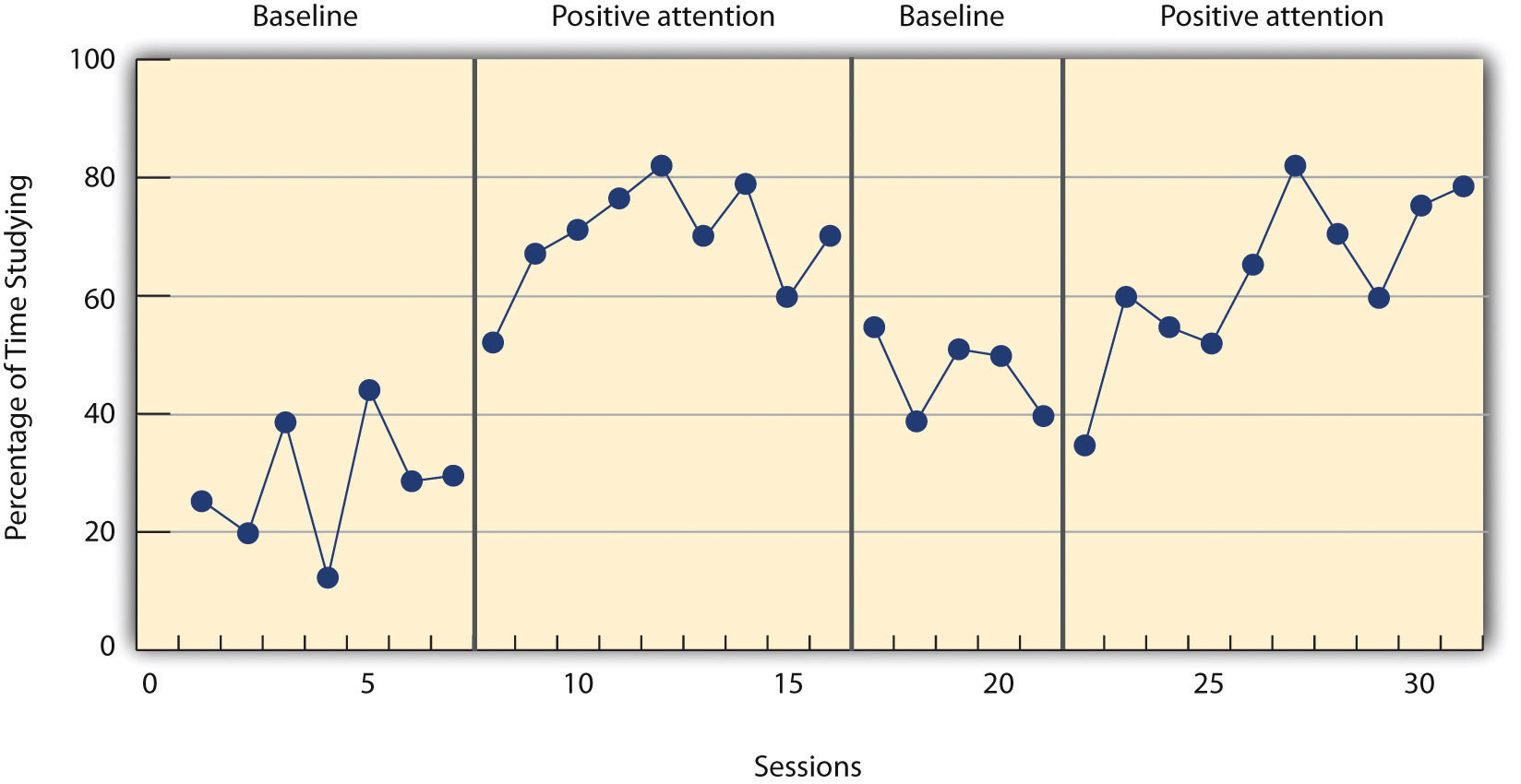
What is alternation reversal designs (ABAB)?
A single case design can be beneficial when researchers run into this problem.
Hint: Voltaire article
Difficulty finding enough people who possess the trait/behavior of interest.
Single case designs are easy to do.
Myth! Single case design has its own tradition of methodology and many considerations must be made to complete successfully.
When working with multiple participants, it is helpful to do this in order to lessen the effect of extraneous variables.
Match participants on specific characteristics.
A quantitative metric used to estimate the magnitude of change in the dependent variable and to compare effects across other studies.
What is effect size?
Baseline data should be this before progressing to a treatment phase in ABAB designs.
What is stable/consistent?
If deciding between a group design and a single case design, researchers might choose a single case due to these practical reasons.
More feasible and flexible, lower cost, less recruitment difficulty, does not need control group or randomization.
Single-subject experiments only require one pre-test/post-test.
Myth! Single case designs require ongoing data collection. We are often looking for trends with SCRD, so the more data points, the better!
This single case design mitigates ethical considerations but introduces order effects.
What are alternation reversal designs?
Attributing a change in the dependent variable (i.e., participant’s behavior) to the independent variable (i.e., intervention or practice) by reasonable controlling for confounding variables. This signifies a causal relation between the independent variable and the dependent variable.
Hint: Page 2 of Hott et. al chapter
What is a functional relation?
We use this design when we know that an intervention permanently changes behaviors. 
What is multiple baseline design (MBD)?
Hott et. al discusses critical attributes of single case designs that, if followed, can allow researchers to make causal claims. Repeatability, temporal extent, and temporal locus are dimensions of one of these attributes.
Hint: Helps us understand and report behaviors.
What are observable target behaviors and operational definitions?
Single case designs cannot make causal claims between an independent and dependent variable.
Myth! When properly designed and executed, SC studies can demonstrate strong internal validity to determine the likelihood of a causal relationship between the intervention and outcomes.
It can be especially unethical to withdraw treatment in cases where these types of behaviors are being addressed.
Aggressive or self-injurious behaviors