Fever, tachycardia, malaise, fatigue, nausea, anorexia, elevated WBCs with a shift to the left.
What are the systemic clinical manifestations of an infection?
A nursing intervention for a bedridden patient
Turn and reposition every 2 hours
Full thickness loss of skin where adipose tissue is visible in the injured area.
What are clinical manifestations of a stage III pressure injury?
This treatment draws the wound edges together by negative pressure
A vacuum-assisted closure device (wound vac)
A laceration with edges that do not approximate an granulation tissue fills the wound.
What is a a wound that heals by second (secondary) intention?
Dietary measures to promote wound healing include...
A diet high in protein, carbohydrates, and vitamins
A type of pressure injury
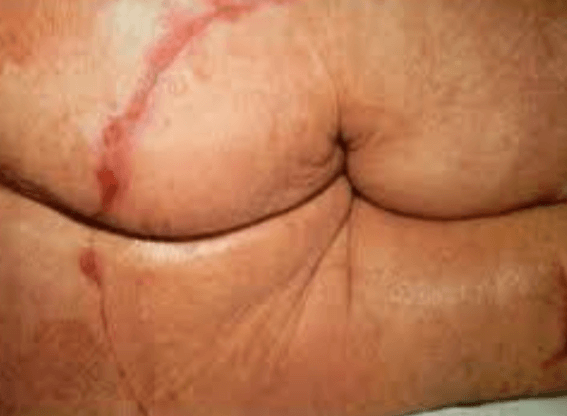
Medical device pressure injury
A nursing action when a wound dehisces.
Cover the wound with a sterile saline dressing.
Systemic and local reactions.
What is the normal response to inflammation?
Three risk factors for pressure injuries include...
Anemia, diabetes, advanced age, incontinence, poor perfusion, immobility
A type of pressure injury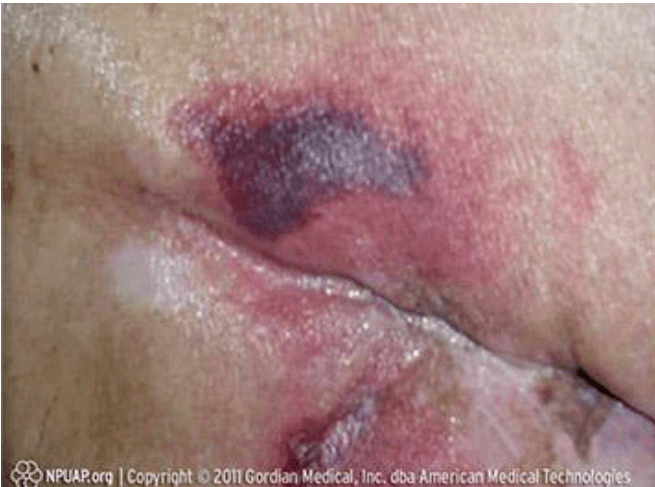
Deep tissue injury
Priority nursing actions for yellow-purulent drainage on a post-op wound
Obtain a wound culture
High wbc count with immature forms of neutrophils is called...
A "shift to the left"
Infection prevention and control includes...
Handwashing, reducing contamination of the wound, astute assessments, obtaining wound cultures, patient/caregiver education
A type of pressure injury requires debridement prior to being staged?
Unstageable pressure injury
Name 5 complications of wound healing
Adhesions, excessive contraction, dehiscence, evisceration, excessive granulation, fistula formation, infection, hemorrhage, hypertrophic scars, keloid formation.