This flat bone is inferior to the manubrium and clavicle, and anterior to the heart.
What is the sternum?
This bone and the scapula make up a ball & socket joint.
What is the humerus?
Osteoclasts break down bones, while these cells rebuild bone using Ca2+ from the blood.
What are osteoblasts?
This injury is caused by a tear or sprain in the tendon that connects muscles from the front of the tibia to the back of the femur.
What is ACL?
This is a tough outer layer of bone where muscles attach.
What is periosteum?
This protein comprises about a third of the human body. It is found in connective tissue and is essential for bone tensile strength.
What is collagen?
This shape of the spine enhances its strength by distributing weight evenly, absorbing shock, and increasing flexible movement.
What is the curvature (of the spine)?
This smaller long bone is lateral to the tibia.
What is the fibula?
This inorganic cation is needed for muscle contraction, sending nerve impulses, blood clotting, and bone maintenance.
What is a calcium ion (Ca2+)?
This degenerative joint disease occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoclasts secrete acid to enlarge this cavity as bones grow, including after a break.
What is medullary?
This process produces new red blood cells in the bone marrow.
What is hematopoiesis?
This spine segment (1 of 5) has facet joints and is posterior to the thoracic cavity.
What is Thoracic?
The distal end of the femur, the proximal end of the tibia, and the patella comprise this type of joint.
What is a hinge?
This process includes incorporating calcium and minerals into cartilage to become bone.
What is ossification (osteogenesis or bone mineralization)?
This disease is caused by a lack of hydroxyapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), which provides bone strength & hardness.
What is Rickets or Osteoporosis?
This internal cartilage divides the diaphysis and epiphysis of a long bone and is crucial for a young person’s growth.
What is the epiphyseal plate?
Bones are classified by their shape. The cranial, ribs, sternum, scapula, and iliac bones are classified this way.
What are flat bones?
Maintaining these fibrocartilaginous cushions through good posture and regular exercise helps reduce the chance of a herniated disk.
What are intervertebral discs?
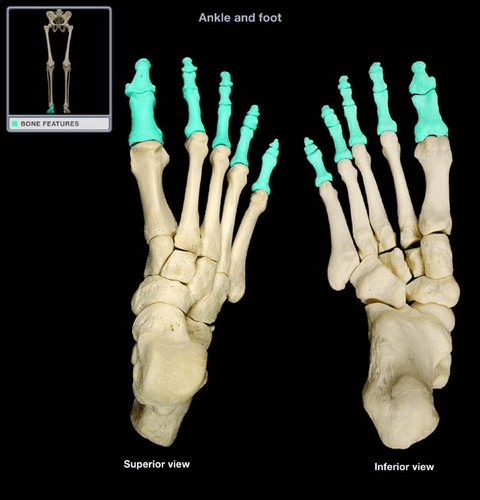 These are at the distal end of the feet.
These are at the distal end of the feet.
What are phalanges?
Two questions: When Ca^2+ blood levels are too low (stimulus), this gland produces a hormone that stimulates osteoclasts (effector) to break down bone. This is the name of that hormone.
What is the parathyroid? What is PTH (parathyroid hormone)?
This birth defect occurs when the spinal cord does not fully close during fetal development, exposing nerves.
What is Spina Bifida?
This smooth white connective tissue covers the ends of long bones to create low-friction movement.
What is articular cartilage?
These types of bones (such as the patella) form to help tendons with leverage and protection.
What is a sesamoid?
These two vertebral segments (out of five) are at the cranial and caudal ends.
What are the cervical and coccyx (vertebrae)?
The distal end of the radius forms a condylar joint with these bones.
What are carpal (bones)?
When the body senses (receptor) a high level of Ca^2+ in the bloodstream, this thyroid gland hormone inhibits osteoclast activity in the bones (effector).
What is calcitonin?
Two questions required: 1. This protein comprises about a third of the human body; it is found in osteoid and is essential for bone tensile strength. 2. This disease is a result of an osteoid deficiency
What is collagen, and what is Brittle Bone Disease (Osteogenesis Imperfecta)?
This is a lattice of trabeculae filled with marrow (where hematopoiesis occurs) and blood vessels, found at the ends of long bones to resist compression.
What is spongy bone (cancellous or epiphysis)?
In detail, these are the 5 functions of the skeletal system.
What are manufacturing red and white blood cells, joints providing movement, protecting essential organs (protection), storing minerals and fat (storage), and supporting the weight (support)?