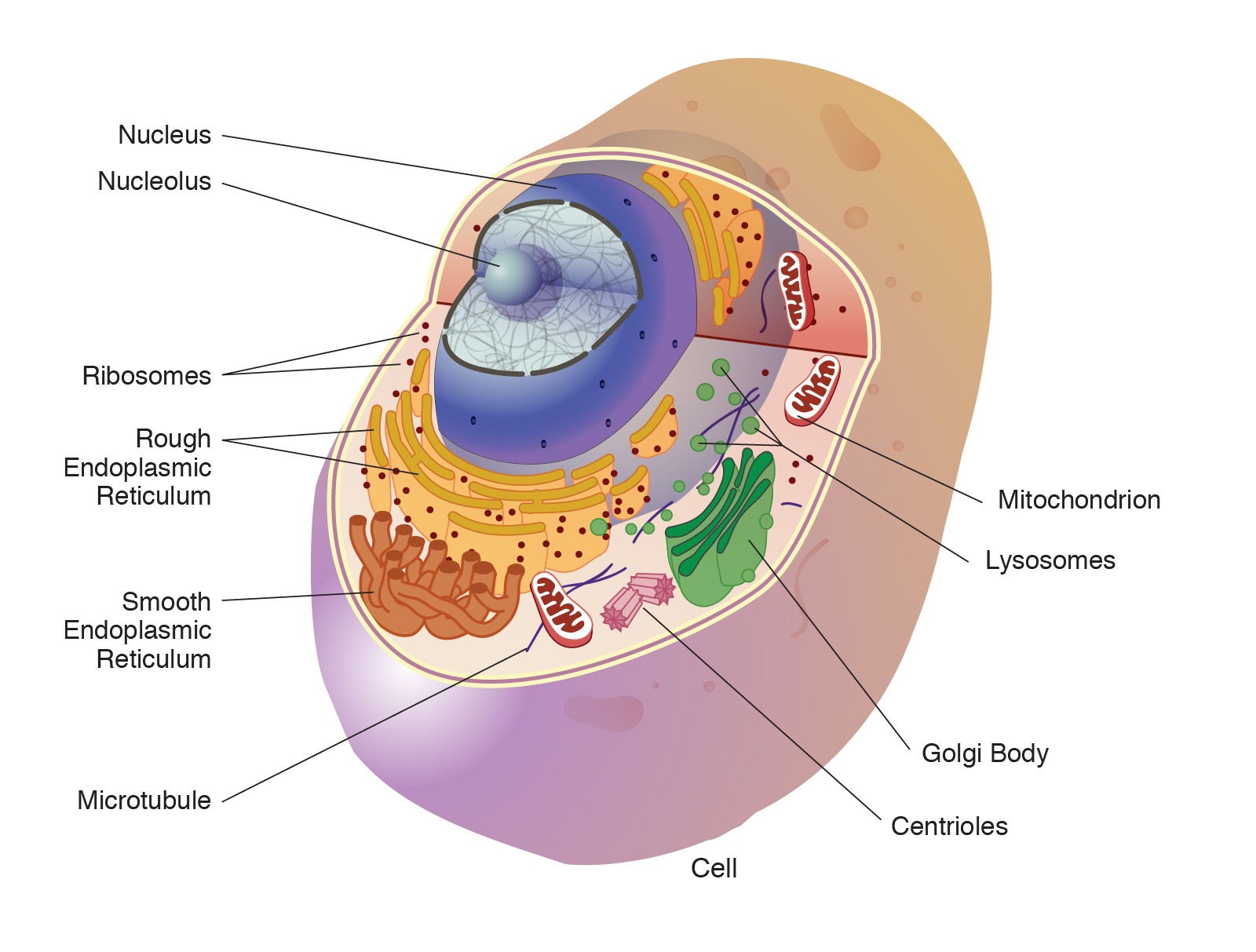
In a cell, organelle where protein synthesis takes place on?
Ribosome
Where in a cell does ENERGY PRODUCTION take place on?
MItochondria
Skeletal System: Medical term for shoulder blade?
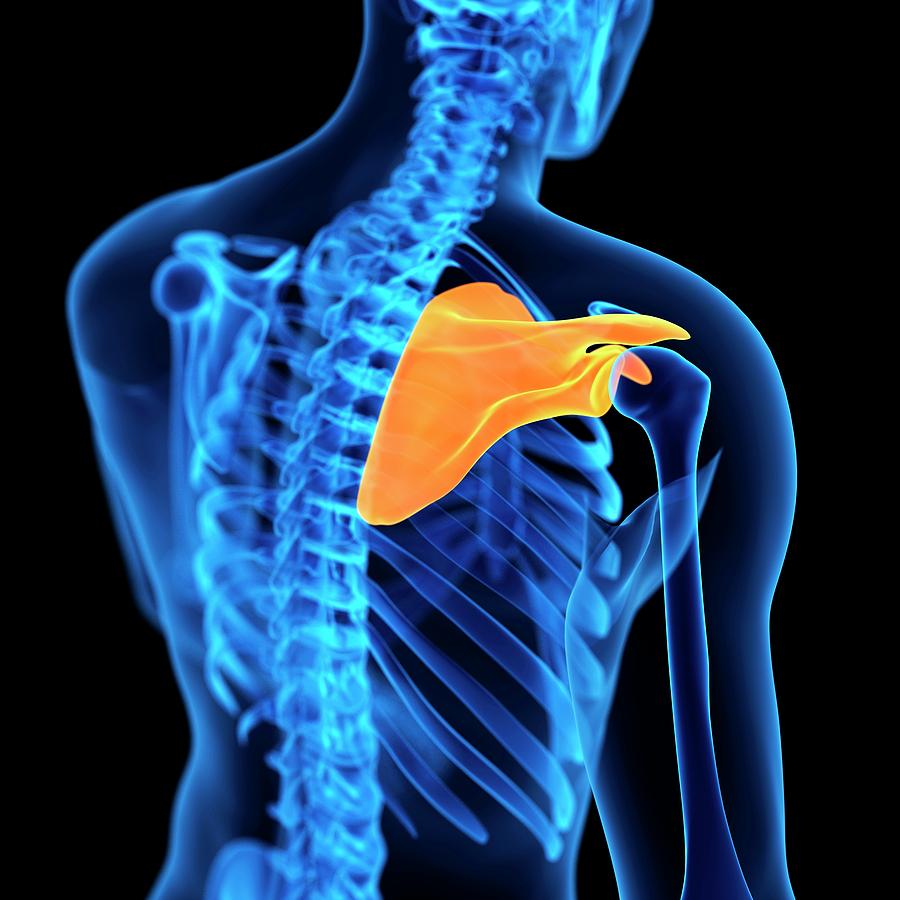
Scapula
What are the 2 proteins called that responsible for building cross-bridges (during muscle contractions)?

Actin and myosin.
TISSUES:
Single layer of flattened cells in epithelial tissue?

Simple squamous cell
Simple = one layer of cells
Squamous = flattened cells
What is the junction called where the muscular system meets the skeletal system?
Neuromuscular Junction
The make up of a muscle from largest to smallest units?
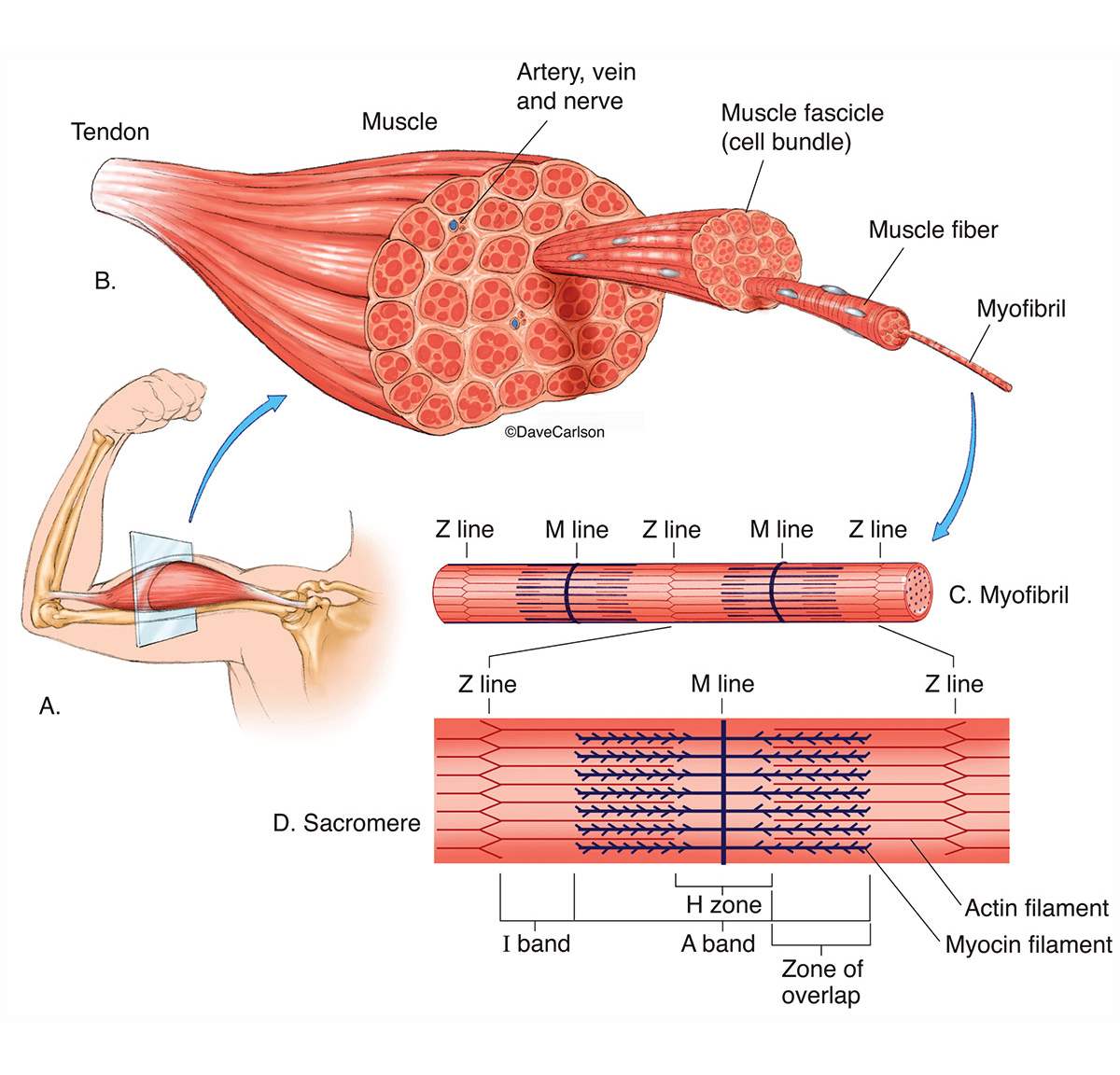
Muscle, fascicles, muscle fibers (muscle cell), myofibril.
TISSUES:
Several layers of flattened cells in epithelial tissue? (Top layer determines if it is flat or cuboidal)
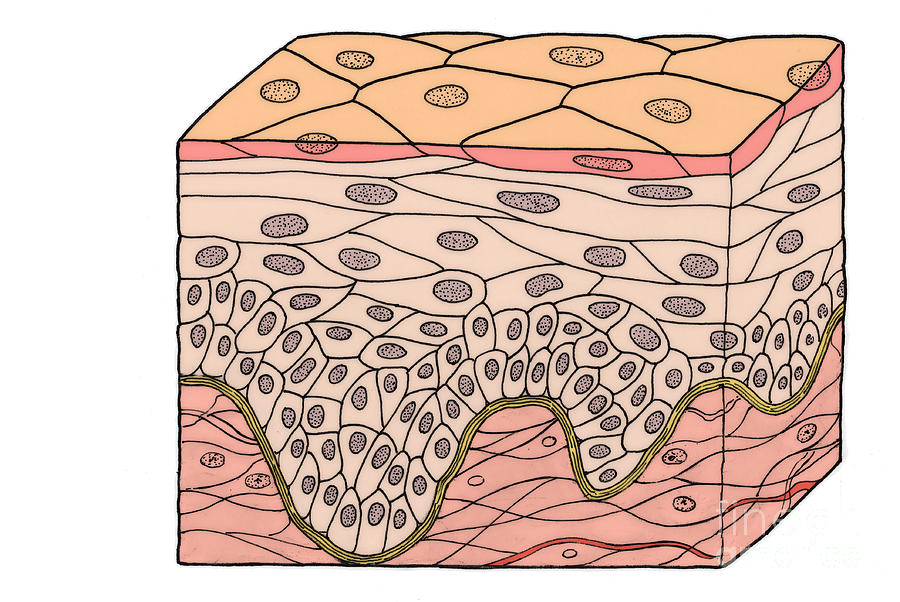
Stratified squamous
Stratified = several layers
Squamous = flattened cells
What is the shoulder muscle called?
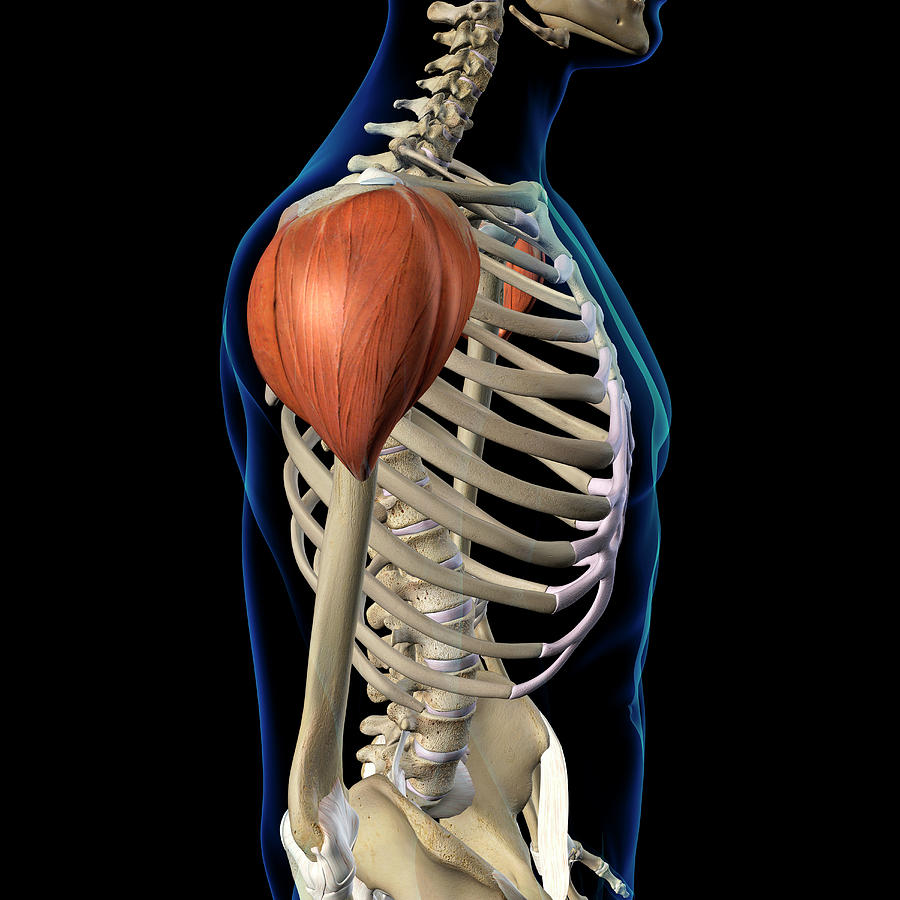
Deltoid
Chest muscle?

Pectoralis major
The large muscle of "your behind?"
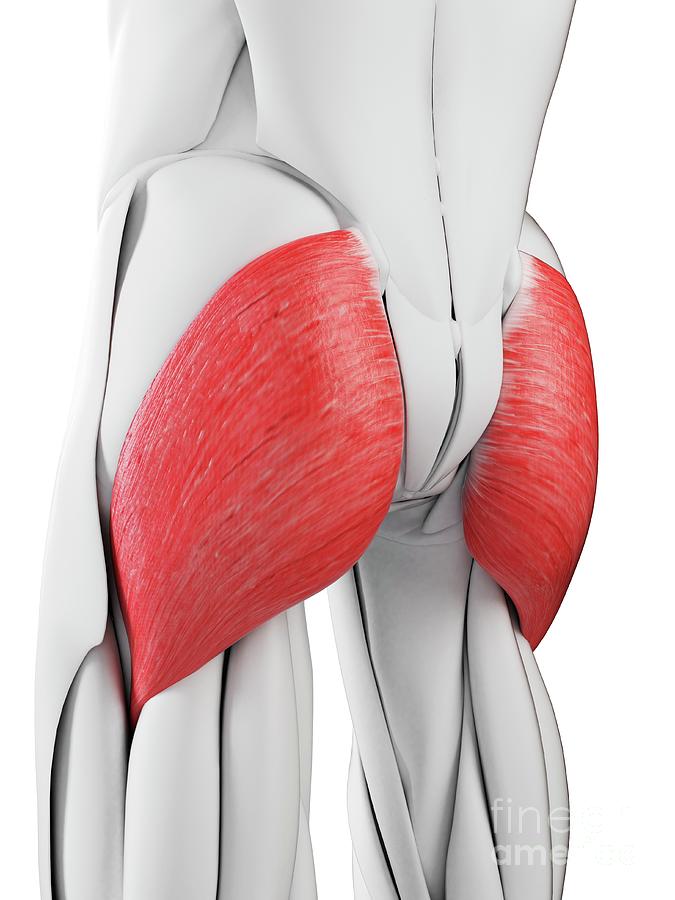
Gluteus maximus
The muscle most often being massaged?
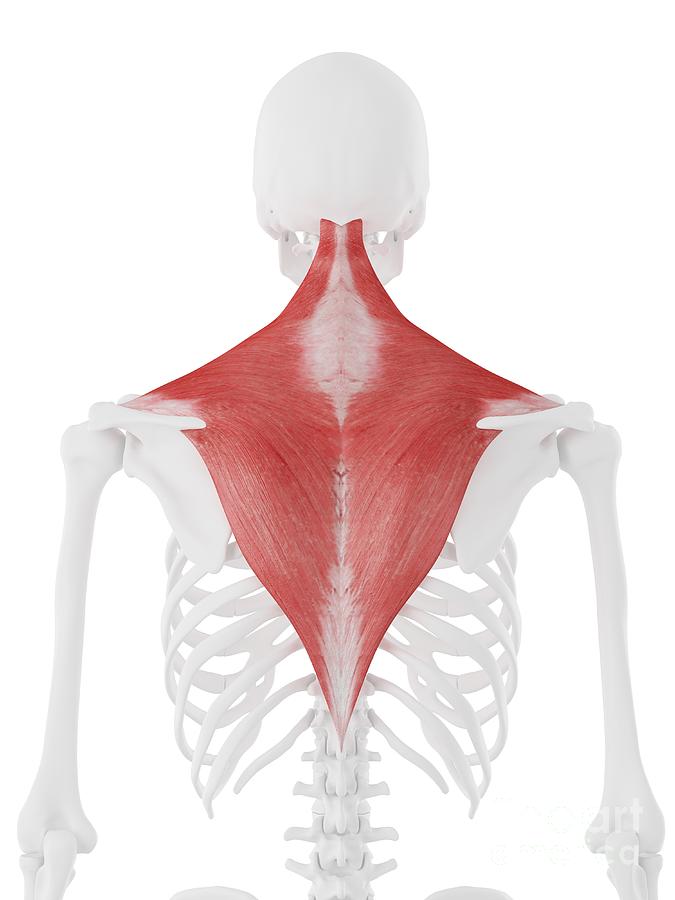
Trapezius
What muscle type has no striations?
Smooth muscle
What is another term for muscle cell?
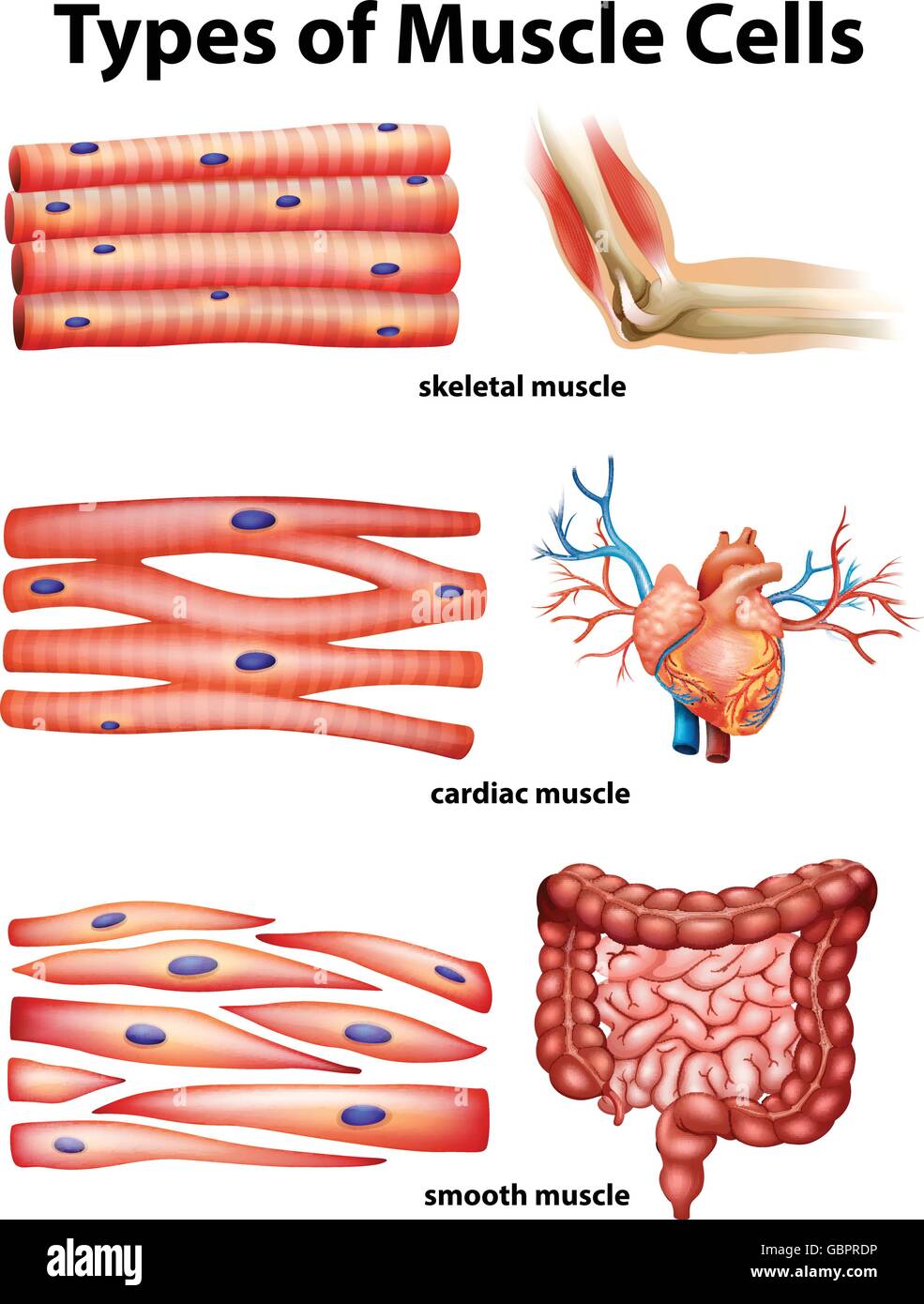
Muscle fiber and yet another is myocyte.
In medical terminology, my/o refers to muscle and cyt/o refers to cell.
Name of protein responsible for stopping muscle growth?
(Remember the story of the 5-year-old boy who was twice the size of other boys his age and was stronger than many adults)
Myostatin
Biochemistry (chemistry of life).
Subatomic particles:
Where on an atom are electrons located?
On shells or orbitals surrounding the nucleus.

Basic function of muscle tissue?
Movement
Biochemistry (chemistry of life)
Which of the following subatomic particles are negatively charged?
Protons, neutrons or electrons?
Electrons

Skeletal System
Medical terminology
What does oste/o pertain to?
Bone
What is the basic chemical make-up of the cell membrane as well as the membrane surrounding all internal cell particles (organelles)?
Phospholipid bilayer
What is the chemical energy called that cells use?
ATP adenosine triphosphate

What two languages are the base for medical terminology
Greek and Latin
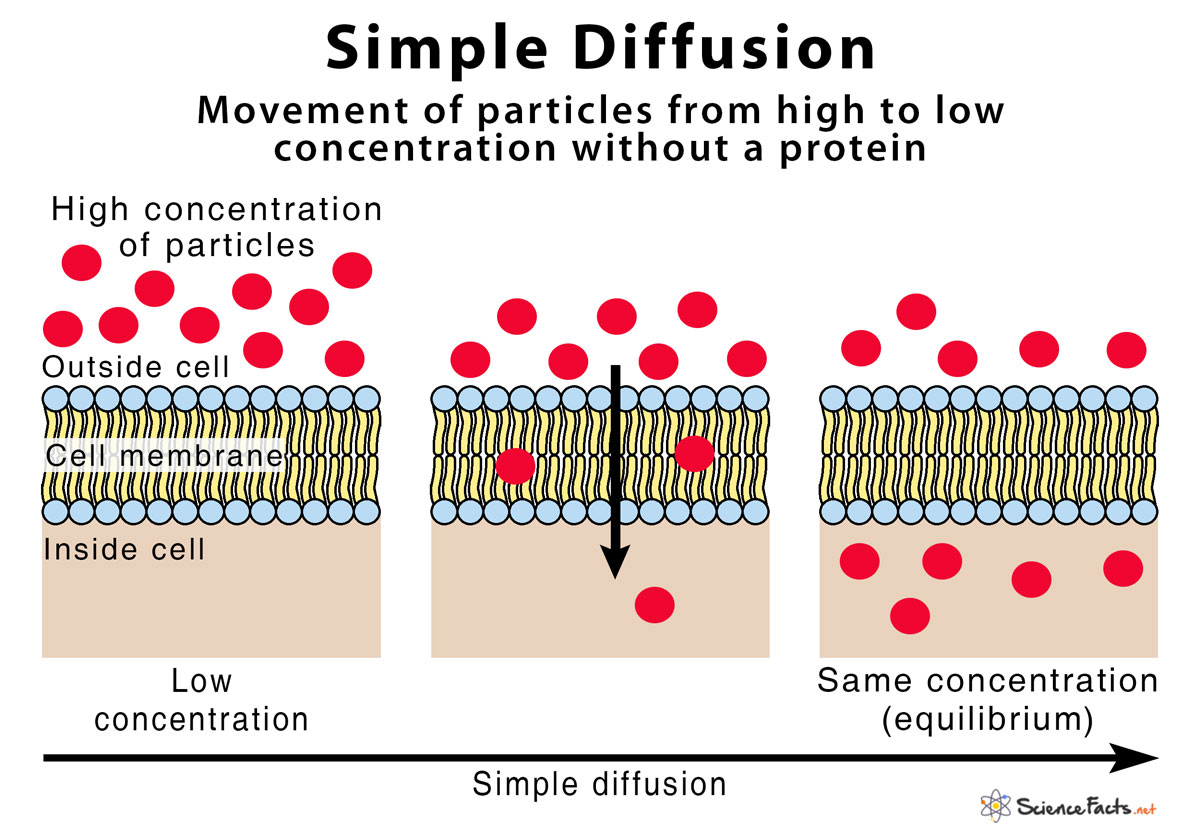
What is the transport through a membrane (such as the cell membrane) called where particles simple flow from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration to equal both sides out?
Simple diffusion
What is the transport through a membrane (such as the cell membrane) called where particles flow from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration to equal both sides out? BUT, now it requires a carrier molecule to aid in the flow.
Facilitated diffusion

Cell eating?
Phagocytosis