Give 4 examples of long bones (You can demonstrate four different long bones on a skeleton).
radius, ulna, tibia, fibula, metacarpals, metatarsals, phalanges, clavicle
How many vertebrae are found in each of the top three regions of the vertebral column? Name each region.
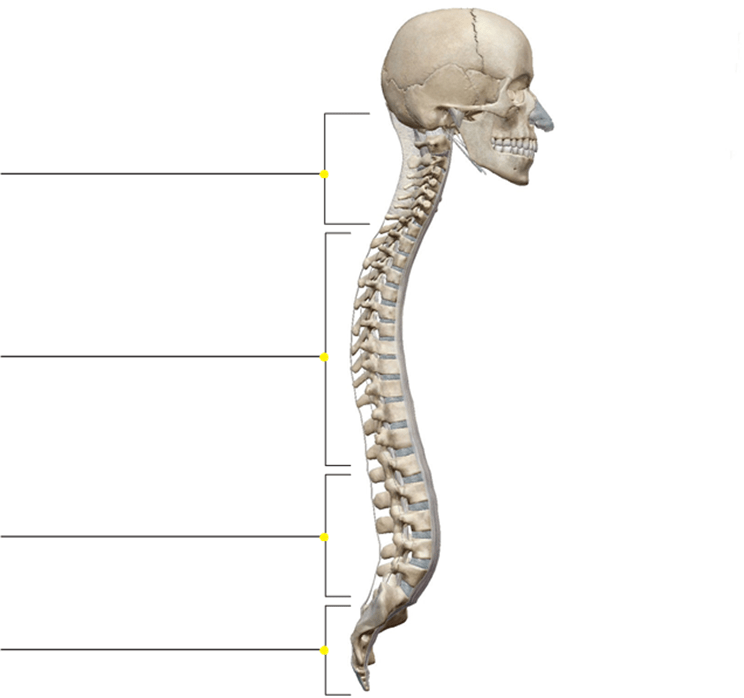
7 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
How many true and false ribs are there?
There are 7 pairs of true ribs and 5 pairs of false ribs
Name the muscles of inspiration.
Diaphragm: Expands thoracic cavity by its contraction, compresses abdominal cavity. When it relaxes, it forces the air out of the lungs.
External intercostal: Elevates the ribs
Serratus anterior: Elevates the ribs when scapula is fixed
Name a sesamoid bone.
Patella (kneecap) and pisiform (carpal)
Name the C1 and C2 vertebrae and what kind of joint do they form?
C1: atlas
C2: axis
Pivot joint.
What is the structure shown with an arrow, and what is its significance?
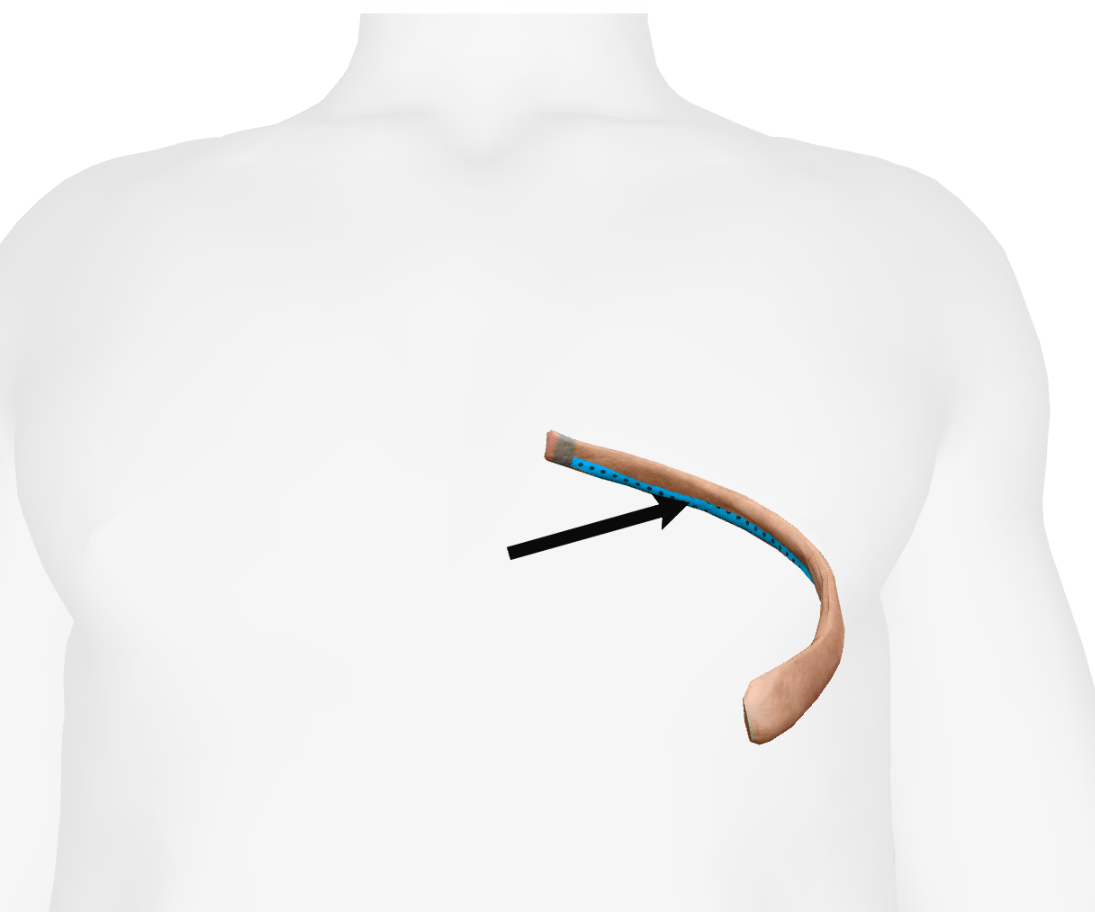
Costal Groove: An indentation of the posterior part of the inferior edge of the rib that contains the intercostal artery, vein, and nerves.
Additional Information: If you want to inject into the thoracic cavity, you should do so at the superior edge (not the inferior edge) so as not to hit the intercostal artery or vein.
Name the muscles of inspiration A-C.
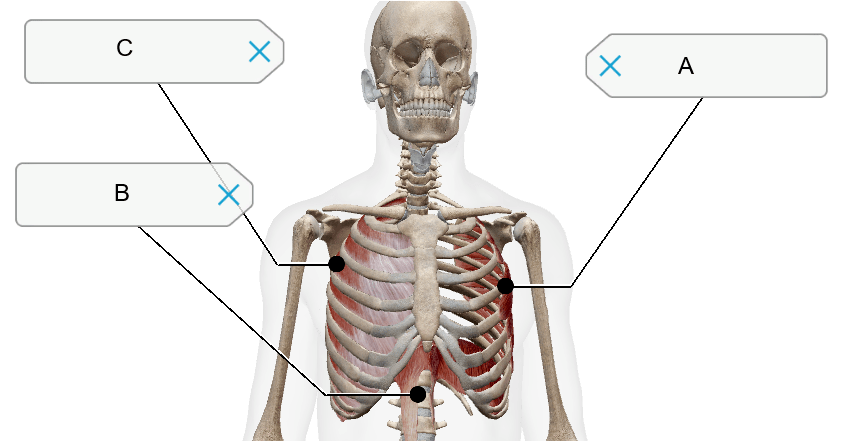
A) Serratus anterior
B) Diaphragm
C) External intercostal
What type of bone are each of the images from #1-#3?
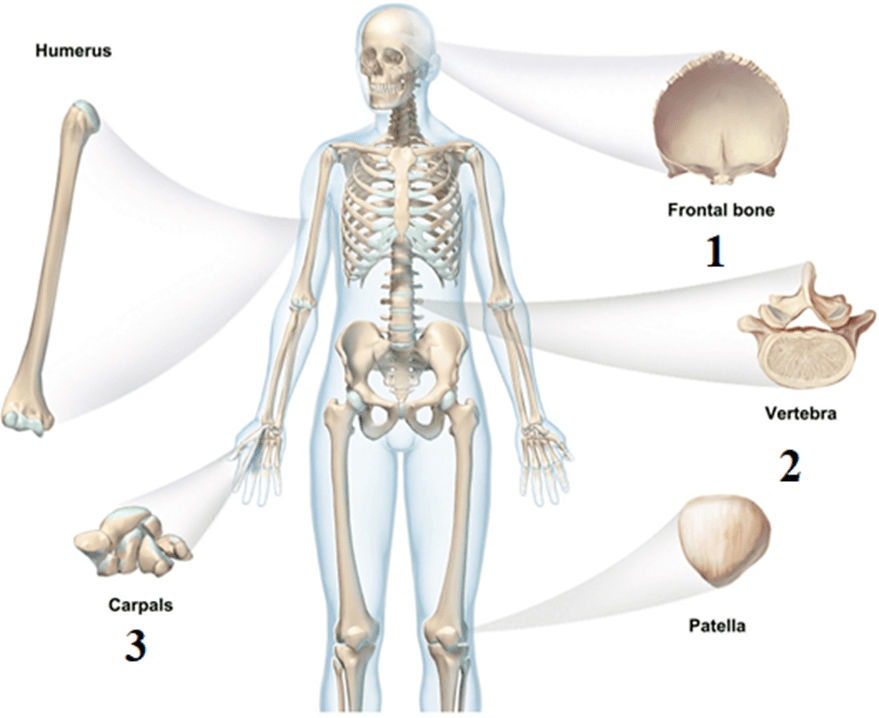
Frontal bone: Flat
Vertebrae: Irregular
Carpals: Short
Match images 1-3 to their lateral view images A-C.
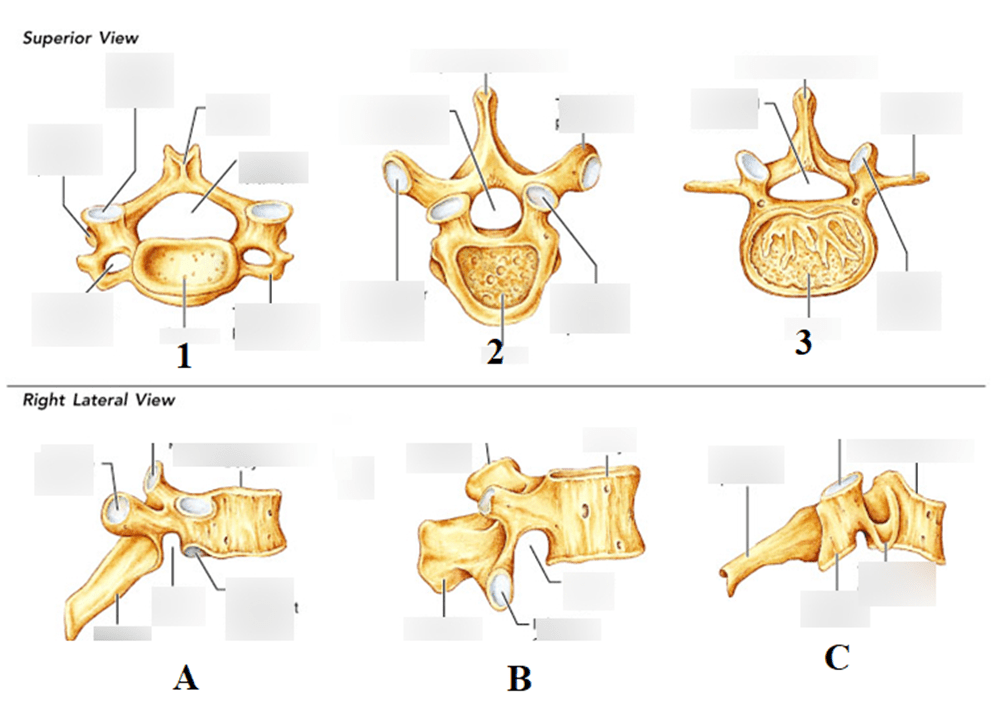
1-C: Cervical
2-A: Thoracic
3-B: Lumbar
What is the arrow pointing at, and what is its significance?
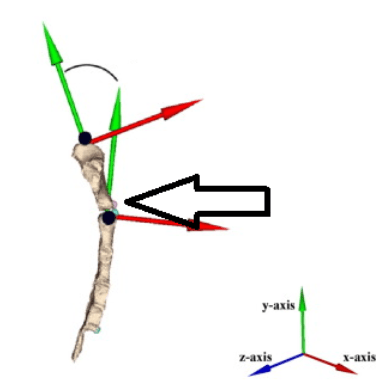
Sternal angle --> The angle made between the body of the sternum and the manubrium.
A line going posterior from the sternal angle bisects the vertebral disc between vertebrae T4 and T5. It also depicts the connection with the costal cartilage of the second rib. Deep to the sternal angle would be the base of the heart, where the great vessels connect to the heart.
Name the two major muscles of the expiration you learned during the previous lab.
Internal intercostal and serratus posterior inferior
Give one example of each of the following types of joints:
1) Hinge joint
2) Pivot joint
3) Ball and socket joint
4) Saddle joint
1) Hinge joint: Elbow/Joints between the finger (phalanges)
2) Pivot joint: Joint between atlas and axis (first and 2nd vertebrae)
3) Ball and socket joint: Shoulder and hip
4) Saddle joint: Thumb (the joint between the first metacarpal and the trapezium, which allows the thumb to cross over the palm.)
Name unique features of cervical and thoracic vertebrae that are not found in other types of vertebrae.
Cervical: Transverse foramina/Bifid spinous process
Thoracic: Costal facets for ribs attachments
What is the arrow pointing at?
Does it have any articulation? If yes, explain.
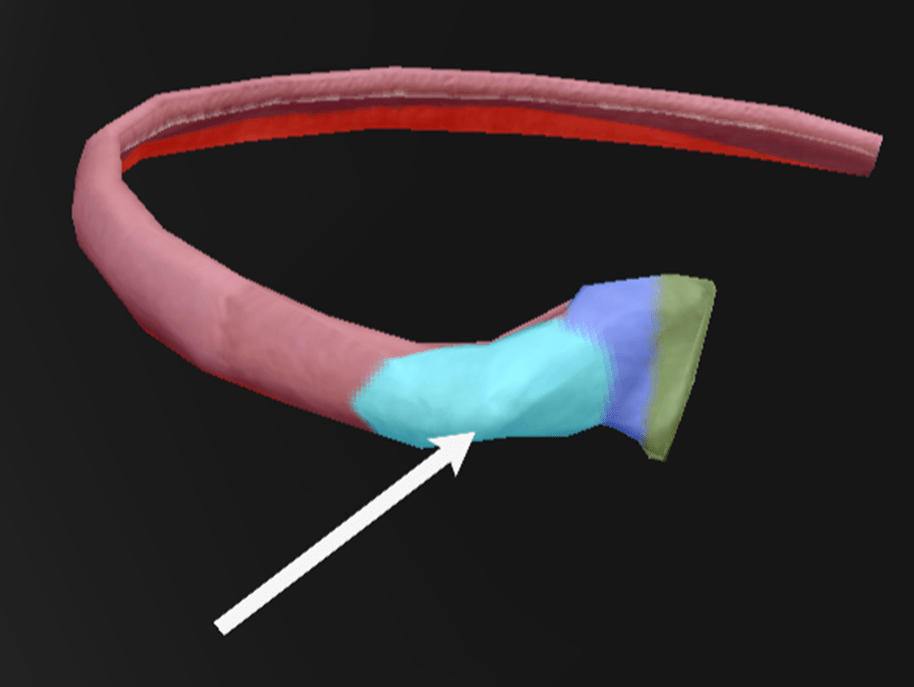
Tubercle: Part that connects the neck with the body and has an articular part that articulates with the transverse process of a vertebra.
Which respiratory muscle may be in a state of contraction (not relaxing) that would affect the spine? Why could this lead to low back pain? Explain the muscle's action.
Diaphragm: it attaches to the lumbar vertebrae
Action: Expands thoracic cavity by its contraction, compresses abdominal cavity. When it relaxes, it forces the air out of the lungs.
Name two types of joints found between the vertebrae. Name the type of each joint.
Intervertebral discs --> Cartilaginous joint
Facet joint between the superior and inferior articular processes of two vertebrae --> It’s a synovial joint (plane joint)
Each vertebra has two sets of facet joints. One pair faces upward (superior articular process) and one downward (inferior articular process). There is one joint on each side (right and left).
Name landmarks #1, #2, #3, #6, and #8.
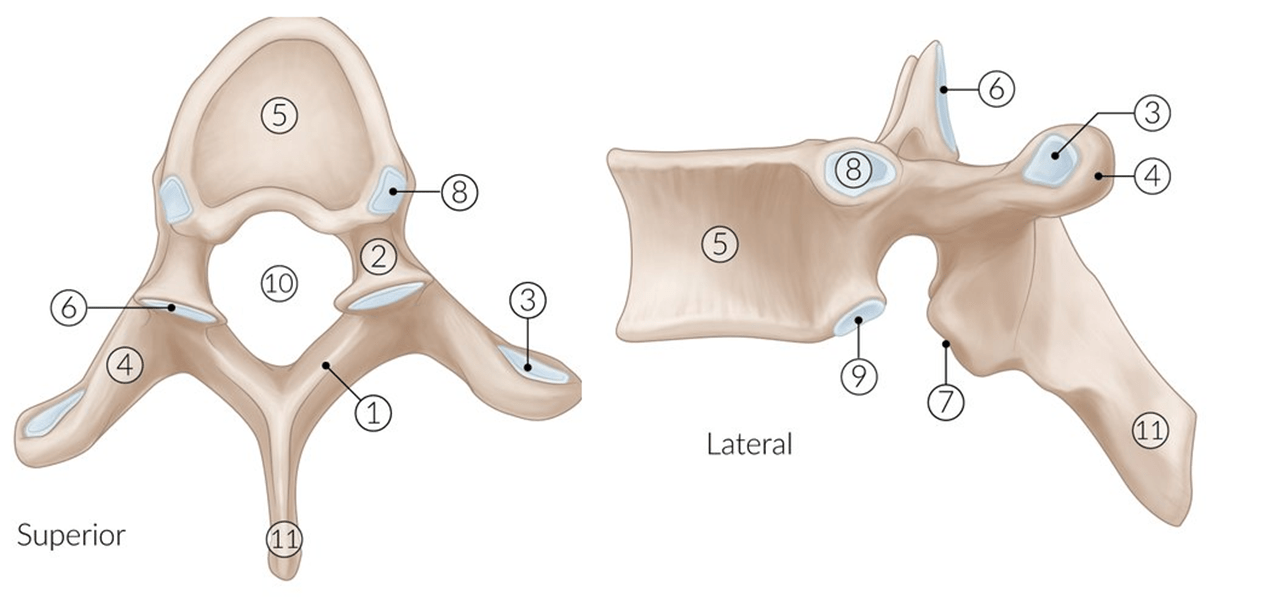
1) Lamina 2) Pedicle 3) Transverse costal facet 4) Transverse process 5) Vertebral body 6) Superior articular process and facet 7) Inferior articular process and facet 8) Superior costal facet 9) Inferior costal facet 10) Vertebral foramen 11) Spinous process
Which pairs of ribs are attached to the body of the sternum?
(ribs 2-7) body of the sternum has 6 costal notches on each side (12 in total)
For manubrium its ribs one and two (two coastal notches on each side)
What movements would feel uncomfortable or painful for someone with facet joint syndrome?
Strengthening which muscle groups would help? Give one example of these strengthening exercises.
Rotation with extension would be painful given the direct compressive and shear forces.
To strengthen the erector spine muscles, you need to workout in a way that you extend your back while having to carry your body weight or some sort of weight or resistance. Some exercises are: Back extensions, deadlifts, prone Superman, kettlebell swings