Vocabulary
Vocabulary
Lungs
System
Multiple Choice
Un pedazo de tejido en la parte superior de la laringe que cubre la abertura de la tráquea cuando uno se alimenta o bebe. A piece of tissue in the upper part of the larynx that covers the opening of the trachea when one feeds or drinks.
Epiglotis/Epiglottis
Cuántos Pulmones tiene un ser humano. How many lungs does a human being have?
2 pulmones/2 Lungs
¿Que se llaman las ramificaciones de los bronquios?What are called the ramifications of the bronchi?
Bronquiolos/Bronchioles

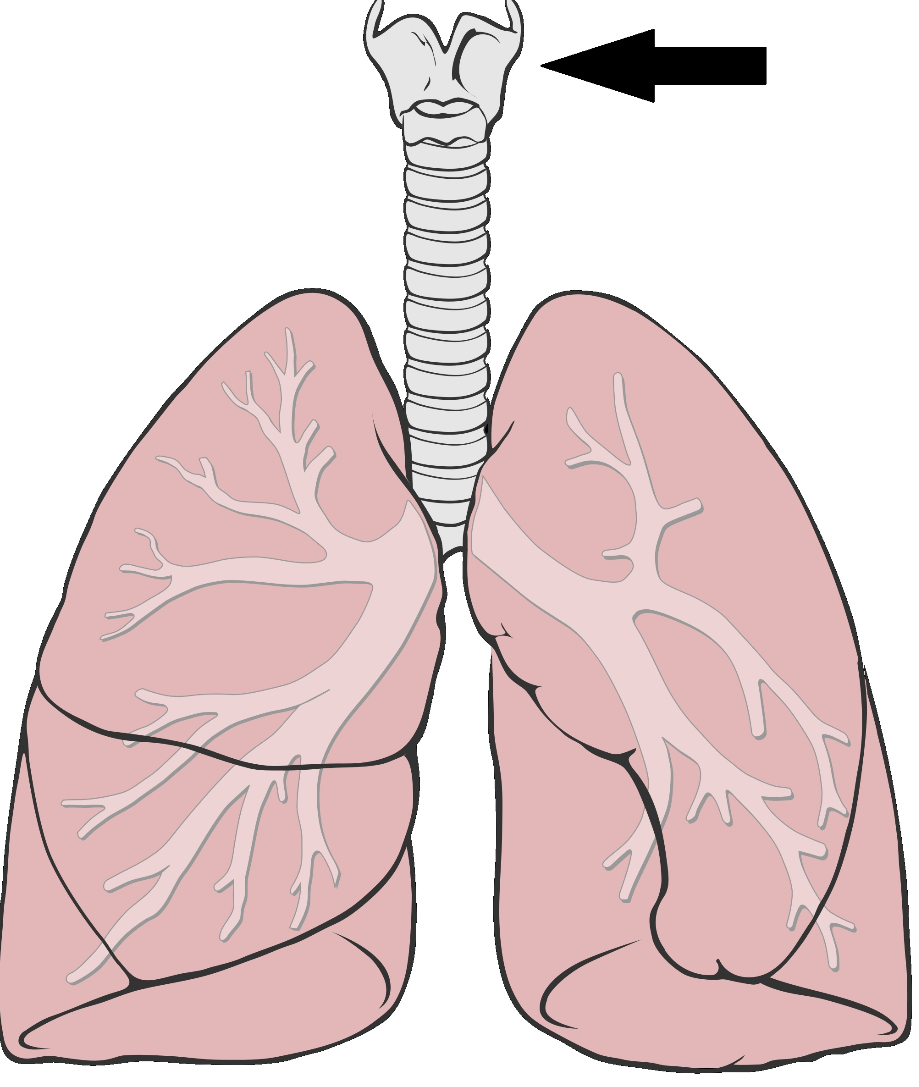
Laringe/Larynx
El sistema respiratorio está formado por la tráquea, los pulmones y: The respiratory system is made up of the trachea, lungs, and:
A) hígado/liver B) diafragma/diaphragm C) esófago/esophagus D) páncreas/pancreas
B) diafragma/diaphragm
Sacos de aire de los pulmones donde sucede el intercambio gaseoso. Air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Alveolos/Alveoli
¿Qué se realiza en los alvéolos pulmonares? What takes place in the pulmonary alveoli?
Intercambio gaseoso/Gas exchange
¿Los pulmones tienen una textura similar a qué objeto? The lungs have a texture similar to what object?
Son dos órganos de color rosado, blandos, con una textura similar a la de una esponja. They are two soft pink organs with a texture similar to that of a sponge.
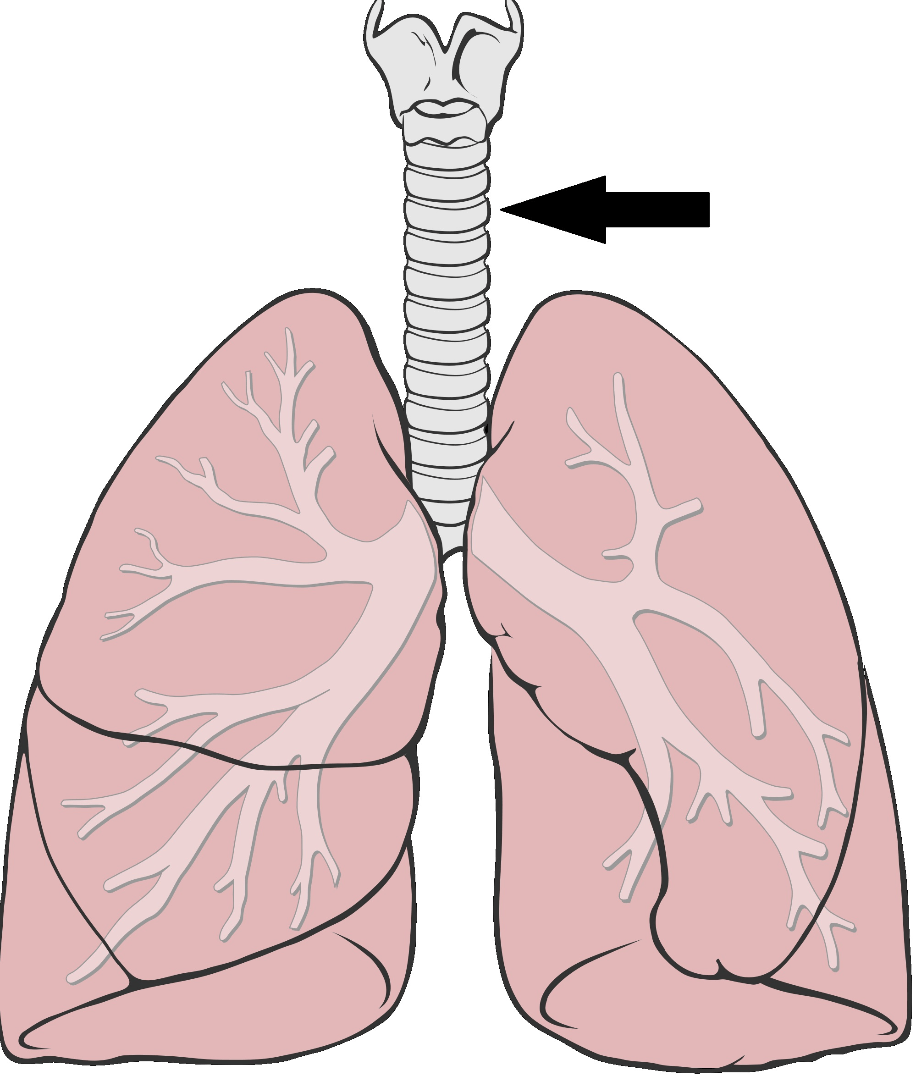
Tráquea/Trachea
Cuando respira aire, lleva oxígeno a los pulmones y expulsa: When you breathe air, it carries oxygen to your lungs and expels:
A) dióxido de carbono/carbon dioxide
B) monóxido de carbono/carbon monoxide
C) oxígeno/oxygen
D) hidrógeno/hydrogen
A) dióxido de carbono/carbon dioxide
Es un músculo largo en forma de domo que se contrae de manera rítmica y continua y, de manera involuntaria cuando respiramos. It is a long, dome-shaped muscle that contracts rhythmically and continuously and involuntarily when we breathe.
Diafragma/Diaphragm
¿A qué se parecen los alvéolos pulmonares? What do the pulmonary alveoli resemble?
racimos de uvas/Bunches of grapes
¿A qué contribuye la inhalación? What does inhalation contribute to?
Oxigenación de la sangre. Oxygenation of the blood.
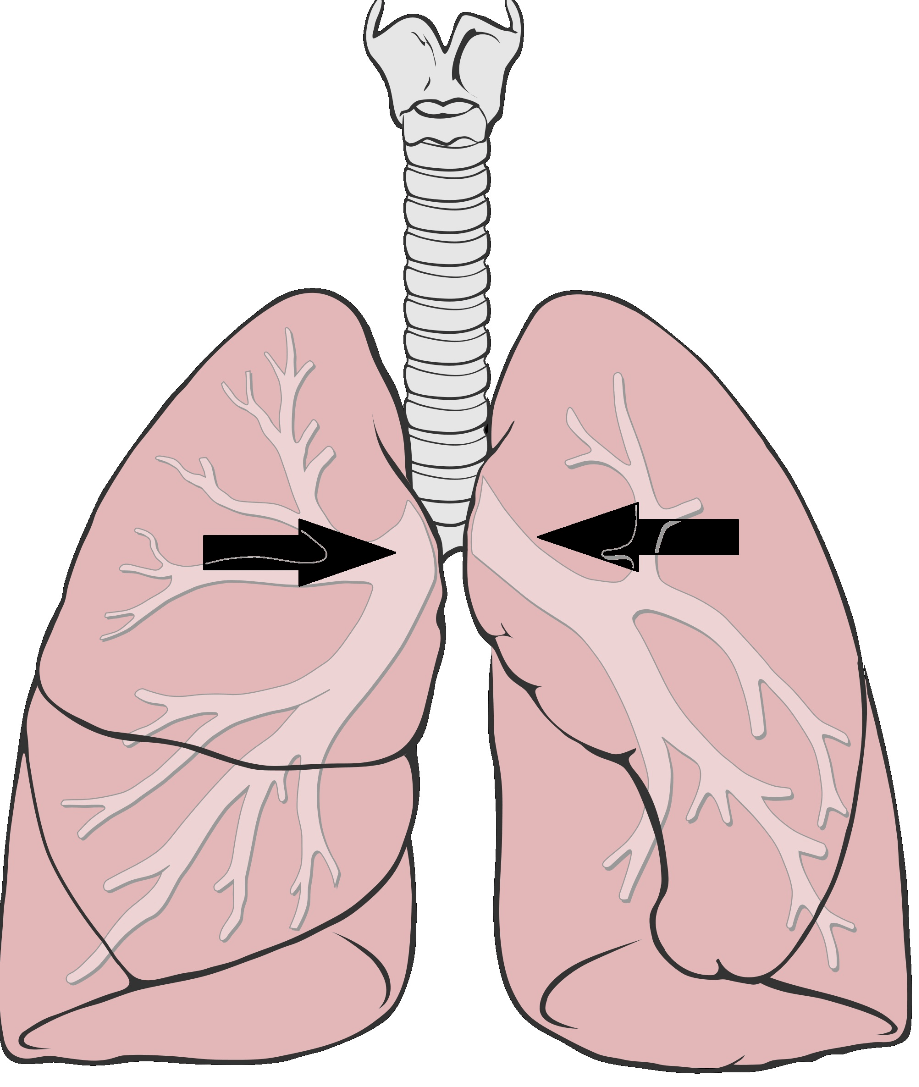
Bronquios/Bronchi
La tráquea también se llama: The trachea is also called:
A) pulmón/lung
B) diafragma/diaphragm
C) conductor de aire/windpipe
D) bronquio/bronchi
R: C) conductor de aire/windpipe
Órgano entre la faringe y la tráquea que contiene las cuerdas vocales. Organ between the pharynx and the trachea that contains the vocal cords.
Laringe/Larynx
¿Con qué están protegidos los pulmones? What are the lungs protected with?
Caja torácica/Rib cage
La tráquea se separa en dos tubos. ¿Esos tubos se llaman? The trachea separates into two tubes. Those tubes are called?
Bronquios/Bronchi
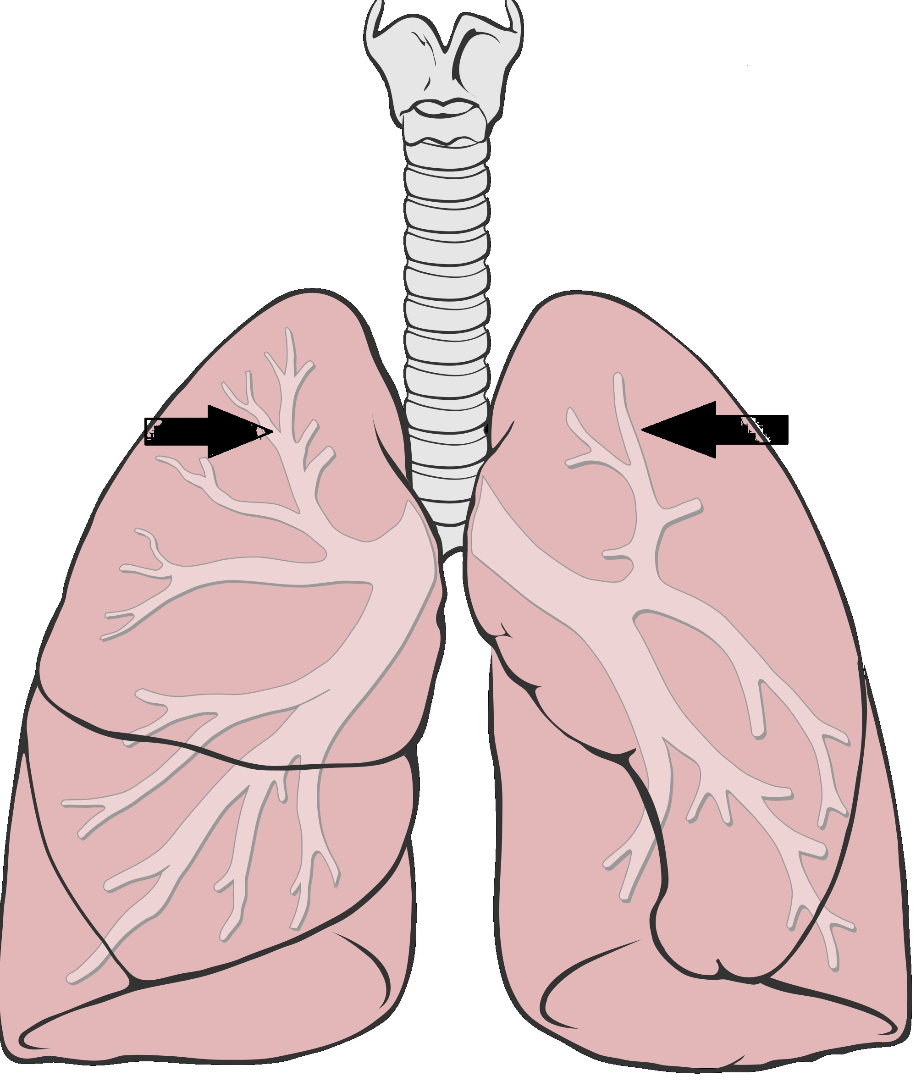
Bronquiolos/Bronchioles
La "caja de voz" también se conoce como: The "voice box" is also known as: The "voice box" is also known as:
A) alvéolos/alveoli B) laringe/larynx C) tráquea/trachea D) boca/mouth
B) laringe/larynx
Rama más grande del árbol bronquial entre la tráquea y los bronquiolos. Largest branch of the bronchial tree between the trachea and the bronchioles.
Bronquios/Bronchi
¿Por qué el pulmón izquierdo es un poco más pequeño que el derecho? Why is the left lung slightly smaller than the right?
Le deja un “lugarcito” para que se ubique el corazón/It leaves a "little place" for the heart to be located
Las vías respiratorias se dividen en...The airways are divided into ...
Vías respiratorias superiores y vías respiratorias inferiores/Superior/Upper respiratory & Inferior/Lower respiratory tract.
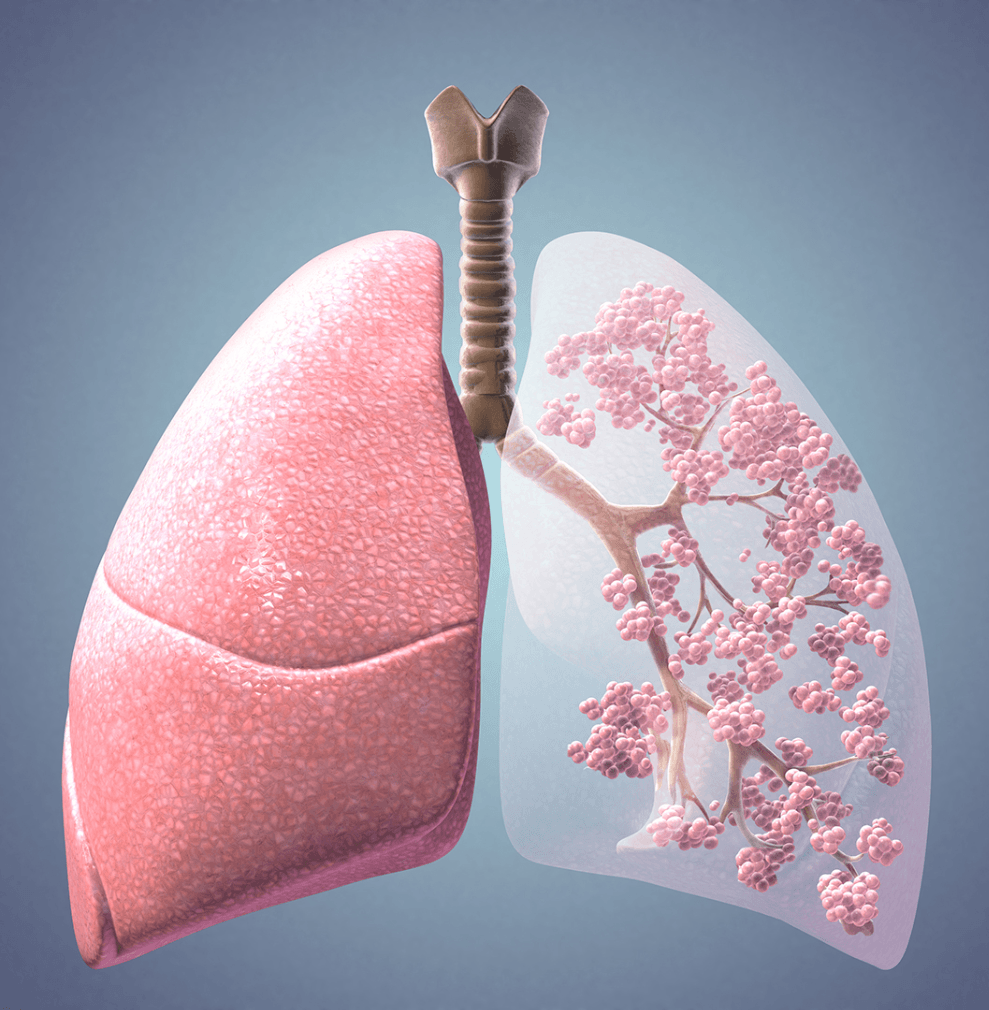
Alvéolos Pulmonares/Pulmonary Alveoli
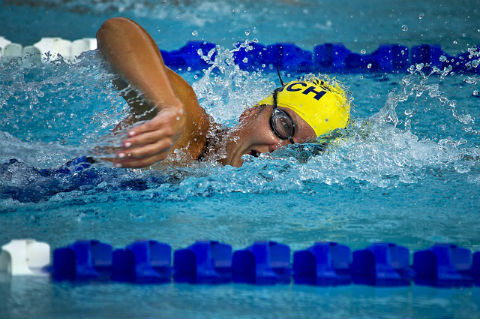
En esta imagen, el nadador está respirando profundamente. ¿Cuál de los siguientes procesos ocurre durante la inhalación? In this image, the swimmer is taking a deep breath. Which of the following processes occurs during inhalation?
A) Los alvéolos están contraídos y cerrando. The alveoli are contracted and closing.
B) El diafragma se relaja y el volumen de aire en el pulmón disminuye. The diaphragm relaxes and the volume of air in the lung decreases.
C) La caja torácica se achique. The rib cage gets smaller.
D) El diafragma se contrae y tira de los pulmones hacia abajo para aumentar el volumen de aire en los pulmones. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lungs down to increase the volume of air in the lungs.
R: D) El diafragma se contrae y tira de los pulmones hacia abajo para aumentar el volumen pulmonar. The diaphragm contracts and pulls the lungs down to increase lung volume.